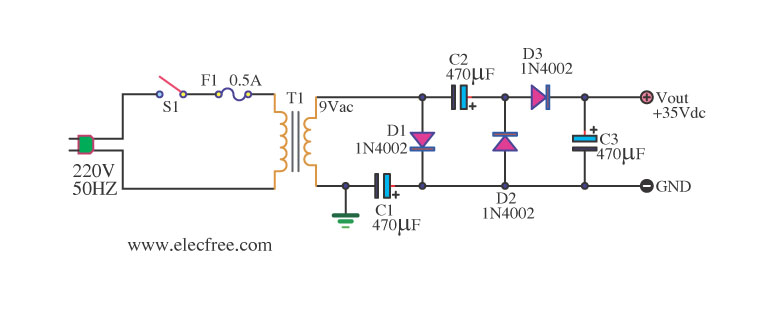
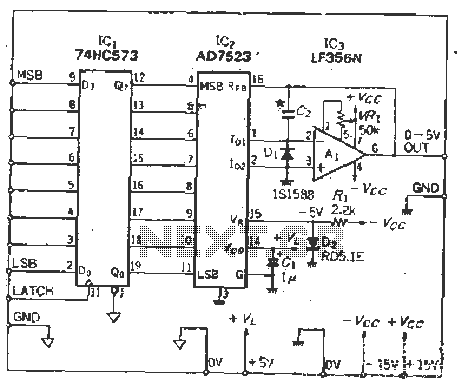
Cheap Switch-Mode DC-DC Converter
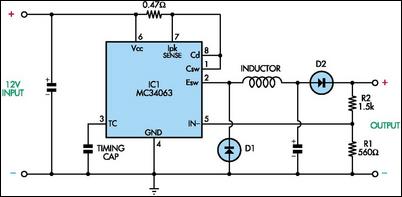
This circuit utilizes mobile phone chargers that incorporate the Motorola MC34063 switch-mode integrated circuit (IC). The output voltage can be adjusted across a broad spectrum by altering the values of the feedback resistors R1 and R2. The output voltage is determined by the formula: Vout = 1.25 (1 + R2/R1). The specified resistor values yield an output of 3V.
The circuit operates as a step-up (boost) converter, leveraging the MC34063, which is designed for efficient voltage regulation. The key components include the MC34063 IC, an inductor, a diode, and the feedback resistors R1 and R2. The inductor stores energy during the ON phase of the switch, while the diode allows current to flow to the output during the OFF phase, effectively increasing the voltage.
To achieve the desired output voltage, it is essential to select appropriate resistor values for R1 and R2. The feedback network formed by these resistors sets the regulation point of the output voltage. For instance, if R1 is set to 100 ohms and R2 is set to 300 ohms, the output voltage can be calculated as follows:
Vout = 1.25 (1 + 300/100) = 1.25 (1 + 3) = 1.25 * 4 = 5V.
This flexibility allows for a wide range of output voltages, making the circuit suitable for powering various devices requiring different voltage levels.
In addition to the resistors, the selection of the inductor is critical, as it must be rated for the desired output current and voltage. The diode should be a Schottky type to ensure minimal voltage drop and faster switching speeds. Proper bypass capacitors should be included at the input and output to filter out any noise and stabilize the voltage levels.
Overall, this circuit design is efficient and versatile, making it ideal for applications in portable electronics where space and power efficiency are paramount. Proper layout considerations should be taken into account to minimize parasitic inductance and resistance, which can affect performance.This circuit is based on mobile phone chargers. These chargers are based on the Motorola MC34063 switchmode IC. By changing the values of the feedback resistors (R1 & R2), the output voltage can be varied over a wide range. Just modify R1 and R2 according to the formula: Vout = 1. 25 (1+R2/R1). The values shown give an output of 3V. 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates as a step-up (boost) converter, leveraging the MC34063, which is designed for efficient voltage regulation. The key components include the MC34063 IC, an inductor, a diode, and the feedback resistors R1 and R2. The inductor stores energy during the ON phase of the switch, while the diode allows current to flow to the output during the OFF phase, effectively increasing the voltage.
To achieve the desired output voltage, it is essential to select appropriate resistor values for R1 and R2. The feedback network formed by these resistors sets the regulation point of the output voltage. For instance, if R1 is set to 100 ohms and R2 is set to 300 ohms, the output voltage can be calculated as follows:
Vout = 1.25 (1 + 300/100) = 1.25 (1 + 3) = 1.25 * 4 = 5V.
This flexibility allows for a wide range of output voltages, making the circuit suitable for powering various devices requiring different voltage levels.
In addition to the resistors, the selection of the inductor is critical, as it must be rated for the desired output current and voltage. The diode should be a Schottky type to ensure minimal voltage drop and faster switching speeds. Proper bypass capacitors should be included at the input and output to filter out any noise and stabilize the voltage levels.
Overall, this circuit design is efficient and versatile, making it ideal for applications in portable electronics where space and power efficiency are paramount. Proper layout considerations should be taken into account to minimize parasitic inductance and resistance, which can affect performance.This circuit is based on mobile phone chargers. These chargers are based on the Motorola MC34063 switchmode IC. By changing the values of the feedback resistors (R1 & R2), the output voltage can be varied over a wide range. Just modify R1 and R2 according to the formula: Vout = 1. 25 (1+R2/R1). The values shown give an output of 3V. 🔗 External reference