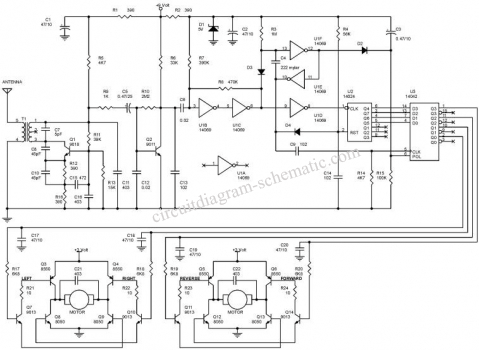
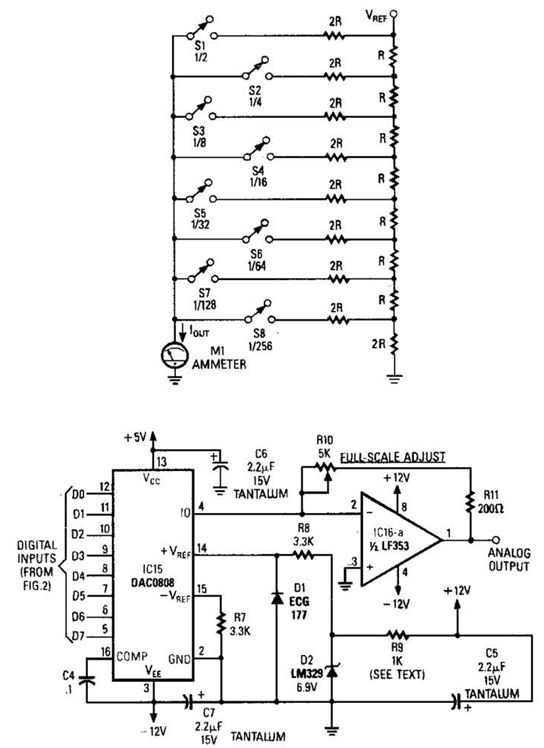
Automatic level control circuit diagram of six
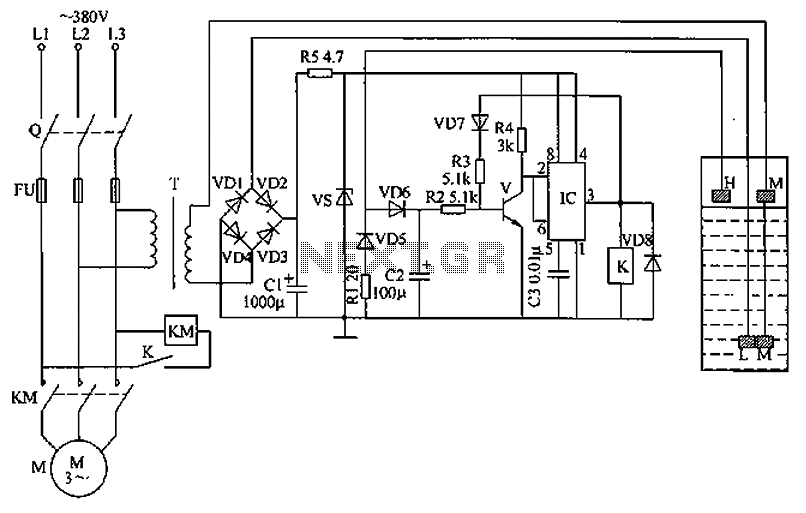
The circuit functions as a liquid level automatic controller, comprising a power circuit, a level detection circuit, and a control execution circuit. The power circuit includes a knife switch (Q), fuse (FU), power transformer (T), rectifier diodes (VD1 to VD4), current-limiting resistors (R1 and R5), a filter capacitor (C1), and a Zener diode (VS). The liquid level detection circuit consists of a high-level electrode (H), a low-level electrode (L), and a main electrode (M). The control execution circuit utilizes a transistor (V), a relay (K), and an integrated circuit (IC), along with diodes (VD5 to VD8) and other peripheral components. When the knife switch (Q) is turned on, 380V AC voltage is reduced by transformer (T). If the liquid level is below the low-level electrode (L), no current flows through the rectifier circuit, preventing the control circuit from operating, and the relay (K) remains in a released state, allowing the normally closed contact to connect to the AC contactor (KM) and power the pump motor (M). When the liquid level rises to the low-level electrode (L), it contacts the main electrode (M), generating a DC voltage output from the rectifier circuit. This DC voltage is filtered by capacitor (C1) and regulated to 12V by resistors (R5) and Zener diode (VS) to supply the control execution circuit. In this scenario, the transistor (V) remains off, resulting in high outputs at pins 2 and 6 of the IC, while pin 3 outputs low, keeping the relay (K) inactive and allowing the pump motor (M) to continue operating. When the liquid level reaches the high-level electrode (H), it also contacts the main electrode (M), turning the transistor (V) on, which changes the outputs at the IC pins: pins 2 and 6 go low, and pin 3 goes high, activating the relay (K) and disconnecting the AC contactor (KM) from the power supply, thus stopping the pump motor (M). When the liquid level drops below the low-level electrode (L), the rectifier circuit disconnects, and the control circuit loses power, releasing the relay (K) and restarting the dosing pump. This cycle continues, enabling unattended automatic liquid supply. Component selection includes 27-ohm wirewound resistors for R1 and R5, 1/4W metal film resistors for R2 to M, a 50V aluminum electrolytic capacitor for C1, a 25V electrolytic capacitor for C2, and monolithic or polyester capacitors for C3. Diodes VD1 to VD8 can be 1N4001 or 1N4007 silicon diodes, while the Zener diode (VS) can be a 1W, 12V type like 1N4742. The transistor (V) can be a C8050, 58050, or 3DG8050 silicon NPN type. The integrated circuit (IC) is of the NE555 type. The relay (K) is a JRX-13F type with a 12V DC coil, while the contactor (KM) should be selected based on the pump motor's power requirements, with a coil voltage of 220V AC. The transformer (T) is a 5W transformer with a secondary voltage of 18V (380V/18V). A carbon rod can be used as a level electrode, with a metal cap welded to one end and sealed with epoxy.
The liquid level automatic controller circuit is designed to maintain desired liquid levels in reservoirs, ensuring efficient operation of pumping systems without manual intervention. The power circuit is crucial for converting high AC voltage to a manageable level for the control circuit. The use of a transformer allows for safe operation, while the rectifier diodes convert AC to DC, which is essential for powering the control execution components.
