Astable Multivibrator

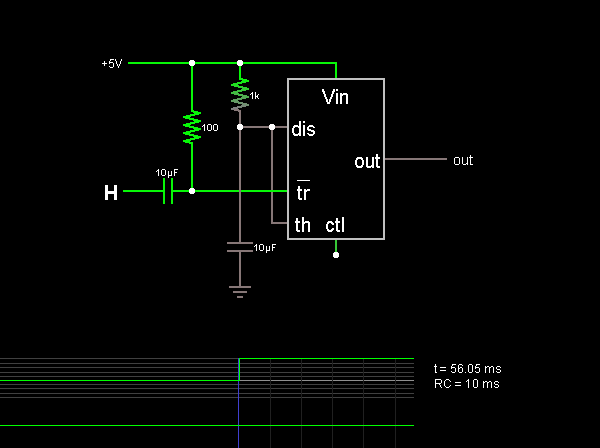
A transistorized astable multivibrator is a cross-coupled transistor network capable of generating a continuous square wave. It operates as a free-running oscillator or a regenerative switching circuit that utilizes positive feedback. The astable multivibrator continuously alternates between its two unstable states without requiring external triggering. The time period of the astable multivibrator can be adjusted by modifying the values of feedback components, such as coupling capacitors and resistors.
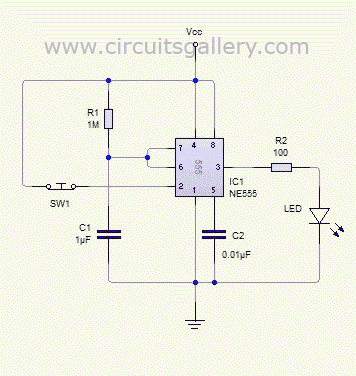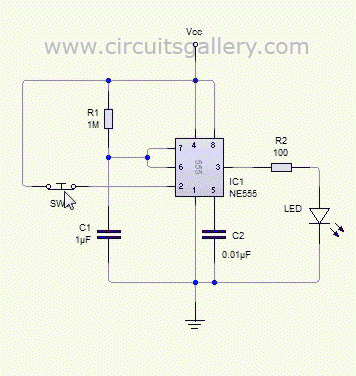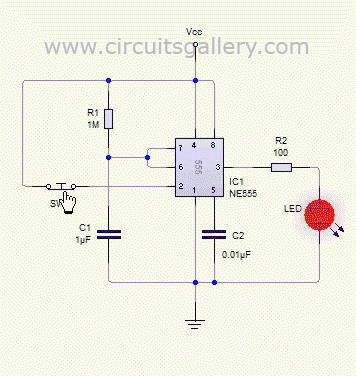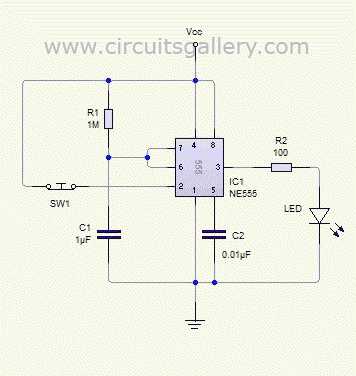
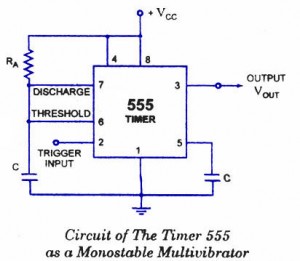
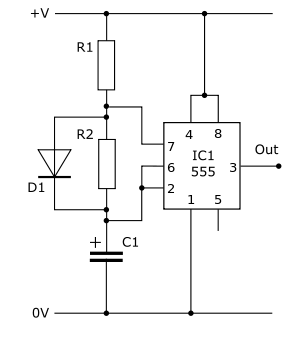
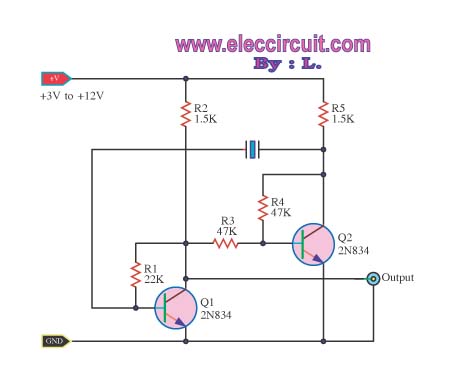
The transistorized astable multivibrator configuration typically employs two NPN transistors arranged in a feedback loop. Each transistor alternately turns on and off, creating a square wave output. The circuit requires a power supply, often a DC source, which powers the transistors. The feedback loop is established through resistors and capacitors, which determine the timing characteristics of the oscillation.
In a standard configuration, two resistors (R1 and R2) are connected to the base of each transistor, while a capacitor (C1) is connected between the collector of one transistor and the base of the other. The second capacitor (C2) is connected similarly, ensuring that the charging and discharging of these capacitors dictate the switching times. The values of R1, R2, C1, and C2 directly influence the frequency and duty cycle of the output waveform.
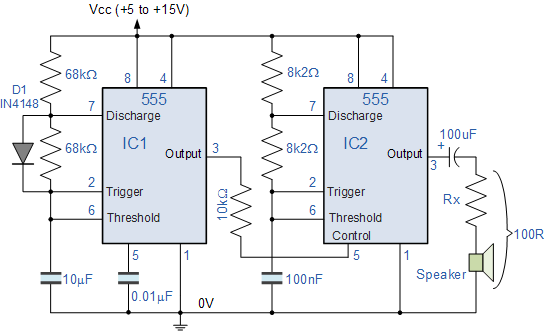
The output can be taken from the collector of one of the transistors, providing a square wave signal that can be used in various applications, such as clock pulses for digital circuits, tone generation in audio applications, or as a simple timer. The design's simplicity and effectiveness make the transistorized astable multivibrator a fundamental building block in electronic circuit design.Transistorised Astable Multivibrator is a cross coupled transistor network capable of producing sharp continuous square wave. It is free running oscillator or simply a regenerative switching circuit using positive feedback. Astable Multivibrator switches continuously between its two unstable states without the need for any external triggering.
Time period of Astable multivibrator can be controlled by changing the values of feedback components such as coupling capacitors and resistors. 🔗 External reference
The transistorized astable multivibrator configuration typically employs two NPN transistors arranged in a feedback loop. Each transistor alternately turns on and off, creating a square wave output. The circuit requires a power supply, often a DC source, which powers the transistors. The feedback loop is established through resistors and capacitors, which determine the timing characteristics of the oscillation.
In a standard configuration, two resistors (R1 and R2) are connected to the base of each transistor, while a capacitor (C1) is connected between the collector of one transistor and the base of the other. The second capacitor (C2) is connected similarly, ensuring that the charging and discharging of these capacitors dictate the switching times. The values of R1, R2, C1, and C2 directly influence the frequency and duty cycle of the output waveform.
The output can be taken from the collector of one of the transistors, providing a square wave signal that can be used in various applications, such as clock pulses for digital circuits, tone generation in audio applications, or as a simple timer. The design's simplicity and effectiveness make the transistorized astable multivibrator a fundamental building block in electronic circuit design.Transistorised Astable Multivibrator is a cross coupled transistor network capable of producing sharp continuous square wave. It is free running oscillator or simply a regenerative switching circuit using positive feedback. Astable Multivibrator switches continuously between its two unstable states without the need for any external triggering.
Time period of Astable multivibrator can be controlled by changing the values of feedback components such as coupling capacitors and resistors. 🔗 External reference