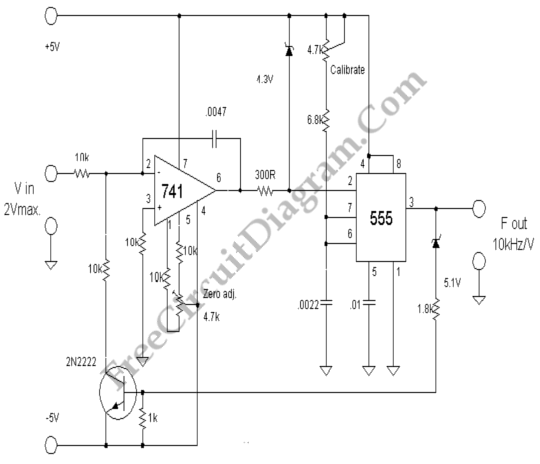
Code Practice Oscillator Using 555 Timer
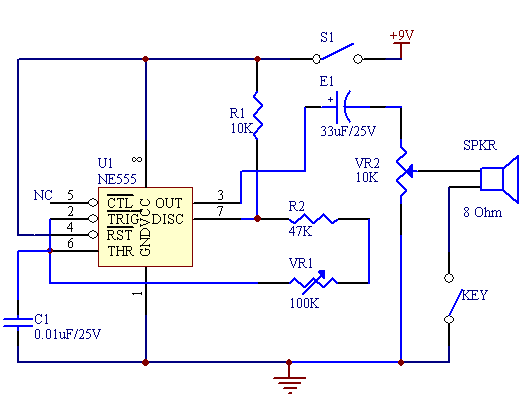
This project is a basic code practice oscillator designed for beginners to learn Continuous Wave Morse Code. It utilizes a 555 timer to produce a "dit" or "dah" sound when the key is pressed.
The circuit employs a 555 timer configured in astable mode, which allows it to generate a square wave output. This output frequency can be adjusted to create the distinct sounds associated with Morse Code. The circuit consists of a few key components: the 555 timer IC, resistors, capacitors, and a push-button switch.
When the push-button switch is pressed, it activates the 555 timer, causing it to oscillate at the predetermined frequency. The frequency of the output signal can be controlled by varying the resistor and capacitor values in the timing circuit. A typical configuration might use a resistor in the range of 1kΩ to 10kΩ and a capacitor of around 10µF to 100µF. This combination will generate the desired frequencies for "dit" (short beep) and "dah" (long beep) sounds.
To ensure the output is audible, the 555 timer is connected to a small speaker or piezo buzzer. The audio output can be further amplified if necessary, depending on the application and the desired volume level. A simple low-pass filter may also be added to smooth out the output waveform, reducing harmonics and providing a cleaner sound.
The circuit can be powered by a standard 9V battery or a DC power supply, making it portable and easy to use in various environments. This project not only serves as a practical introduction to the 555 timer and basic electronics but also provides a fun way to learn Morse Code through auditory signals.This simple code practice oscillator project for beginners to Continuous Wave Morse Code uses a 555 timer to generate a dit or dah sound when the key is pressed 🔗 External reference
The circuit employs a 555 timer configured in astable mode, which allows it to generate a square wave output. This output frequency can be adjusted to create the distinct sounds associated with Morse Code. The circuit consists of a few key components: the 555 timer IC, resistors, capacitors, and a push-button switch.
When the push-button switch is pressed, it activates the 555 timer, causing it to oscillate at the predetermined frequency. The frequency of the output signal can be controlled by varying the resistor and capacitor values in the timing circuit. A typical configuration might use a resistor in the range of 1kΩ to 10kΩ and a capacitor of around 10µF to 100µF. This combination will generate the desired frequencies for "dit" (short beep) and "dah" (long beep) sounds.
To ensure the output is audible, the 555 timer is connected to a small speaker or piezo buzzer. The audio output can be further amplified if necessary, depending on the application and the desired volume level. A simple low-pass filter may also be added to smooth out the output waveform, reducing harmonics and providing a cleaner sound.
The circuit can be powered by a standard 9V battery or a DC power supply, making it portable and easy to use in various environments. This project not only serves as a practical introduction to the 555 timer and basic electronics but also provides a fun way to learn Morse Code through auditory signals.This simple code practice oscillator project for beginners to Continuous Wave Morse Code uses a 555 timer to generate a dit or dah sound when the key is pressed 🔗 External reference