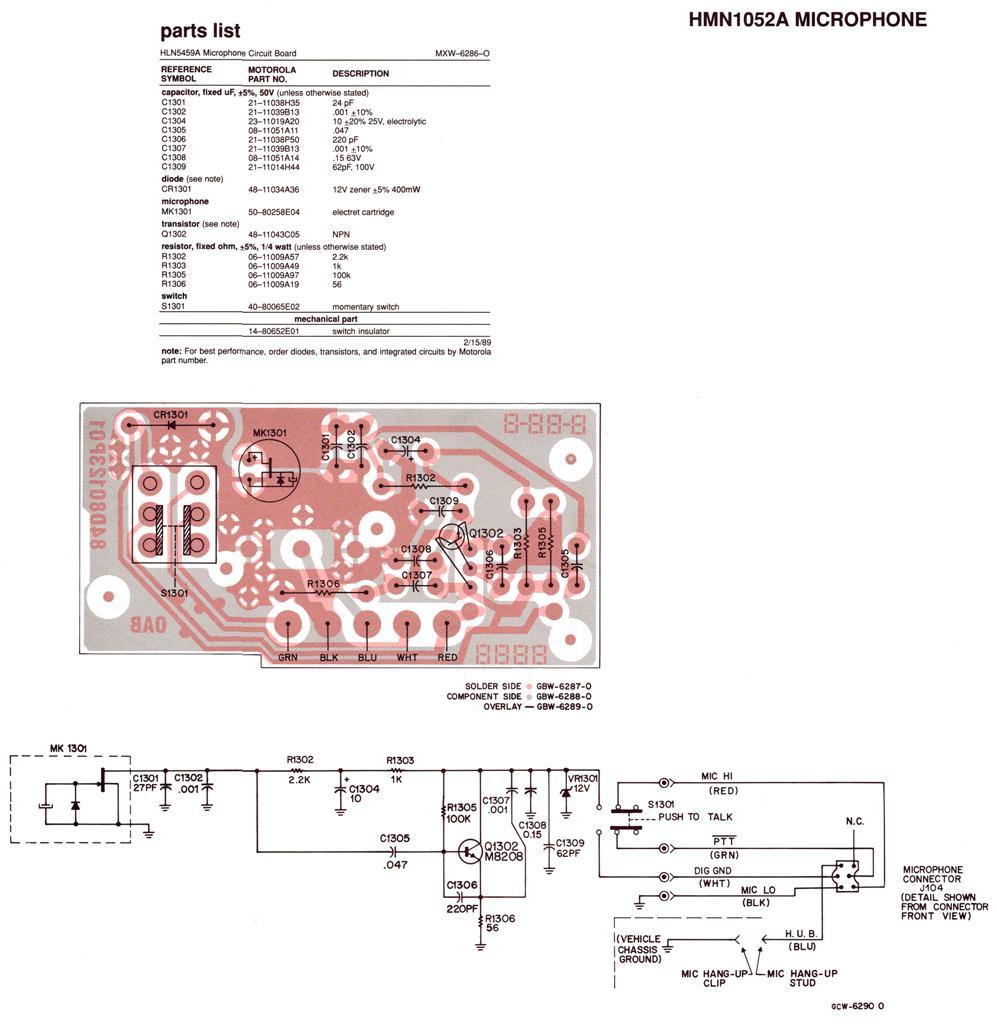
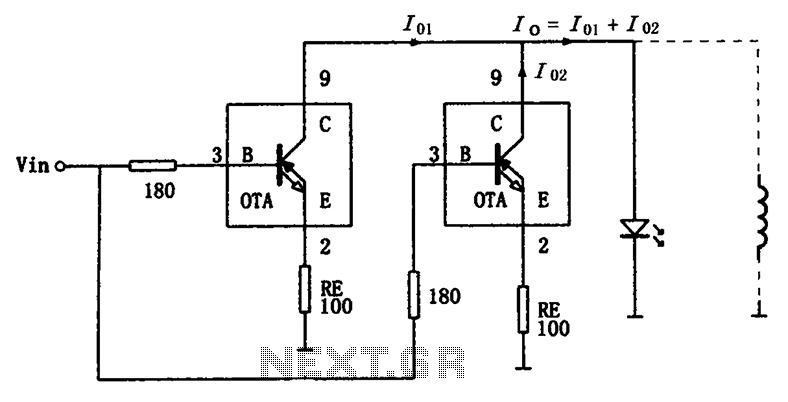
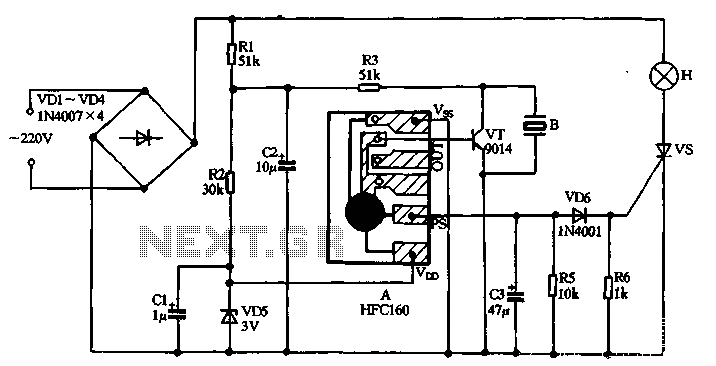
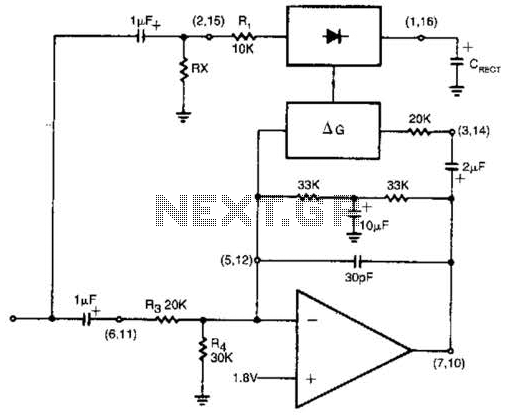
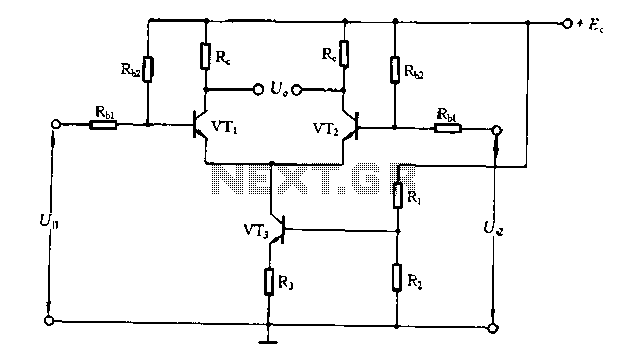
two-speed motor contactor control circuit two speeds in the same direction
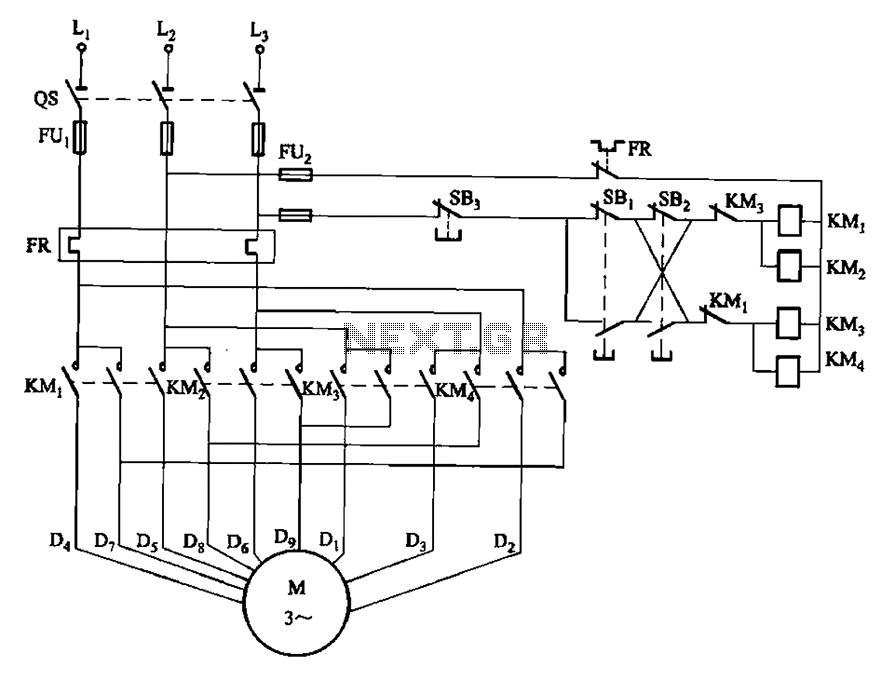
The circuit depicted in Figure 3-112 features two operation buttons: SBi, which serves as the first speed operation button, and SBz, which operates the second speed class. Both buttons facilitate two speeds in the same direction.
The circuit design incorporates two operational buttons, SBi and SBz, that control the speed of a motor or similar device. SBi is designated for the first speed setting, while SBz is utilized for the second speed setting. Both buttons are configured to allow the device to operate at two distinct speeds in the same directional flow, enhancing versatility in applications that require varying operational speeds.
In typical implementations, SBi and SBz may be connected to a motor driver circuit that interprets the button presses and adjusts the power supplied to the motor accordingly. The circuit could utilize a microcontroller or a dedicated speed controller IC to manage the input from the buttons and modulate the output to the motor.
