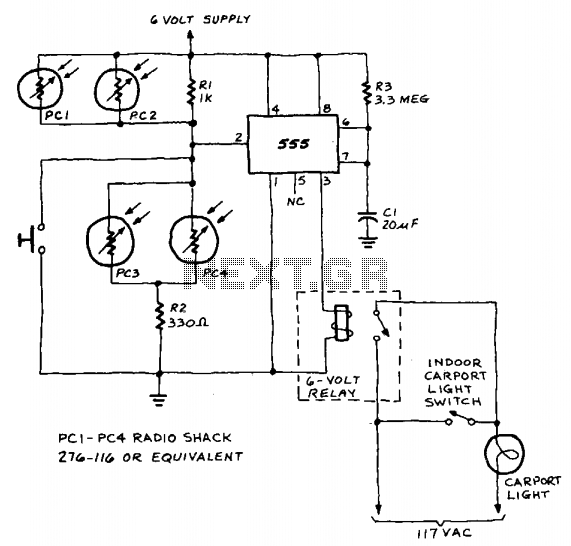
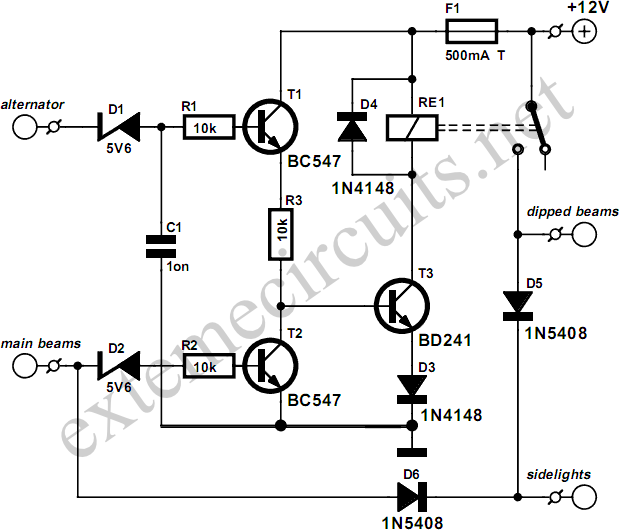
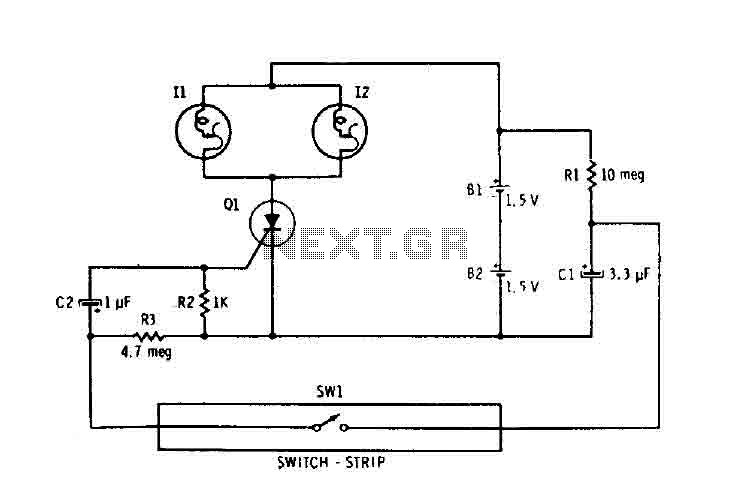
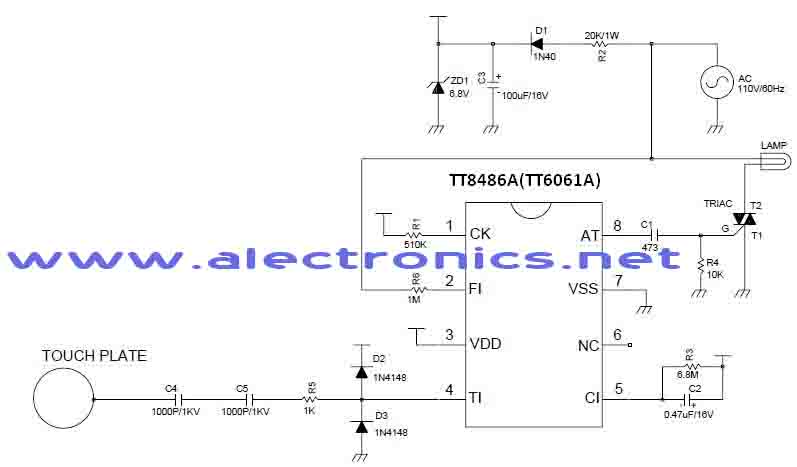
800W LIGHT DIMMER
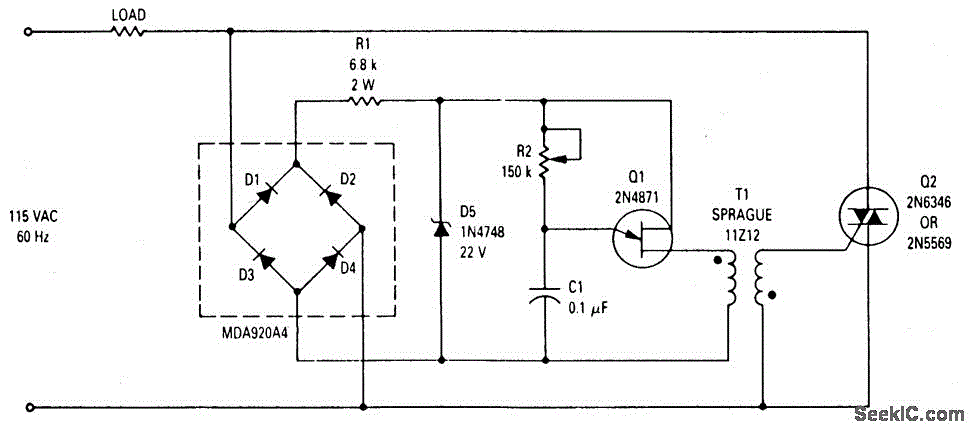
This wide-range light dimmer circuit utilizes a unijunction transistor and a pulse transformer to implement phase control for the TRIAC. It operates from a 115-volt, 60 Hz source and is capable of controlling up to 800 watts of power for incandescent lights. The power delivered to the lights is regulated by adjusting the conduction angle of the TRIAC from 0° to approximately 170°.
The circuit design incorporates a unijunction transistor (UJT) as a triggering device for the TRIAC, which is a semiconductor device used for switching and controlling power. The UJT generates a pulse that is fed into the gate of the TRIAC, allowing it to turn on and off in a controlled manner. The timing of these pulses is influenced by the resistance and capacitance in the circuit, which determines the phase angle at which the TRIAC is triggered.
The pulse transformer serves to isolate the control circuit from the high voltage AC supply, ensuring safety and reducing the risk of electrical interference. The transformer also helps to shape the pulse signal to the appropriate level for triggering the TRIAC effectively.
The circuit is designed to handle a maximum load of 800 watts, making it suitable for various lighting applications. The ability to adjust the conduction angle allows for fine control over the brightness of the lights, providing versatility in lighting scenarios. The dimming range from 0° to 170° enables users to achieve a wide range of illumination levels, from off to nearly full brightness.
In summary, this light dimmer circuit is an effective solution for controlling incandescent lighting, leveraging the properties of unijunction transistors and TRIACs to provide smooth and adjustable dimming capabilities while ensuring safety and reliability in operation.This wide-range light dimmer circuit uses a unijunction transistor and a pulse transformer to provide phase control for the TRIAC. The circuit operates from a 115 volt, 60 Hz source and can control up to 800 watts of power to incandescent tights.
