Automatic headlight dim switch
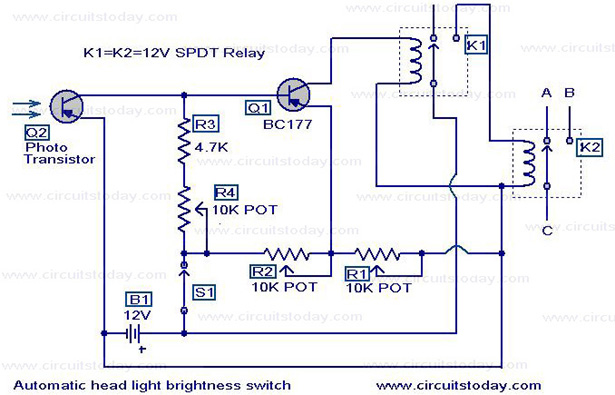
This circuit, integrated into a car's headlight system, allows for automatic adjustment of the headlight beams. It dims the headlights when oncoming vehicles are detected and restores high beams once they have passed. The circuit utilizes a phototransistor (Q1) to sense approaching vehicles and a second transistor (Q2, BC177) to control relays that manage the headlight operation. When light from an oncoming vehicle strikes Q2, its collector current increases, activating Q1, which in turn triggers the relay to dim the headlights. The headlights return to high beam once the vehicle has passed.
This headlight control circuit offers a practical solution for enhancing nighttime driving safety by automatically adjusting the beam intensity based on surrounding traffic conditions. The core components include a phototransistor (Q1) that is sensitive to light changes, allowing it to detect when an oncoming vehicle approaches. The phototransistor's response to light is crucial; when illuminated by the headlights of an approaching vehicle, Q1 conducts, leading to increased current flow.
Transistor Q2 (BC177) functions as a switch in this configuration. It is connected to the relay that controls the headlight power. When Q1 is activated by light, it allows current to flow into the base of Q2, thereby turning it on. This action energizes the relay, which interrupts the high beam circuit and dims the headlights to low beam, reducing glare for oncoming drivers.
Once the oncoming vehicle passes and the light source is no longer detected by Q1, the circuit resets. The reduced light on Q2 causes it to turn off, which deactivates the relay, allowing the headlights to return to high beam. This automatic switching enhances driving comfort and safety by ensuring that high beams are only used when appropriate.
For optimal performance, the circuit should be designed with appropriate resistor values to ensure that both Q1 and Q2 operate within their specified ranges. Additionally, the relay must be rated to handle the current load of the vehicle's headlights. Proper placement of the phototransistor is also critical; it should be positioned to effectively capture the light from oncoming vehicles while being shielded from ambient light sources that could cause false triggering. This system not only improves visibility for the driver but also contributes to the overall safety of nighttime driving.With this cool circuit integrated to your cars headlight system, you can drive cool headed in high beam. The circuit will take over the duty of low beaming the headlight when vehicles approach against, and high beams the lights when they pass over.
The circuit is based on a photo transistor(Q1) for sensing the approaching vehicles and transistor Q2 (BC177) for switching the relays for controlling the headlight. When the light from the opposite vehicle falls on Q2, it`s collector current increases and turns ON Q1. The relay will be activated and the head light will be dimmed. When the vehicle pass over the reverse will happen. 🔗 External reference
This headlight control circuit offers a practical solution for enhancing nighttime driving safety by automatically adjusting the beam intensity based on surrounding traffic conditions. The core components include a phototransistor (Q1) that is sensitive to light changes, allowing it to detect when an oncoming vehicle approaches. The phototransistor's response to light is crucial; when illuminated by the headlights of an approaching vehicle, Q1 conducts, leading to increased current flow.
Transistor Q2 (BC177) functions as a switch in this configuration. It is connected to the relay that controls the headlight power. When Q1 is activated by light, it allows current to flow into the base of Q2, thereby turning it on. This action energizes the relay, which interrupts the high beam circuit and dims the headlights to low beam, reducing glare for oncoming drivers.
Once the oncoming vehicle passes and the light source is no longer detected by Q1, the circuit resets. The reduced light on Q2 causes it to turn off, which deactivates the relay, allowing the headlights to return to high beam. This automatic switching enhances driving comfort and safety by ensuring that high beams are only used when appropriate.
For optimal performance, the circuit should be designed with appropriate resistor values to ensure that both Q1 and Q2 operate within their specified ranges. Additionally, the relay must be rated to handle the current load of the vehicle's headlights. Proper placement of the phototransistor is also critical; it should be positioned to effectively capture the light from oncoming vehicles while being shielded from ambient light sources that could cause false triggering. This system not only improves visibility for the driver but also contributes to the overall safety of nighttime driving.With this cool circuit integrated to your cars headlight system, you can drive cool headed in high beam. The circuit will take over the duty of low beaming the headlight when vehicles approach against, and high beams the lights when they pass over.
The circuit is based on a photo transistor(Q1) for sensing the approaching vehicles and transistor Q2 (BC177) for switching the relays for controlling the headlight. When the light from the opposite vehicle falls on Q2, it`s collector current increases and turns ON Q1. The relay will be activated and the head light will be dimmed. When the vehicle pass over the reverse will happen. 🔗 External reference