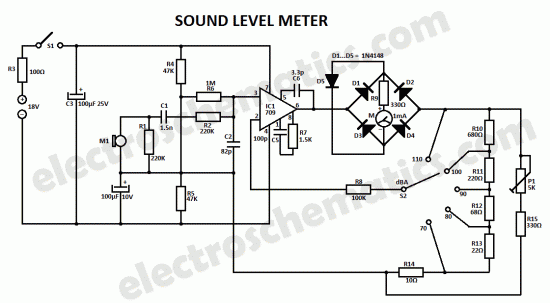
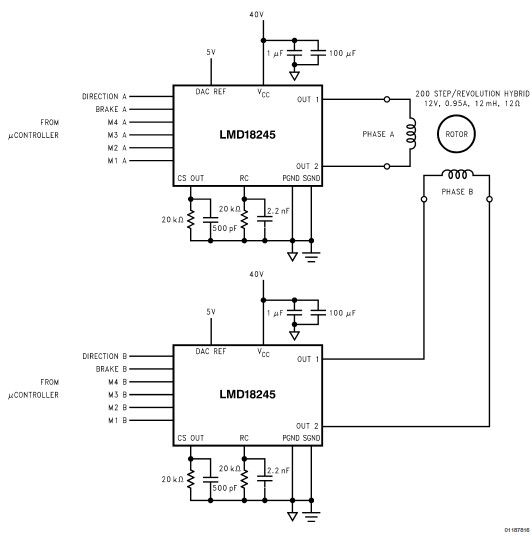
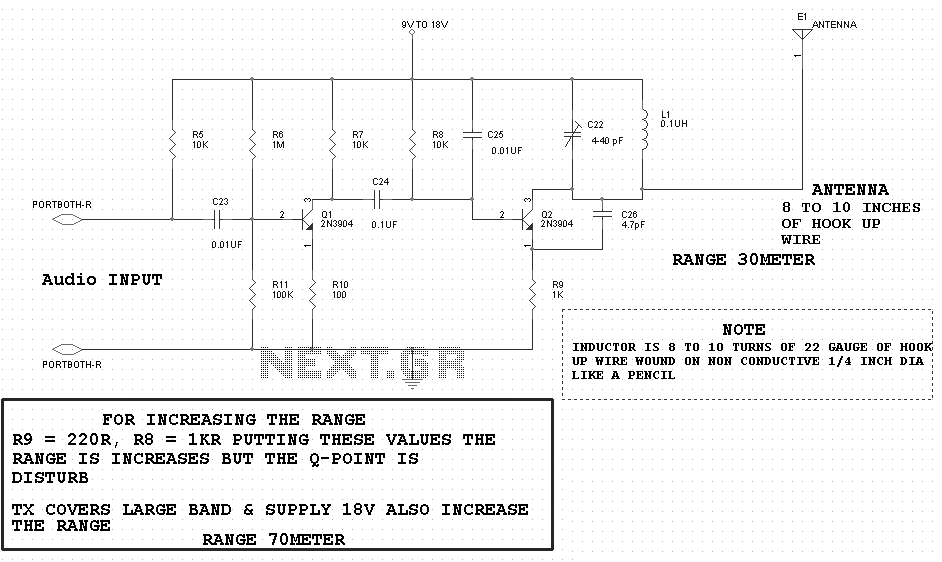
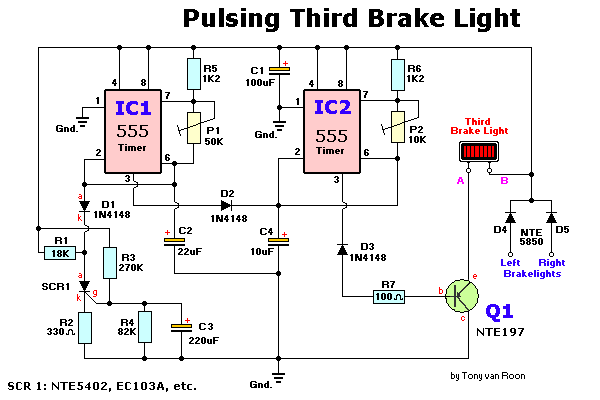
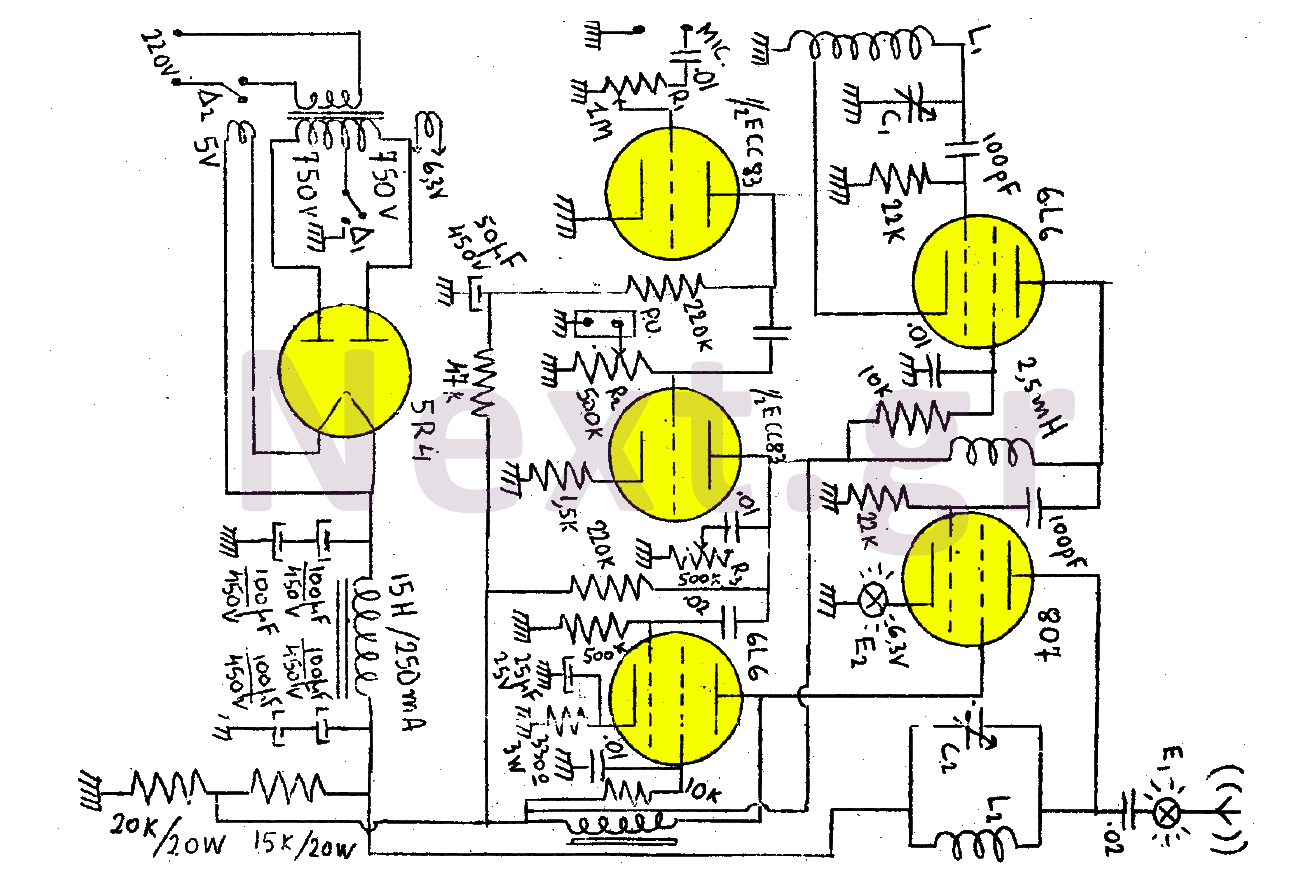
circuit diagram download
The transmitter's function is to modulate the original signal frequency of the message-carrying signal, a process known as modulation. The circuit realization of this function is referred to as a frequency modulation (FM) circuit. FM tuners are categorized into direct and indirect modulation types. Direct FM modulation involves direct control from the oscillator circuit parameters and operating status, where the oscillation frequency is modulated by a varactor diode. FM oscillators utilizing relaxation reactance tubes also fall into this category. Klystrons are commonly used devices in the microwave frequency band. In indirect FM, the modulation signal is adjusted so that the output amplitude is inversely proportional to the modulation angular frequency, requiring phase modulation for FM signals. Although indirect FM offers a relatively stable carrier frequency, it involves a more complex circuit with a small frequency shift and significant parasitic amplitude modulation, often necessitating multiple frequency increases to achieve the desired frequency shift. The basic requirements for an FM tuner include the ability to frequently adjust and maintain good frequency characteristics with minimal parasitic amplitude modulation. FM tuners are widely used in radio, television audio, microwave communications, and phase-locked circuits. FM radio is known for its robust anti-interference capabilities and sound clarity, contributing to its rapid development. The FM radio frequency band typically ranges from 200 to 250 kHz, with a bandwidth ten times that of AM radio, allowing for the transmission of high-fidelity stereo signals. Due to amplitude bandwidth limitations, the receiver's passband width may encounter interference conflicts, restricting audio signals to a frequency range of 30 to 8000 Hz. In contrast, FM can extend audio signal frequencies from 30 to 15,000 Hz, yielding richer spectral components and significantly improved sound quality. Many small and medium-power FM transmitters utilize direct modulation varactor diode technology, where the carrier frequency is directly modulated by an LC oscillator. Crystal oscillators and phase-locked loops are employed to stabilize the center frequency. Direct frequency modulation offers a simple circuit design with good performance, minimal spurious signals, and ease of maintenance, making it an advanced frequency modulation scheme. Consequently, research and design of frequency modulation circuits hold significant importance. The course design aims to provide practical value in designing a tuner to achieve frequency modulation of audio signals.
