Brake lights flasher circuits
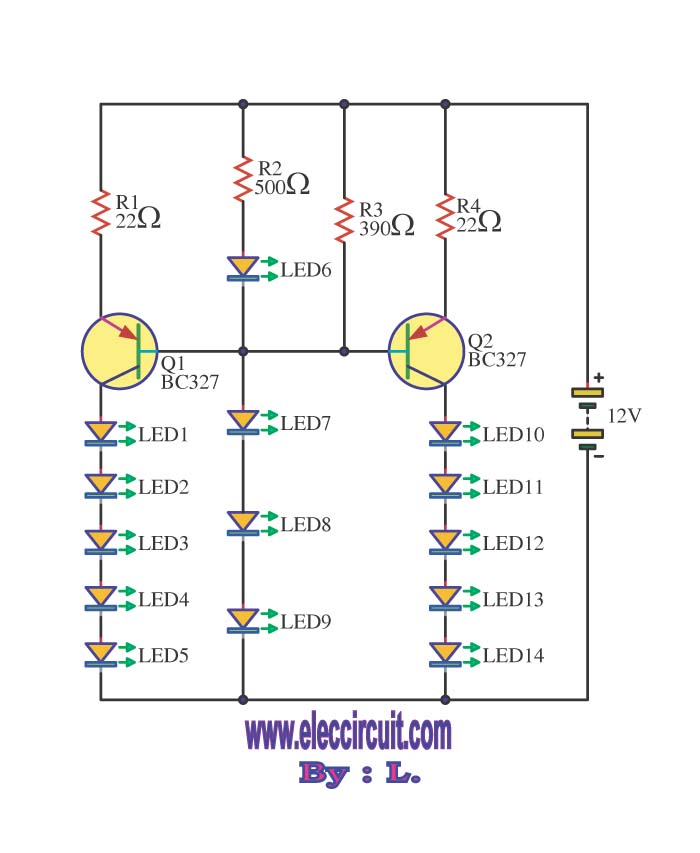
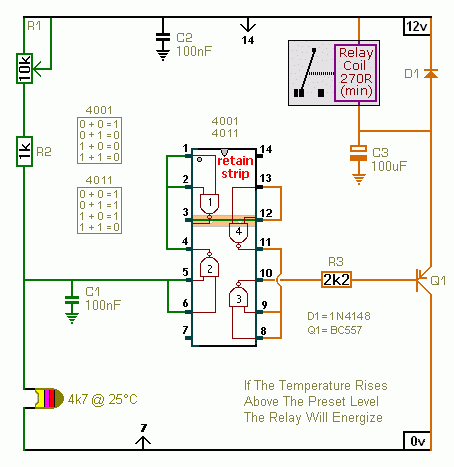
This circuit enables the brake light to flash. The default behavior occurs when power is supplied to the circuit or when the brake is engaged. The timer IC (IC2) drives current to the transistor (Q2), producing an oscillating output pulse signal at pin 3, which is fed into pin 1 of the CD4024 (IC1). The circuit counts the pulses and stops counting after eight pulses, with pin 2 of IC1 serving as the reset. When the brake is tapped and held, the brake lights will flash at a rate of approximately six times per second, a frequency determined by resistors R3 and capacitor C3. The duration between each flash is defined by capacitor C2 and resistor R1. The circuit operates on a 12-volt DC power supply, typically sourced from a vehicle. Capacitor C1 functions as a filter to smooth the current flow. Transistor Q2 can be substituted with any equivalent part, such as the SM3180.
This brake light flashing circuit incorporates fundamental electronic components to achieve its functionality. The circuit begins with a 12V DC power supply, which is standard in automotive applications. The power enters the circuit and is filtered by capacitor C1 to eliminate any voltage spikes or noise, ensuring stable operation.
The heart of the circuit is the timer IC (IC2), which is configured to generate a pulse-width modulation (PWM) signal. This signal is output at pin 3 of IC2 and is responsible for driving the transistor (Q2). The transistor acts as a switch, allowing current to flow to the brake lights when activated. The frequency of the output pulse is primarily determined by the values of resistor R3 and capacitor C3, which set the oscillation rate.
As the brake is pressed, the output pulse is sent to the CD4024 (IC1), a binary counter IC. The pulses are counted until the circuit reaches eight counts, at which point the output at pin 2 of IC1 resets the counter, stopping the flashing sequence. The timing of the flashes is influenced by the configuration of capacitor C2 and resistor R1, which dictate the intervals between each flash.
In summary, this circuit design effectively allows for a visual indication of braking through flashing lights, enhancing vehicle safety. The ability to customize the timing components (R1, R3, C2, and C3) allows for flexibility in adjusting the flash rate and duration, making it adaptable to various user preferences or vehicle requirements. The choice of the transistor (Q2) is also flexible, permitting the use of different components while maintaining the circuit's functionality.This circuit will allow the brake light was flashing. The default behavior. When the power supply to the circuit, Or tap the brake it. The IC timer IC2 drive current to transistor Q2 and producing oscillator output, pulse signal output at pin 3 to input pin 1 of IC1-CD4024. Count pulse and stops counting after 8 pulses, with pin 2 of IC1 is reset. N ow, tap and hold the brake, the brake lights will flash the set, about 6 times per second. Which is determined by R3 and C3. The distance between each set, is defined by the C2 and R1. The Voltage input to the circuit, used 12 volt DC power from a car at all. The section capacitor C1 as a filter to smooth the flow. Transistor Q2 may be any number SM3180. 🔗 External reference
This brake light flashing circuit incorporates fundamental electronic components to achieve its functionality. The circuit begins with a 12V DC power supply, which is standard in automotive applications. The power enters the circuit and is filtered by capacitor C1 to eliminate any voltage spikes or noise, ensuring stable operation.
The heart of the circuit is the timer IC (IC2), which is configured to generate a pulse-width modulation (PWM) signal. This signal is output at pin 3 of IC2 and is responsible for driving the transistor (Q2). The transistor acts as a switch, allowing current to flow to the brake lights when activated. The frequency of the output pulse is primarily determined by the values of resistor R3 and capacitor C3, which set the oscillation rate.
As the brake is pressed, the output pulse is sent to the CD4024 (IC1), a binary counter IC. The pulses are counted until the circuit reaches eight counts, at which point the output at pin 2 of IC1 resets the counter, stopping the flashing sequence. The timing of the flashes is influenced by the configuration of capacitor C2 and resistor R1, which dictate the intervals between each flash.
In summary, this circuit design effectively allows for a visual indication of braking through flashing lights, enhancing vehicle safety. The ability to customize the timing components (R1, R3, C2, and C3) allows for flexibility in adjusting the flash rate and duration, making it adaptable to various user preferences or vehicle requirements. The choice of the transistor (Q2) is also flexible, permitting the use of different components while maintaining the circuit's functionality.This circuit will allow the brake light was flashing. The default behavior. When the power supply to the circuit, Or tap the brake it. The IC timer IC2 drive current to transistor Q2 and producing oscillator output, pulse signal output at pin 3 to input pin 1 of IC1-CD4024. Count pulse and stops counting after 8 pulses, with pin 2 of IC1 is reset. N ow, tap and hold the brake, the brake lights will flash the set, about 6 times per second. Which is determined by R3 and C3. The distance between each set, is defined by the C2 and R1. The Voltage input to the circuit, used 12 volt DC power from a car at all. The section capacitor C1 as a filter to smooth the flow. Transistor Q2 may be any number SM3180. 🔗 External reference