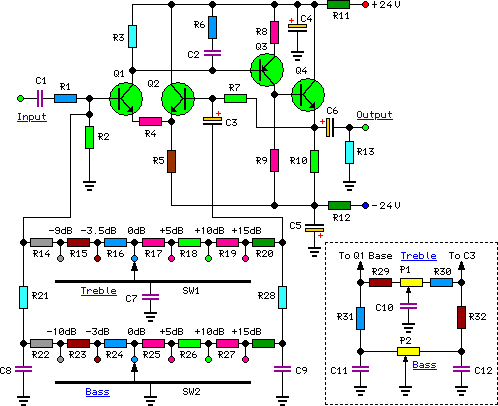
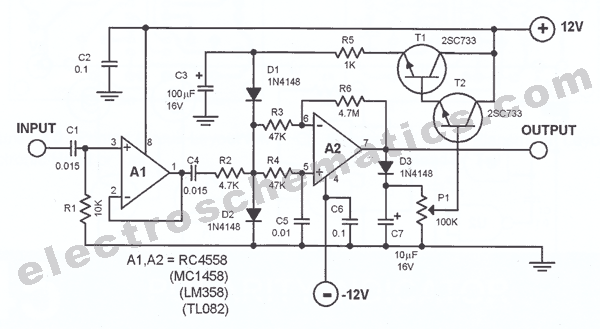
cellular phone calling detector circuit schematic
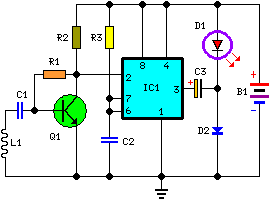
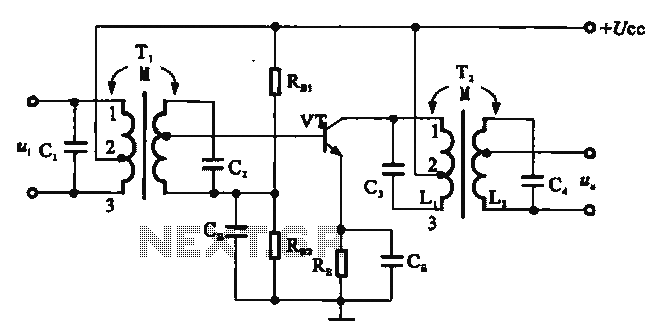
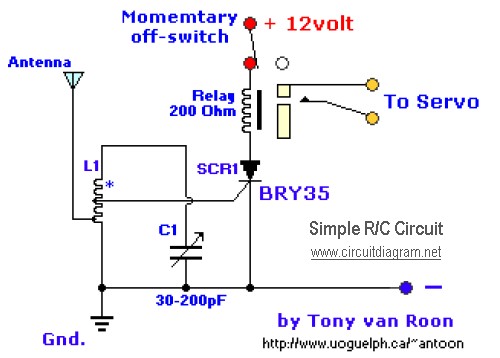
This circuit is designed to detect incoming calls on a cellular phone, even when the phone's ringer is turned off, by utilizing a flashing LED. The device should be positioned a few centimeters away from the cellular phone, allowing its sensor coil L1 to detect the electromagnetic field emitted by the phone's receiver during an incoming call.
The circuit operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where the sensor coil L1 picks up the electromagnetic waves generated by the cellular phone when a call is received. The coil is tuned to the specific frequency range of the phone's signal, ensuring optimal sensitivity and responsiveness to incoming calls.
Upon detection of the electromagnetic field, the circuit activates a light-emitting diode (LED) to provide a visual indication of the incoming call. The LED flashes at a rate that can be adjusted based on the circuit design, allowing for customization of the visual alert.
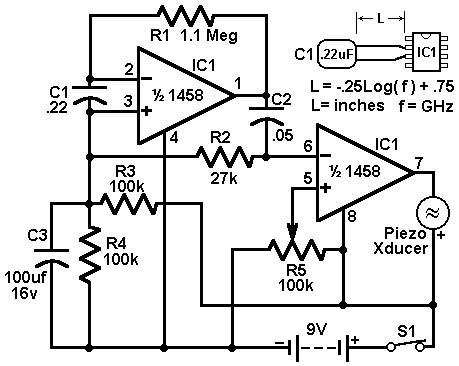
Key components of the circuit include the sensor coil L1, which is typically constructed using insulated copper wire wound around a non-conductive core. The circuit may also incorporate a transistor or operational amplifier to amplify the signal from the coil, ensuring reliable detection of the phone's electromagnetic emissions. Additionally, resistors and capacitors may be used to filter noise and stabilize the circuit operation.
Power for the circuit can be supplied by a small battery or a USB power source, depending on the design requirements. The compact size of the circuit allows for easy integration into various environments, making it a versatile solution for users who may need a discreet alert system for incoming calls.
Overall, this circuit provides an effective solution for alerting users to incoming calls without relying on the traditional ringer of a cellular phone, enhancing usability in situations where sound notifications may be impractical.This circuit was designed to detect when a call is incoming in a cellular phone (even when the calling tone of the device is switched-off) by means of a flashing LED. The device must be placed a few centimeters from the cellular phone, so its sensor coil L1 can detect the field emitted by the phone receiver during an incoming call..
🔗 External reference
The circuit operates on the principle of electromagnetic induction, where the sensor coil L1 picks up the electromagnetic waves generated by the cellular phone when a call is received. The coil is tuned to the specific frequency range of the phone's signal, ensuring optimal sensitivity and responsiveness to incoming calls.
Upon detection of the electromagnetic field, the circuit activates a light-emitting diode (LED) to provide a visual indication of the incoming call. The LED flashes at a rate that can be adjusted based on the circuit design, allowing for customization of the visual alert.
Key components of the circuit include the sensor coil L1, which is typically constructed using insulated copper wire wound around a non-conductive core. The circuit may also incorporate a transistor or operational amplifier to amplify the signal from the coil, ensuring reliable detection of the phone's electromagnetic emissions. Additionally, resistors and capacitors may be used to filter noise and stabilize the circuit operation.
Power for the circuit can be supplied by a small battery or a USB power source, depending on the design requirements. The compact size of the circuit allows for easy integration into various environments, making it a versatile solution for users who may need a discreet alert system for incoming calls.
Overall, this circuit provides an effective solution for alerting users to incoming calls without relying on the traditional ringer of a cellular phone, enhancing usability in situations where sound notifications may be impractical.This circuit was designed to detect when a call is incoming in a cellular phone (even when the calling tone of the device is switched-off) by means of a flashing LED. The device must be placed a few centimeters from the cellular phone, so its sensor coil L1 can detect the field emitted by the phone receiver during an incoming call..
🔗 External reference