The frequency modulation circuit serves as a critical component in the transmission of audio signals, particularly in FM radio applications. The circuit typically consists of an oscillator, modulator, and demodulator. The oscillator generates a carrier frequency, which is then modulated by the audio signal using a varactor diode for direct modulation or a more complex arrangement for indirect modulation. The choice of modulation type influences the circuit's complexity and performance characteristics.
In direct FM modulation, the oscillator's frequency is varied directly in response to the audio signal, allowing for a straightforward implementation. The varactor diode's capacitance changes with the applied voltage, enabling fine control over the oscillator's frequency. This method is particularly advantageous for small and medium-power applications due to its simplicity and efficiency.
On the other hand, indirect FM modulation involves a more sophisticated approach where the modulation affects the amplitude of the signal, which is subsequently converted to a phase modulation. This method can yield a more stable carrier frequency, albeit at the cost of increased circuit complexity. The phase-locked loop is often employed in this configuration to maintain frequency stability, ensuring that the output remains consistent despite variations in the input signal.
The design of the FM tuner must address several key factors, including frequency stability, bandwidth, and resistance to interference. A well-designed tuner will have a high-quality factor (Q-factor) to minimize signal loss and enhance selectivity. Additionally, the circuit should be capable of handling the specified frequency range while providing a clear and distortion-free audio output.
Overall, the advancements in frequency modulation technology have significantly enhanced the quality of audio transmission, making FM radio a popular choice for broadcasting applications. The ongoing research and development in this field continue to improve circuit designs, enabling higher fidelity and more reliable communication systems.The transmitter function is to modulate the original signal frequency of the signal carrying the message, the process is called modulation, the circuit realization of this function is called frequency modulation circuit. al of the circuit. FM tuner is divided into direct and indirect modulation types. Direct FM modulation signal is directly controlled from the oscillator circuit parameters and operating status, so the oscillation frequency by the modulation varactor diode frequency modulation, frequency modulation and relaxation reactance tube FM oscillators fall into this category. Klystron as the microwave frequency band commonly used devices. Integral circuit indirect FM is the modulation signal points so that the output amplitude is inversely proportional to the modulation angular frequency, then the phase modulation of the phase modulation device, then the output phase modulation is required for FM signals.
FM has the advantage of an indirect carrier frequency is relatively stable, but more complex circuit, frequency shift is small, and large parasitic amplitude modulation, it normally takes several times to increase frequency to frequency shift. The basic requirements of the tuner is adjusted frequently move large frequency characteristics of a good, small parasitic amplitude modulation.
Widely used in FM radio tuner, TV audio, microwave communications, phase-locked circuits and other electronic equipment Sweep. FM radio has a strong anti-interference performance, sound clarity, etc. , gained rapid development. FM radio frequency band is usually about 200 ~ 250kHz, the band width is ten times the number of AM radio, easy to send high-fidelity stereo signal.
The amplitude by the bandwidth limitations, there is in the receiver passband width and interference conflicts, so the audio signal is limited to 30 ~ 8000Hz frequency range. In FM, the frequency of the audio signal can be extended to 30 ~ 15000Hz, spectral components of the audio signal is more abundant, the sound quality greatly improved.
