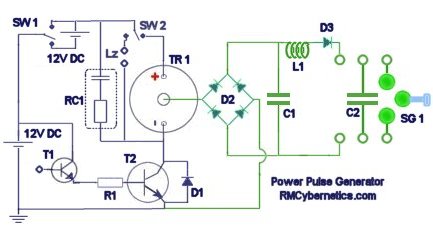
Cmos Piezo Driver Using 4049 Circuit

This circuit utilizes a 4049 integrated circuit (IC) to control a 2N2222 switching transistor. The transistor, in turn, drives a piezo transducer known as crystal 1.
The circuit design begins with the 4049 IC, which is a hex inverter capable of converting input signals into corresponding output signals. Each inverter within the IC can be utilized to control the base of the 2N2222 transistor. The 2N2222 is a versatile NPN transistor commonly used for switching applications due to its ability to handle moderate currents and voltages.
The piezo transducer, referred to as crystal 1 in this context, is an electromechanical device that converts electrical energy into mechanical vibrations, generating sound waves. When the transistor is activated by the output from the 4049 IC, it allows current to flow from the collector to the emitter, effectively powering the piezo transducer.
In this circuit, proper biasing of the 2N2222 transistor is crucial to ensure it operates in the saturation region when activated. This involves connecting a resistor in series with the base of the transistor to limit the base current while ensuring sufficient current to switch the transistor fully on. The output from the 4049 IC should be designed to provide a suitable voltage level to turn on the transistor, typically around 0.7V for silicon transistors like the 2N2222.
The overall functionality of this circuit can be enhanced by adding additional components such as capacitors for noise filtering, diodes for flyback protection (if inductive loads are involved), and resistors to set the gain and operating conditions of the transistor. This configuration allows for efficient control of the piezo transducer, enabling various applications such as sound generation in alarms, notifications, or signal transmission in electronic devices. This circuit uses a 4049 IC to drive a 2N2222 switching transistor. The transistor drives crystal 1 a piezo transducer.
The circuit design begins with the 4049 IC, which is a hex inverter capable of converting input signals into corresponding output signals. Each inverter within the IC can be utilized to control the base of the 2N2222 transistor. The 2N2222 is a versatile NPN transistor commonly used for switching applications due to its ability to handle moderate currents and voltages.
The piezo transducer, referred to as crystal 1 in this context, is an electromechanical device that converts electrical energy into mechanical vibrations, generating sound waves. When the transistor is activated by the output from the 4049 IC, it allows current to flow from the collector to the emitter, effectively powering the piezo transducer.
In this circuit, proper biasing of the 2N2222 transistor is crucial to ensure it operates in the saturation region when activated. This involves connecting a resistor in series with the base of the transistor to limit the base current while ensuring sufficient current to switch the transistor fully on. The output from the 4049 IC should be designed to provide a suitable voltage level to turn on the transistor, typically around 0.7V for silicon transistors like the 2N2222.
The overall functionality of this circuit can be enhanced by adding additional components such as capacitors for noise filtering, diodes for flyback protection (if inductive loads are involved), and resistors to set the gain and operating conditions of the transistor. This configuration allows for efficient control of the piezo transducer, enabling various applications such as sound generation in alarms, notifications, or signal transmission in electronic devices. This circuit uses a 4049 IC to drive a 2N2222 switching transistor. The transistor drives crystal 1 a piezo transducer.