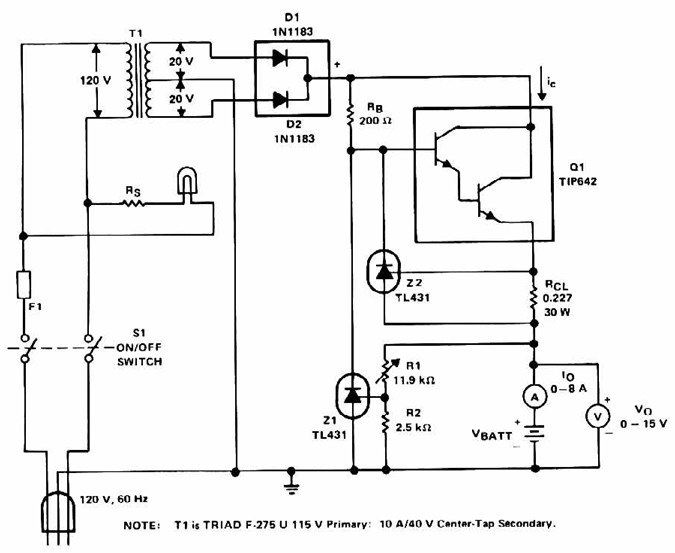
Battery Test Circuit Circuit
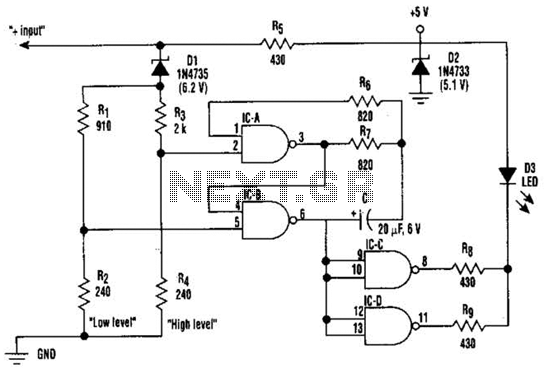
This circuit displays three voltage levels: normal (11 to 15 V), high (greater than 15 V), and low (below 11 V). When the voltage is low, the LED illuminates steadily. In the normal voltage range, the LED remains off. When the voltage is high, the LED blinks at a rate of 1 Hz. This circuit is beneficial for ensuring proper operation of electrical systems.
The circuit employs a voltage comparator to monitor the input voltage and determine its level. The reference voltages for low and high thresholds can be set using a voltage divider network, which typically consists of resistors. For the low voltage threshold (11 V), the circuit can be designed using an operational amplifier configured as a comparator. When the input voltage drops below this threshold, the output of the comparator switches, turning the LED on steadily to indicate a low voltage condition.
In the normal voltage range (11 to 15 V), the comparator output remains low, keeping the LED off. To detect the high voltage condition (greater than 15 V), a second comparator can be implemented. This comparator would be configured to activate when the input voltage exceeds the high threshold. Upon activation, a timer circuit, such as a 555 timer in astable mode, can be integrated to cause the LED to blink at a frequency of 1 Hz, providing a visual indication of the high voltage status.
The circuit's design ensures that it can handle a range of input voltages while providing clear visual feedback through the LED. Additionally, the use of appropriate resistors and capacitors will stabilize the circuit operation and prevent false triggering due to transient voltage spikes. This voltage level indicator circuit serves as a critical tool in monitoring electrical systems, ensuring they operate within safe voltage ranges, and alerting users to potential issues before they escalate. Using this circuit, tiiree levels of voltage can be displayednormal (11 to 15 V), liigh (>15 V), and low (11 V). When the voltage is low, the LED glows steadily. In the normal range, the LED is off. When the voltage is high, the LED blinks at a 1-Hz rate. This circuit is useful for assuring proper electrical system operation.
The circuit employs a voltage comparator to monitor the input voltage and determine its level. The reference voltages for low and high thresholds can be set using a voltage divider network, which typically consists of resistors. For the low voltage threshold (11 V), the circuit can be designed using an operational amplifier configured as a comparator. When the input voltage drops below this threshold, the output of the comparator switches, turning the LED on steadily to indicate a low voltage condition.
In the normal voltage range (11 to 15 V), the comparator output remains low, keeping the LED off. To detect the high voltage condition (greater than 15 V), a second comparator can be implemented. This comparator would be configured to activate when the input voltage exceeds the high threshold. Upon activation, a timer circuit, such as a 555 timer in astable mode, can be integrated to cause the LED to blink at a frequency of 1 Hz, providing a visual indication of the high voltage status.
The circuit's design ensures that it can handle a range of input voltages while providing clear visual feedback through the LED. Additionally, the use of appropriate resistors and capacitors will stabilize the circuit operation and prevent false triggering due to transient voltage spikes. This voltage level indicator circuit serves as a critical tool in monitoring electrical systems, ensuring they operate within safe voltage ranges, and alerting users to potential issues before they escalate. Using this circuit, tiiree levels of voltage can be displayednormal (11 to 15 V), liigh (>15 V), and low (11 V). When the voltage is low, the LED glows steadily. In the normal range, the LED is off. When the voltage is high, the LED blinks at a 1-Hz rate. This circuit is useful for assuring proper electrical system operation.