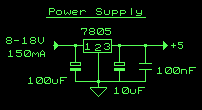
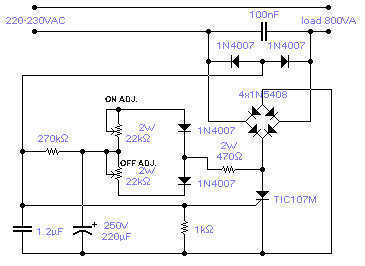
Rf Preamplifiers Circuit
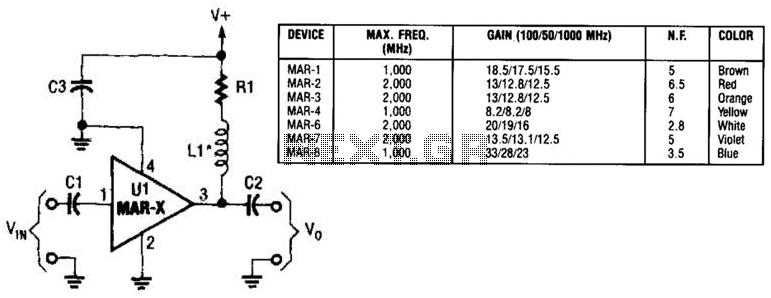
In this basic MAR-x-based circuit, both the input and output consist of a single DC-blocking capacitor (C1 for the input and C2 for the output, respectively). The DC power supply network, which includes L1 and R1, is connected to the MAR-x through the RF output terminal (lead 3).
The MAR-x circuit configuration utilizes two crucial DC-blocking capacitors, C1 and C2, which serve to prevent any DC voltage from affecting the subsequent stages of the circuit while allowing AC signals to pass. The input capacitor, C1, is positioned at the input stage to filter out any DC components present in the incoming signal, ensuring that only the desired AC signal is processed by the MAR-x device. Similarly, the output capacitor, C2, performs the same function at the output stage, allowing for the clean transmission of the AC signal to the next stage of the circuit without any DC offset.
The power supply network, consisting of an inductor (L1) and a resistor (R1), plays a critical role in providing the necessary DC voltage and current to the MAR-x. The inductor L1 is typically chosen to provide a stable current supply while minimizing any potential ripple that could affect performance. The resistor R1 may be used for current limiting or to provide a specific load to the circuit, ensuring that the MAR-x operates within its specified parameters.
The connection of the power supply network to the MAR-x via the RF output terminal (lead 3) is essential for proper operation. This connection allows the MAR-x to receive the necessary power while also facilitating the transfer of the RF signal, which is critical for the overall functionality of the circuit. Proper attention must be given to the layout and component selection to ensure optimal performance and reliability of the MAR-x circuit. In this basic MAR-x-based circuit, both the input and output are comprised of a single dc-blocking capacitor (CI and C2 for the input and output, respectively). The dc power-supply network (comprised of LI and Rl) is attached to the MAR-x via the RF-output terminal (lead 3).
The MAR-x circuit configuration utilizes two crucial DC-blocking capacitors, C1 and C2, which serve to prevent any DC voltage from affecting the subsequent stages of the circuit while allowing AC signals to pass. The input capacitor, C1, is positioned at the input stage to filter out any DC components present in the incoming signal, ensuring that only the desired AC signal is processed by the MAR-x device. Similarly, the output capacitor, C2, performs the same function at the output stage, allowing for the clean transmission of the AC signal to the next stage of the circuit without any DC offset.
The power supply network, consisting of an inductor (L1) and a resistor (R1), plays a critical role in providing the necessary DC voltage and current to the MAR-x. The inductor L1 is typically chosen to provide a stable current supply while minimizing any potential ripple that could affect performance. The resistor R1 may be used for current limiting or to provide a specific load to the circuit, ensuring that the MAR-x operates within its specified parameters.
The connection of the power supply network to the MAR-x via the RF output terminal (lead 3) is essential for proper operation. This connection allows the MAR-x to receive the necessary power while also facilitating the transfer of the RF signal, which is critical for the overall functionality of the circuit. Proper attention must be given to the layout and component selection to ensure optimal performance and reliability of the MAR-x circuit. In this basic MAR-x-based circuit, both the input and output are comprised of a single dc-blocking capacitor (CI and C2 for the input and output, respectively). The dc power-supply network (comprised of LI and Rl) is attached to the MAR-x via the RF-output terminal (lead 3).