Many small and medium-power FM transmitter are used direct modulation varactor diode technology, which work on the launch of the carrier frequency LC oscillator frequency directly back on the road, using the crystal oscillator and phase-locked loop to stabilize the center frequency. Frequency modulation and frequency than the approach that the circuit is simple, good performance, less vice waves, easy maintenance, is an advanced frequency modulation scheme.
Therefore, for frequency modulation circuit research, design, of great significance. The course design I am going to have some practical value to design the tuner in order to achieve frequency modulation of the audio signal. Beijing University of Posts 2008 Fall Specialty: Software Engineering Master Time: training ended 🔗 External reference
The frequency modulation circuit serves as a critical component in the transmission of audio signals, particularly in FM radio applications. The circuit typically consists of an oscillator, modulator, and demodulator. The oscillator generates a carrier frequency, which is then modulated by the audio signal using a varactor diode for direct modulation or a more complex arrangement for indirect modulation. The choice of modulation type influences the circuit's complexity and performance characteristics.
In direct FM modulation, the oscillator's frequency is varied directly in response to the audio signal, allowing for a straightforward implementation. The varactor diode's capacitance changes with the applied voltage, enabling fine control over the oscillator's frequency. This method is particularly advantageous for small and medium-power applications due to its simplicity and efficiency.
On the other hand, indirect FM modulation involves a more sophisticated approach where the modulation affects the amplitude of the signal, which is subsequently converted to a phase modulation. This method can yield a more stable carrier frequency, albeit at the cost of increased circuit complexity. The phase-locked loop is often employed in this configuration to maintain frequency stability, ensuring that the output remains consistent despite variations in the input signal.
The design of the FM tuner must address several key factors, including frequency stability, bandwidth, and resistance to interference. A well-designed tuner will have a high-quality factor (Q-factor) to minimize signal loss and enhance selectivity. Additionally, the circuit should be capable of handling the specified frequency range while providing a clear and distortion-free audio output.
Overall, the advancements in frequency modulation technology have significantly enhanced the quality of audio transmission, making FM radio a popular choice for broadcasting applications. The ongoing research and development in this field continue to improve circuit designs, enabling higher fidelity and more reliable communication systems.The transmitter function is to modulate the original signal frequency of the signal carrying the message, the process is called modulation, the circuit realization of this function is called frequency modulation circuit. al of the circuit. FM tuner is divided into direct and indirect modulation types. Direct FM modulation signal is directly controlled from the oscillator circuit parameters and operating status, so the oscillation frequency by the modulation varactor diode frequency modulation, frequency modulation and relaxation reactance tube FM oscillators fall into this category. Klystron as the microwave frequency band commonly used devices. Integral circuit indirect FM is the modulation signal points so that the output amplitude is inversely proportional to the modulation angular frequency, then the phase modulation of the phase modulation device, then the output phase modulation is required for FM signals.
FM has the advantage of an indirect carrier frequency is relatively stable, but more complex circuit, frequency shift is small, and large parasitic amplitude modulation, it normally takes several times to increase frequency to frequency shift. The basic requirements of the tuner is adjusted frequently move large frequency characteristics of a good, small parasitic amplitude modulation.
Widely used in FM radio tuner, TV audio, microwave communications, phase-locked circuits and other electronic equipment Sweep. FM radio has a strong anti-interference performance, sound clarity, etc. , gained rapid development. FM radio frequency band is usually about 200 ~ 250kHz, the band width is ten times the number of AM radio, easy to send high-fidelity stereo signal.
The amplitude by the bandwidth limitations, there is in the receiver passband width and interference conflicts, so the audio signal is limited to 30 ~ 8000Hz frequency range. In FM, the frequency of the audio signal can be extended to 30 ~ 15000Hz, spectral components of the audio signal is more abundant, the sound quality greatly improved.
Many small and medium-power FM transmitter are used direct modulation varactor diode technology, which work on the launch of the carrier frequency LC oscillator frequency directly back on the road, using the crystal oscillator and phase-locked loop to stabilize the center frequency. Frequency modulation and frequency than the approach that the circuit is simple, good performance, less vice waves, easy maintenance, is an advanced frequency modulation scheme.
Therefore, for frequency modulation circuit research, design, of great significance. The course design I am going to have some practical value to design the tuner in order to achieve frequency modulation of the audio signal. Beijing University of Posts 2008 Fall Specialty: Software Engineering Master Time: training ended 🔗 External reference