The first speed setting, activated by SBi, may provide a lower voltage or PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signal to the motor, resulting in a slower rotational speed. In contrast, the second speed setting, controlled by SBz, could increase the voltage or modify the PWM duty cycle, allowing for a higher speed operation.
Additionally, protective components such as diodes may be included to prevent back EMF generated by the motor from damaging the circuit. Capacitors may also be employed to filter noise and stabilize the voltage supply, ensuring smooth operation at both speed settings.
This circuit design is applicable in various scenarios, including robotics, conveyor systems, and other automated machinery where speed control is essential for performance optimization. Circuit shown in Figure 3-112. Figure, SBi as the first speed operation button, SBz is run by the second speed class. Two speeds in the same direction.
The circuit design incorporates two operational buttons, SBi and SBz, that control the speed of a motor or similar device. SBi is designated for the first speed setting, while SBz is utilized for the second speed setting. Both buttons are configured to allow the device to operate at two distinct speeds in the same directional flow, enhancing versatility in applications that require varying operational speeds.
In typical implementations, SBi and SBz may be connected to a motor driver circuit that interprets the button presses and adjusts the power supplied to the motor accordingly. The circuit could utilize a microcontroller or a dedicated speed controller IC to manage the input from the buttons and modulate the output to the motor.
The first speed setting, activated by SBi, may provide a lower voltage or PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signal to the motor, resulting in a slower rotational speed. In contrast, the second speed setting, controlled by SBz, could increase the voltage or modify the PWM duty cycle, allowing for a higher speed operation.
Additionally, protective components such as diodes may be included to prevent back EMF generated by the motor from damaging the circuit. Capacitors may also be employed to filter noise and stabilize the voltage supply, ensuring smooth operation at both speed settings.
This circuit design is applicable in various scenarios, including robotics, conveyor systems, and other automated machinery where speed control is essential for performance optimization. Circuit shown in Figure 3-112. Figure, SBi as the first speed operation button, SBz is run by the second speed class. Two speeds in the same direction.