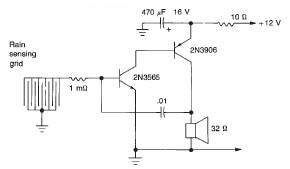
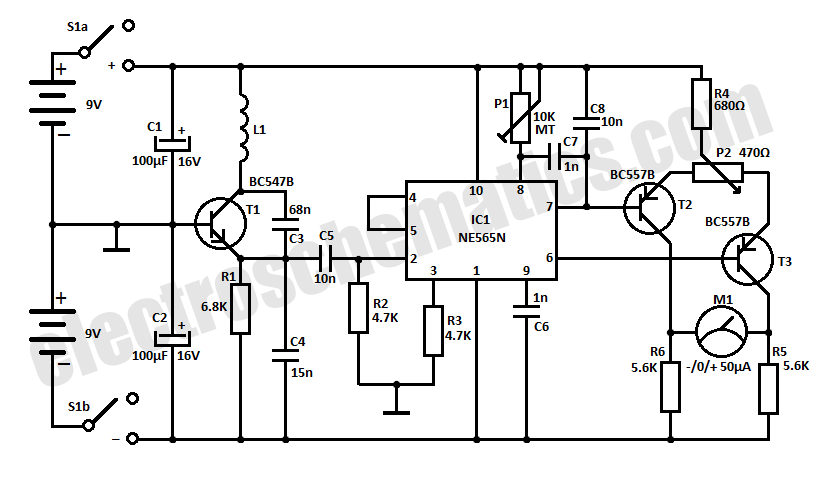
Contactless Live Line Detector
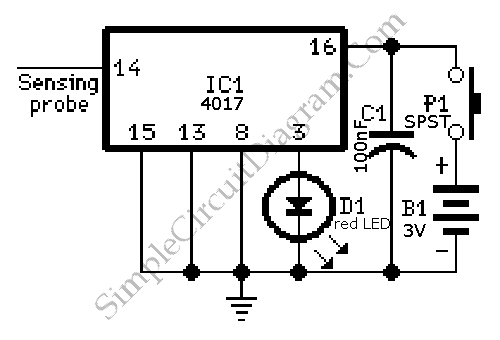
A live-line detector is a circuit designed to identify the presence of a live mains conductor through capacitive coupling between the live conductor and the detection circuit.
The live-line detector operates on the principle of capacitive coupling, which allows it to detect alternating current (AC) without direct electrical contact with the live conductor. The circuit typically consists of a capacitive sensor that is placed near the live wire, which picks up the electric field generated by the AC current flowing through the conductor.
In a standard configuration, the capacitive sensor is connected to an operational amplifier (op-amp) configured as a voltage follower or amplifier. The output of the op-amp can be fed into a microcontroller or a simple indicator light, such as an LED, to provide a visual indication of the presence of voltage.
The circuit may also include a resistor divider network to scale the detected voltage to a safe level for processing. It is important to incorporate safety features, such as isolation and over-voltage protection, to ensure that the circuit operates reliably without posing a risk to users or damaging components.
The design considerations for a live-line detector include sensitivity adjustments to ensure it can detect low voltages while avoiding false positives from nearby electrical devices. The layout of the circuit should minimize interference from other sources of electromagnetic fields, and the choice of components should reflect the desired operating frequency and environmental conditions.
In summary, a live-line detector provides a crucial function in electrical safety by enabling the detection of live conductors, thereby preventing accidental contact and enhancing safety protocols in electrical maintenance and inspection.Live-line detector is a circuit that detects the presence of a live mains conductor circuit operation: capacitive coupling between the live conductor and the.. 🔗 External reference
The live-line detector operates on the principle of capacitive coupling, which allows it to detect alternating current (AC) without direct electrical contact with the live conductor. The circuit typically consists of a capacitive sensor that is placed near the live wire, which picks up the electric field generated by the AC current flowing through the conductor.
In a standard configuration, the capacitive sensor is connected to an operational amplifier (op-amp) configured as a voltage follower or amplifier. The output of the op-amp can be fed into a microcontroller or a simple indicator light, such as an LED, to provide a visual indication of the presence of voltage.
The circuit may also include a resistor divider network to scale the detected voltage to a safe level for processing. It is important to incorporate safety features, such as isolation and over-voltage protection, to ensure that the circuit operates reliably without posing a risk to users or damaging components.
The design considerations for a live-line detector include sensitivity adjustments to ensure it can detect low voltages while avoiding false positives from nearby electrical devices. The layout of the circuit should minimize interference from other sources of electromagnetic fields, and the choice of components should reflect the desired operating frequency and environmental conditions.
In summary, a live-line detector provides a crucial function in electrical safety by enabling the detection of live conductors, thereby preventing accidental contact and enhancing safety protocols in electrical maintenance and inspection.Live-line detector is a circuit that detects the presence of a live mains conductor circuit operation: capacitive coupling between the live conductor and the.. 🔗 External reference