The level detection mechanism relies on the interaction of the electrodes submerged in the liquid. The electrodes serve as sensors that detect the liquid level changes. When the liquid touches the electrodes, it creates a conductive path that enables the control circuit to function. The integrated circuit (IC) plays a pivotal role in processing these signals and controlling the relay, which in turn manages the operation of the pump motor.
The selection of components is critical for the reliability and efficiency of the circuit. The resistors must handle the specified power ratings, and the capacitors should be chosen based on their voltage ratings to prevent failure under operational conditions. The use of silicon diodes ensures efficient rectification with minimal voltage drop, while the Zener diode provides voltage regulation to protect the circuit from voltage spikes.
Overall, this circuit provides a robust solution for automatic liquid level control, suitable for various applications in industrial and agricultural settings where maintaining fluid levels is essential for operational efficiency. Circuit works The liquid level automatic controller circuit from the power circuit, a level detection circuit and control the implementation of circuit, as shown in FIG. Power circuit from the knife switch Q, fuse FU, power transformer T, rectifier diode VD1 ~ VD4, current-limiting resistors R1 and R5, filter capacitor C1 and Zener diode VS composition. Liquid level detection circuit by the high level electrode H, L low level electrode and the main electrode M components.
Control the implementation of circuit by the transistor V, relay K, when the base integrated circuit IC, diodes VD5 ~ VD8 RC components and peripherals. ON knife switch Q, AC 380V voltage by T Buck, when no liquid or liquid pool level is below the low level electrode L, no current rectifier circuit, the control circuit without the implementation of the operating voltage, the relay K is the release state, the normally closed contact connected to AC contactor KM power pull, plus pump motor M powered job and began dosing.
When the liquid level reaches the lower pool level electrode L, L low level electrode through the liquid in contact with the main electrode M, the rectifier circuit DC voltage output. The DC voltage by C1 filtering, R5 and VS limiting buck regulator to generate 12V DC voltage supply control execution circuit.
In this case, V in the off state, IC 2 feet and 6 feet are high, 3 feet output low, the relay K is not action, plus dosing pump motor M continues. FIG automatic level control circuit When the liquid level reaches the high level electrode tanks H, H high level electrode through the liquid and the main electrode traders turned on, so that V conduction, IC 2 feet and 6 feet into a low, 3 feet high output level, the relay K pull its normally closed contact K disconnect the AC contactor KM power release, plus pump motor M off the power supply, plus pump stops dosing.
When the reservoir pool level drops to a low level electrode L or less, input rectifier circuit and disconnect the control circuit to perform power lose their jobs, the relay K release, plus dosing pump again. Again and again, enabling unattended automatic liquid supply. Component selection R1 and R5 selects 27 wirewound resistors; R2 ~ M selected 1/4W metal film is electrically positive.