The power to the lights is controlled by varying the conduction angle of the TRIAC from 0° to about 170°. The p.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit design incorporates a unijunction transistor (UJT) as a triggering device for the TRIAC, which is a semiconductor device used for switching and controlling power. The UJT generates a pulse that is fed into the gate of the TRIAC, allowing it to turn on and off in a controlled manner. The timing of these pulses is influenced by the resistance and capacitance in the circuit, which determines the phase angle at which the TRIAC is triggered.
The pulse transformer serves to isolate the control circuit from the high voltage AC supply, ensuring safety and reducing the risk of electrical interference. The transformer also helps to shape the pulse signal to the appropriate level for triggering the TRIAC effectively.
The circuit is designed to handle a maximum load of 800 watts, making it suitable for various lighting applications. The ability to adjust the conduction angle allows for fine control over the brightness of the lights, providing versatility in lighting scenarios. The dimming range from 0° to 170° enables users to achieve a wide range of illumination levels, from off to nearly full brightness.
In summary, this light dimmer circuit is an effective solution for controlling incandescent lighting, leveraging the properties of unijunction transistors and TRIACs to provide smooth and adjustable dimming capabilities while ensuring safety and reliability in operation.This wide-range light dimmer circuit uses a unijunction transistor and a pulse transformer to provide phase control for the TRIAC. The circuit operates from a 115 volt, 60 Hz source and can control up to 800 watts of power to incandescent tights.
The power to the lights is controlled by varying the conduction angle of the TRIAC from 0° to about 170°. The p.. 🔗 External reference
Warning: include(partials/cookie-banner.php): Failed to open stream: Permission denied in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713
Warning: include(): Failed opening 'partials/cookie-banner.php' for inclusion (include_path='.:/usr/share/php') in /var/www/html/nextgr/view-circuit.php on line 713