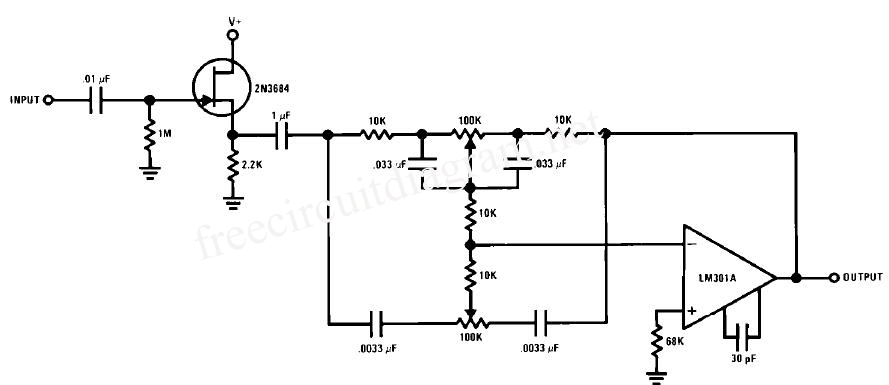
analog How to analyze this diode circuit
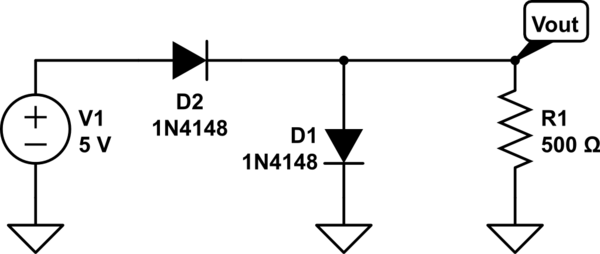
The two diodes will fail. It is advisable to include series resistors for them. If the simulation is successful, the current through the diodes will be excessive. Both diodes do not necessarily need to fail; one may become a Smoke Emitting Diode (SED), allowing for analysis of the remaining diode. It is recommended to verify the schematic to ensure the polarity of D1 is correct. It may also be prudent to document the circuit issue as drawn, consider a scenario where D1 has failed, and analyze the circuit assuming D1 was reversed, as this may have been the original intention. When faced with such situations, it is important to recognize that some assumptions made during simplification may not hold true, particularly those related to the constant voltage drop model.
In the described circuit, the use of two diodes suggests a configuration that may be intended for rectification or signal clipping. The inclusion of series resistors is critical to limit the current flowing through the diodes, thereby preventing potential damage due to excessive current. Diodes, when subjected to currents beyond their rated specifications, can fail, resulting in one or both diodes becoming non-functional. The term "Smoke Emitting Diode" humorously refers to a diode that has been damaged to the point of emitting smoke, indicating a catastrophic failure.
To ensure proper functionality, it is essential to verify the orientation of the diodes in the schematic. Diodes are polarized components, and incorrect placement can lead to reverse bias conditions that may damage the diode or alter circuit behavior. If D1 is incorrectly oriented, it is advisable to analyze the circuit under the assumption that D1 has failed. This analysis should include recalculating the expected currents and voltages throughout the circuit to understand the implications of the failure.
Additionally, it is important to consider the assumptions made during the simplification of the circuit model. The constant voltage drop model, which assumes a fixed voltage drop across the diodes, may not accurately represent real-world behavior under varying current conditions. This discrepancy can lead to significant errors in circuit analysis, necessitating a more detailed examination of the diode characteristics and the overall circuit behavior.
In summary, the circuit design involving diodes requires careful consideration of component orientation, current limiting strategies, and the validity of assumptions made during analysis. Properly addressing these factors will enhance circuit reliability and performance, while also providing valuable insights into the behavior of the system under various conditions.The two diodes will be fried. You`ll want some series resistors for them. If the simulation runs, the current through the diodes will be huge. jippie Apr 30 `13 at 9:40 @jippie Both diodes need not be fried :-) One will become a SED (Smoke Emitting Diode), then we can always analyze for the remaining one! Anindo Ghosh Apr 30 `13 at 9:42 If you drew the schematic yourself, I`d double check the reference to make sure you got the D1 polarity correct. In this situation, I would probably make a note of the problem with the circuit as drawn, possibly solve it assuming D1 died, and then additionally solve it assuming D1 was reversed (which was likely the intention).
darron Apr 30 `13 at 15:26 When you encounter a situation like this, you should realize that some assumption you`ve made when simplifying isn`t valid. In this case, it`s the assumptions of the constant voltage drop model that are being violated. DrFriedParts Apr 30 `13 at 15:50 🔗 External reference
In the described circuit, the use of two diodes suggests a configuration that may be intended for rectification or signal clipping. The inclusion of series resistors is critical to limit the current flowing through the diodes, thereby preventing potential damage due to excessive current. Diodes, when subjected to currents beyond their rated specifications, can fail, resulting in one or both diodes becoming non-functional. The term "Smoke Emitting Diode" humorously refers to a diode that has been damaged to the point of emitting smoke, indicating a catastrophic failure.
To ensure proper functionality, it is essential to verify the orientation of the diodes in the schematic. Diodes are polarized components, and incorrect placement can lead to reverse bias conditions that may damage the diode or alter circuit behavior. If D1 is incorrectly oriented, it is advisable to analyze the circuit under the assumption that D1 has failed. This analysis should include recalculating the expected currents and voltages throughout the circuit to understand the implications of the failure.
Additionally, it is important to consider the assumptions made during the simplification of the circuit model. The constant voltage drop model, which assumes a fixed voltage drop across the diodes, may not accurately represent real-world behavior under varying current conditions. This discrepancy can lead to significant errors in circuit analysis, necessitating a more detailed examination of the diode characteristics and the overall circuit behavior.
In summary, the circuit design involving diodes requires careful consideration of component orientation, current limiting strategies, and the validity of assumptions made during analysis. Properly addressing these factors will enhance circuit reliability and performance, while also providing valuable insights into the behavior of the system under various conditions.The two diodes will be fried. You`ll want some series resistors for them. If the simulation runs, the current through the diodes will be huge. jippie Apr 30 `13 at 9:40 @jippie Both diodes need not be fried :-) One will become a SED (Smoke Emitting Diode), then we can always analyze for the remaining one! Anindo Ghosh Apr 30 `13 at 9:42 If you drew the schematic yourself, I`d double check the reference to make sure you got the D1 polarity correct. In this situation, I would probably make a note of the problem with the circuit as drawn, possibly solve it assuming D1 died, and then additionally solve it assuming D1 was reversed (which was likely the intention).
darron Apr 30 `13 at 15:26 When you encounter a situation like this, you should realize that some assumption you`ve made when simplifying isn`t valid. In this case, it`s the assumptions of the constant voltage drop model that are being violated. DrFriedParts Apr 30 `13 at 15:50 🔗 External reference