Anatek Lab Supply
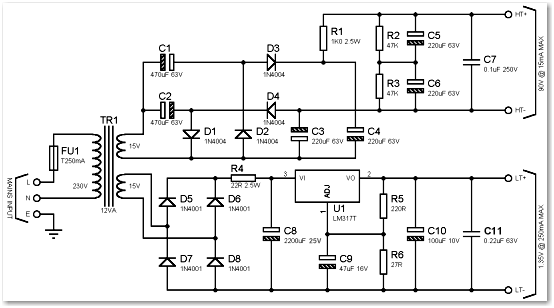
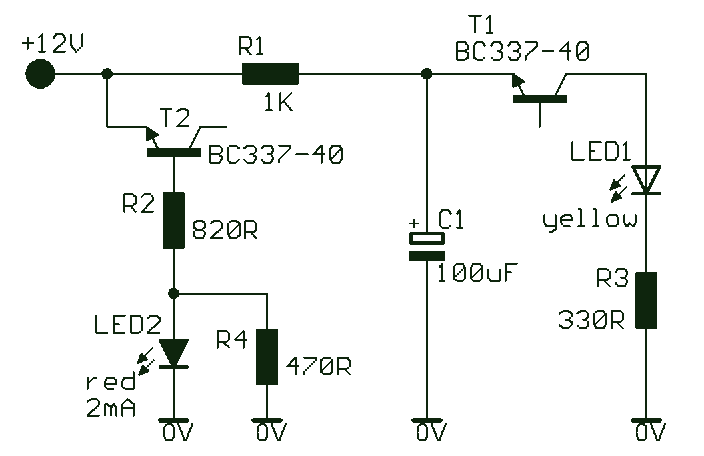
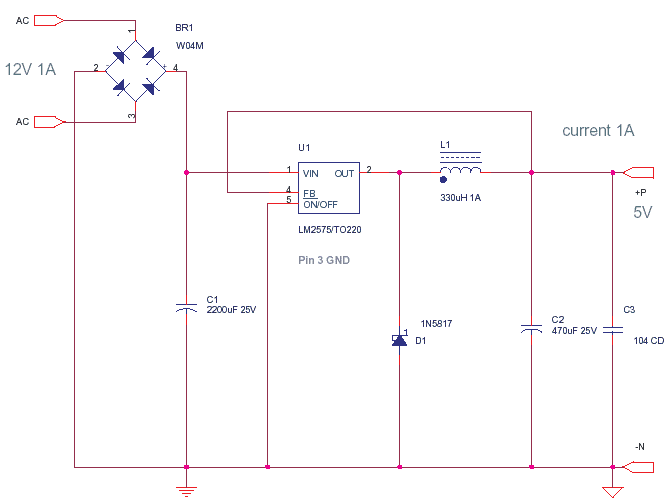
The unit is designed around a standard operational amplifier and utilizes easily obtainable components. The reverse-engineered circuit diagram of the Anatek 50-1S variable power supply is shown below. The layout of the circuit board does not appear to be particularly critical. As indicated in the schematic, the sense wires connected to the circuit board have their own dedicated connectors, separate from the output wires. Although the unit employs a single transformer with two output windings, the circuit functions effectively with either a larger transformer or a smaller transformer. The test point at pin 8 of the operational amplifier activates when the variable power supply operates in current-limited mode, which can be utilized to drive an LED.
The Anatek 50-1S variable power supply circuit is based on a straightforward operational amplifier configuration, which serves as the core of the voltage regulation system. The design incorporates a feedback loop that stabilizes the output voltage while allowing for variable adjustments. The op-amp is configured in a non-inverting mode, where the reference voltage is set using a potentiometer, enabling fine-tuning of the output voltage.
The power supply utilizes a transformer with dual output windings, providing the necessary AC voltage for rectification and regulation. The rectification stage typically employs a bridge rectifier, converting the AC voltage to pulsating DC, which is then smoothed using filter capacitors. The choice of transformer size can vary, as the circuit is adaptable to both larger and smaller transformers, maintaining functionality regardless of the transformer’s power rating.
The circuit board layout is designed with flexibility in mind, allowing for variations in component placement without significant impact on performance. The separate connectors for sense wires ensure accurate voltage sensing at the load, minimizing voltage drop caused by wiring resistance.
The operational amplifier's pin 8 serves as a crucial test point, indicating when the circuit is in current-limited mode. This feature is essential for protecting sensitive loads from excessive current, and the high signal at this pin can be used to drive an LED, providing a visual indication of the current limiting status. Overall, the Anatek 50-1S variable power supply is a robust and versatile design suitable for a range of applications, leveraging common components and straightforward circuit principles.The unit is designed around an ordinary op-amp and easy to obtain parts. Reverse engineered circuit diagram of Anatek 50-1S variable power supply shown below. Circuit board layout does not seem all that critical and as you can see from the schematic that sense wires to the circuit board have their own stake on connectors separate from the output w ires. Although the unit uses a single transformer with two output windings the circuit works equally well using a big transformer and a little transformer. The test point at pin 8 of the op-amp goes high when the variable power supply is operating in current limited mode and it could be used to drive an LED.
🔗 External reference
The Anatek 50-1S variable power supply circuit is based on a straightforward operational amplifier configuration, which serves as the core of the voltage regulation system. The design incorporates a feedback loop that stabilizes the output voltage while allowing for variable adjustments. The op-amp is configured in a non-inverting mode, where the reference voltage is set using a potentiometer, enabling fine-tuning of the output voltage.
The power supply utilizes a transformer with dual output windings, providing the necessary AC voltage for rectification and regulation. The rectification stage typically employs a bridge rectifier, converting the AC voltage to pulsating DC, which is then smoothed using filter capacitors. The choice of transformer size can vary, as the circuit is adaptable to both larger and smaller transformers, maintaining functionality regardless of the transformer’s power rating.
The circuit board layout is designed with flexibility in mind, allowing for variations in component placement without significant impact on performance. The separate connectors for sense wires ensure accurate voltage sensing at the load, minimizing voltage drop caused by wiring resistance.
The operational amplifier's pin 8 serves as a crucial test point, indicating when the circuit is in current-limited mode. This feature is essential for protecting sensitive loads from excessive current, and the high signal at this pin can be used to drive an LED, providing a visual indication of the current limiting status. Overall, the Anatek 50-1S variable power supply is a robust and versatile design suitable for a range of applications, leveraging common components and straightforward circuit principles.The unit is designed around an ordinary op-amp and easy to obtain parts. Reverse engineered circuit diagram of Anatek 50-1S variable power supply shown below. Circuit board layout does not seem all that critical and as you can see from the schematic that sense wires to the circuit board have their own stake on connectors separate from the output w ires. Although the unit uses a single transformer with two output windings the circuit works equally well using a big transformer and a little transformer. The test point at pin 8 of the op-amp goes high when the variable power supply is operating in current limited mode and it could be used to drive an LED.
🔗 External reference