C1 selected voltage is 50V aluminum electrolytic capacitors; C2 use of electrolytic capacitors voltage is 25V for; C3 use monolithic capacitors or polyester capacitors. VD1 ~ VD8 selects 1N4001 or Model 1N4007 silicon diodes. VS selection of 1W, 12V zener diode, such as 1N4742 and other models. V selects C8050 or 58050,3DG8050 silicon NPN transistor. IC NE555 type used when the base integrated circuit. K selects JRX-13F type 12V DC relay. KM choose coil voltage is 220V AC contactor, the contact current capacity should be added according to pump motor power may be.
T use 5W, the second voltage of 18V (380V/18V) power transformer. You can use 1 level electrode inside the battery carbon rod (a metal cap on carbon rod with one end of the lead after a good weld, then epoxy sealing).
The liquid level automatic controller circuit is designed to maintain desired liquid levels in reservoirs, ensuring efficient operation of pumping systems without manual intervention. The power circuit is crucial for converting high AC voltage to a manageable level for the control circuit. The use of a transformer allows for safe operation, while the rectifier diodes convert AC to DC, which is essential for powering the control execution components.
The level detection mechanism relies on the interaction of the electrodes submerged in the liquid. The electrodes serve as sensors that detect the liquid level changes. When the liquid touches the electrodes, it creates a conductive path that enables the control circuit to function. The integrated circuit (IC) plays a pivotal role in processing these signals and controlling the relay, which in turn manages the operation of the pump motor.
The selection of components is critical for the reliability and efficiency of the circuit. The resistors must handle the specified power ratings, and the capacitors should be chosen based on their voltage ratings to prevent failure under operational conditions. The use of silicon diodes ensures efficient rectification with minimal voltage drop, while the Zener diode provides voltage regulation to protect the circuit from voltage spikes.
Overall, this circuit provides a robust solution for automatic liquid level control, suitable for various applications in industrial and agricultural settings where maintaining fluid levels is essential for operational efficiency. Circuit works The liquid level automatic controller circuit from the power circuit, a level detection circuit and control the implementation of circuit, as shown in FIG. Power circuit from the knife switch Q, fuse FU, power transformer T, rectifier diode VD1 ~ VD4, current-limiting resistors R1 and R5, filter capacitor C1 and Zener diode VS composition. Liquid level detection circuit by the high level electrode H, L low level electrode and the main electrode M components.
Control the implementation of circuit by the transistor V, relay K, when the base integrated circuit IC, diodes VD5 ~ VD8 RC components and peripherals. ON knife switch Q, AC 380V voltage by T Buck, when no liquid or liquid pool level is below the low level electrode L, no current rectifier circuit, the control circuit without the implementation of the operating voltage, the relay K is the release state, the normally closed contact connected to AC contactor KM power pull, plus pump motor M powered job and began dosing.
When the liquid level reaches the lower pool level electrode L, L low level electrode through the liquid in contact with the main electrode M, the rectifier circuit DC voltage output. The DC voltage by C1 filtering, R5 and VS limiting buck regulator to generate 12V DC voltage supply control execution circuit.
In this case, V in the off state, IC 2 feet and 6 feet are high, 3 feet output low, the relay K is not action, plus dosing pump motor M continues. FIG automatic level control circuit When the liquid level reaches the high level electrode tanks H, H high level electrode through the liquid and the main electrode traders turned on, so that V conduction, IC 2 feet and 6 feet into a low, 3 feet high output level, the relay K pull its normally closed contact K disconnect the AC contactor KM power release, plus pump motor M off the power supply, plus pump stops dosing.
When the reservoir pool level drops to a low level electrode L or less, input rectifier circuit and disconnect the control circuit to perform power lose their jobs, the relay K release, plus dosing pump again. Again and again, enabling unattended automatic liquid supply. Component selection R1 and R5 selects 27 wirewound resistors; R2 ~ M selected 1/4W metal film is electrically positive.
C1 selected voltage is 50V aluminum electrolytic capacitors; C2 use of electrolytic capacitors voltage is 25V for; C3 use monolithic capacitors or polyester capacitors. VD1 ~ VD8 selects 1N4001 or Model 1N4007 silicon diodes. VS selection of 1W, 12V zener diode, such as 1N4742 and other models. V selects C8050 or 58050,3DG8050 silicon NPN transistor. IC NE555 type used when the base integrated circuit. K selects JRX-13F type 12V DC relay. KM choose coil voltage is 220V AC contactor, the contact current capacity should be added according to pump motor power may be.
T use 5W, the second voltage of 18V (380V/18V) power transformer. You can use 1 level electrode inside the battery carbon rod (a metal cap on carbon rod with one end of the lead after a good weld, then epoxy sealing).