Blue White LED Driver Circuit Joule Thief
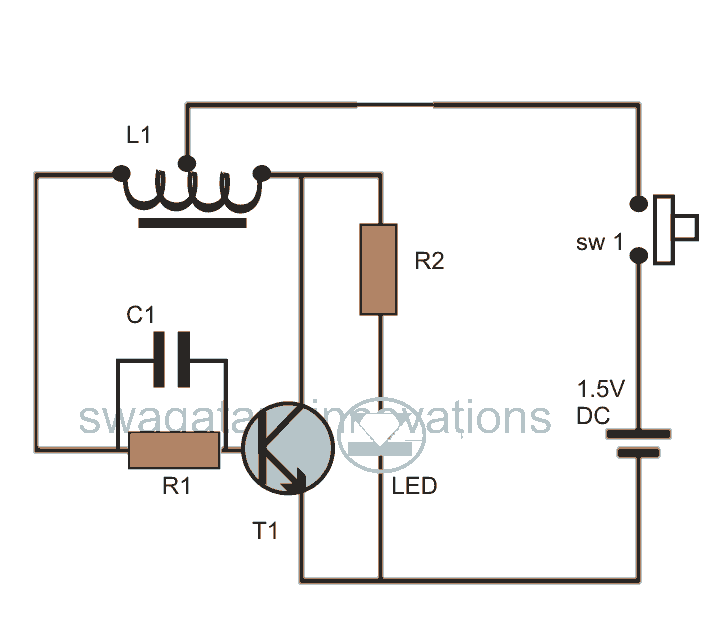
This post discusses blue and white LED drivers utilizing a joule thief circuit. Further exploration of the circuit's functionality is provided, along with simulation points.
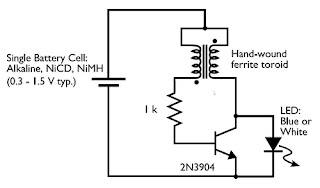
The joule thief circuit is a simple and efficient boost converter that allows for the operation of LEDs at low input voltages, such as those from depleted batteries. It operates on the principle of energy storage and transfer, utilizing an inductor to step up the voltage to a level suitable for powering blue and white LEDs, which typically require higher forward voltages than standard red or green LEDs.
The circuit typically consists of a few key components: a transistor, an inductor, a resistor, and two diodes. The transistor is used to switch the current through the inductor on and off, creating a magnetic field. When the transistor is turned off, the magnetic field collapses, inducing a voltage across the inductor that is higher than the input voltage. This induced voltage is then used to drive the LEDs.
For simulation purposes, the parameters of the circuit can be adjusted to observe the effects on LED brightness and efficiency. Key simulation points include the input voltage range, the type and value of the inductor, the switching frequency of the transistor, and the load resistance represented by the LEDs. It is essential to ensure that the transistor is appropriately rated for the current and voltage levels in the circuit to avoid damage.
The joule thief circuit's simplicity and effectiveness make it an excellent choice for applications where maximizing battery life is critical, such as in portable or low-power devices. By understanding the operation and characteristics of this circuit, designers can create efficient LED drivers that extend the usability of energy sources.Blue and white LED drivers using joule thief circuit has been covered in this post, lets learn more. The circuit may be simulated with the following points 🔗 External reference
The joule thief circuit is a simple and efficient boost converter that allows for the operation of LEDs at low input voltages, such as those from depleted batteries. It operates on the principle of energy storage and transfer, utilizing an inductor to step up the voltage to a level suitable for powering blue and white LEDs, which typically require higher forward voltages than standard red or green LEDs.
The circuit typically consists of a few key components: a transistor, an inductor, a resistor, and two diodes. The transistor is used to switch the current through the inductor on and off, creating a magnetic field. When the transistor is turned off, the magnetic field collapses, inducing a voltage across the inductor that is higher than the input voltage. This induced voltage is then used to drive the LEDs.
For simulation purposes, the parameters of the circuit can be adjusted to observe the effects on LED brightness and efficiency. Key simulation points include the input voltage range, the type and value of the inductor, the switching frequency of the transistor, and the load resistance represented by the LEDs. It is essential to ensure that the transistor is appropriately rated for the current and voltage levels in the circuit to avoid damage.
The joule thief circuit's simplicity and effectiveness make it an excellent choice for applications where maximizing battery life is critical, such as in portable or low-power devices. By understanding the operation and characteristics of this circuit, designers can create efficient LED drivers that extend the usability of energy sources.Blue and white LED drivers using joule thief circuit has been covered in this post, lets learn more. The circuit may be simulated with the following points 🔗 External reference