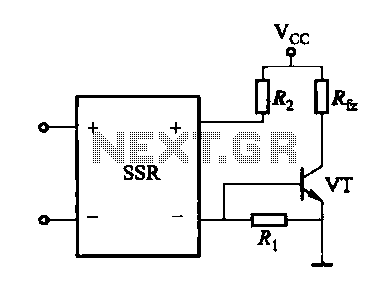
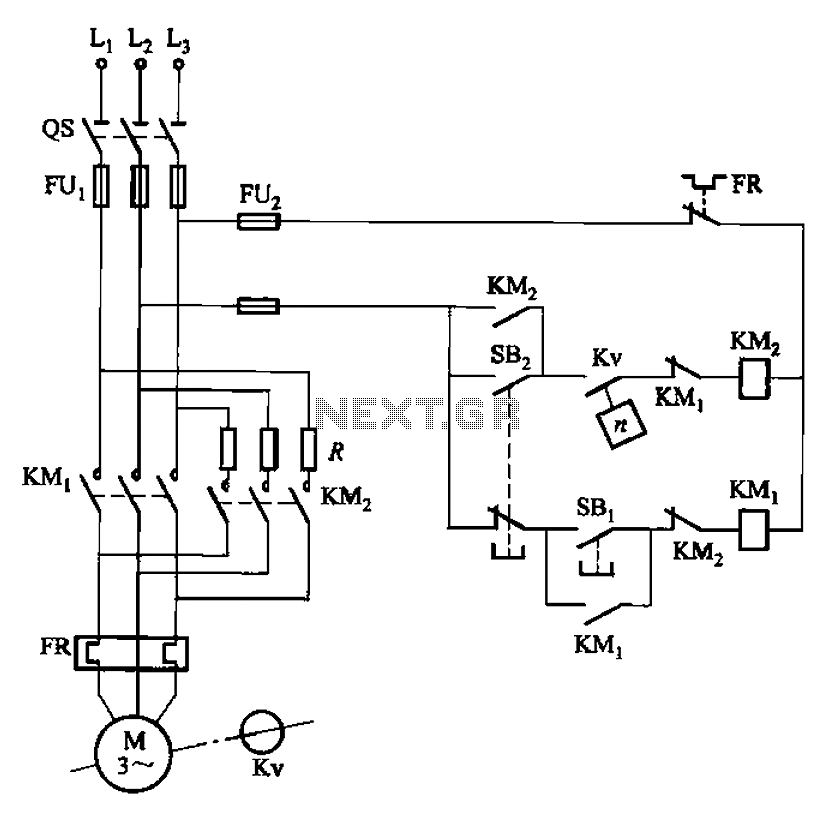
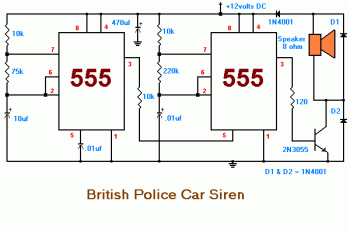
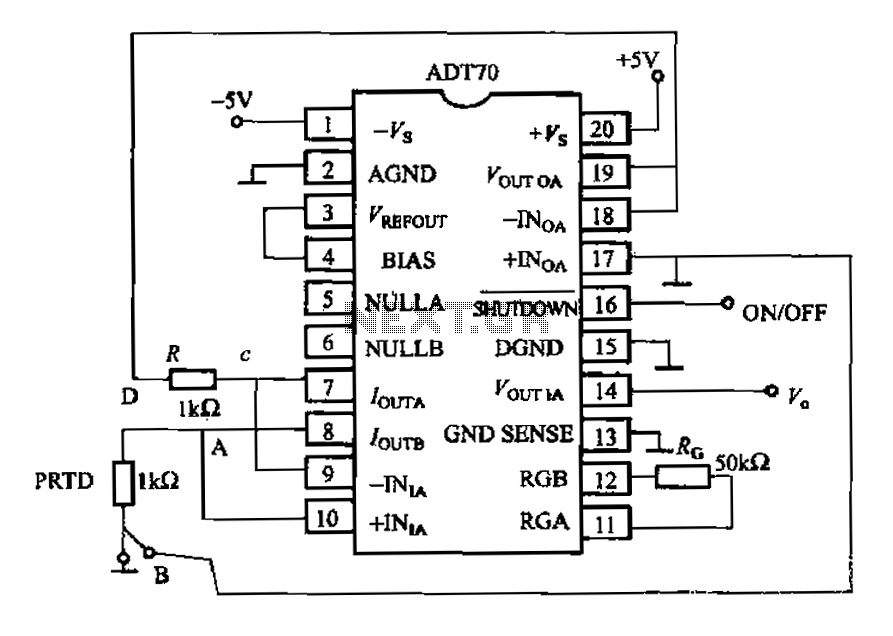
The time delay circuit diagram composed of transistor
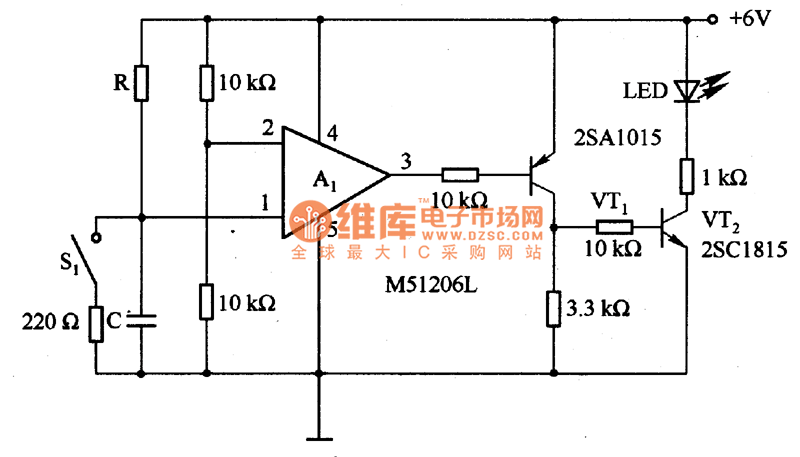
The circuit is designed to set a delay time based on the voltage Us and the resistor R. In this configuration, S1 acts as the discharge switch for capacitor C. When switch S1 is closed, the stored charge in capacitor C is released through S1, ensuring the accuracy of the delay time for subsequent operations. Diodes VD1 and VD2 are employed to mitigate any impact from voltage fluctuations.
The circuit operates by utilizing a timing mechanism that relies on the charging and discharging characteristics of capacitor C, influenced by the resistor R. The delay time is adjustable by varying the resistance value or the input voltage Us. When switch S1 is closed, capacitor C discharges rapidly, allowing the circuit to reset and prepare for the next timing cycle. The role of diodes VD1 and VD2 is crucial; they provide a path for reverse current, protecting sensitive components from voltage spikes that could arise during the discharge phase.
The timing circuit may include additional components such as a microcontroller or timer IC to enhance functionality, enabling more precise control over the delay intervals. The choice of resistor R and capacitor C values directly affects the time constant of the circuit, which is defined by the formula τ = R × C, where τ represents the time constant in seconds. This relationship allows for the calculation of the expected delay time, which can be fine-tuned based on the application requirements.
In practical applications, this circuit can be utilized in various timing-related tasks, such as in delay relays, pulse generators, or as part of more complex control systems in automation and robotics. Proper selection of components and careful layout design are essential to ensure reliable operation and to minimize noise and interference in the timing signal.It can set delay time according to the voltage Us and resistor R. In the circuit, S1 is the the discharge switch of capacitor C. When the switch S1 is closed, the stored charge on C will be released through S1 to ensure the accuracy of the delay time the next time. VD1 and VD2 are used to eliminate the impa.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by utilizing a timing mechanism that relies on the charging and discharging characteristics of capacitor C, influenced by the resistor R. The delay time is adjustable by varying the resistance value or the input voltage Us. When switch S1 is closed, capacitor C discharges rapidly, allowing the circuit to reset and prepare for the next timing cycle. The role of diodes VD1 and VD2 is crucial; they provide a path for reverse current, protecting sensitive components from voltage spikes that could arise during the discharge phase.
The timing circuit may include additional components such as a microcontroller or timer IC to enhance functionality, enabling more precise control over the delay intervals. The choice of resistor R and capacitor C values directly affects the time constant of the circuit, which is defined by the formula τ = R × C, where τ represents the time constant in seconds. This relationship allows for the calculation of the expected delay time, which can be fine-tuned based on the application requirements.
In practical applications, this circuit can be utilized in various timing-related tasks, such as in delay relays, pulse generators, or as part of more complex control systems in automation and robotics. Proper selection of components and careful layout design are essential to ensure reliable operation and to minimize noise and interference in the timing signal.It can set delay time according to the voltage Us and resistor R. In the circuit, S1 is the the discharge switch of capacitor C. When the switch S1 is closed, the stored charge on C will be released through S1 to ensure the accuracy of the delay time the next time. VD1 and VD2 are used to eliminate the impa.. 🔗 External reference