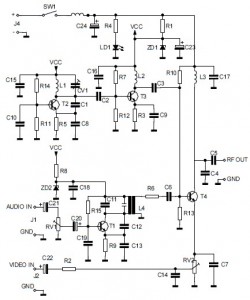
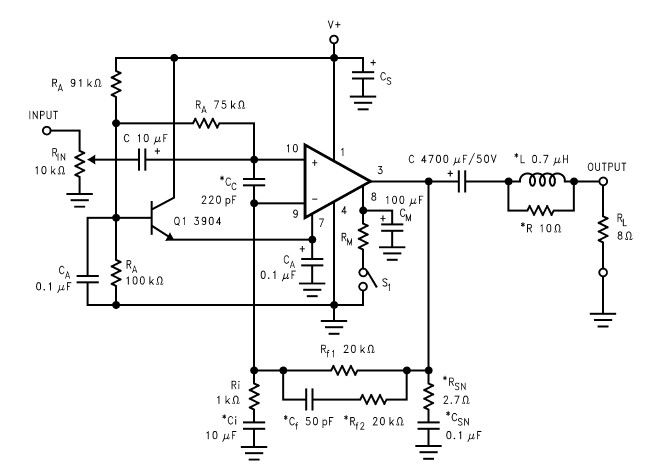
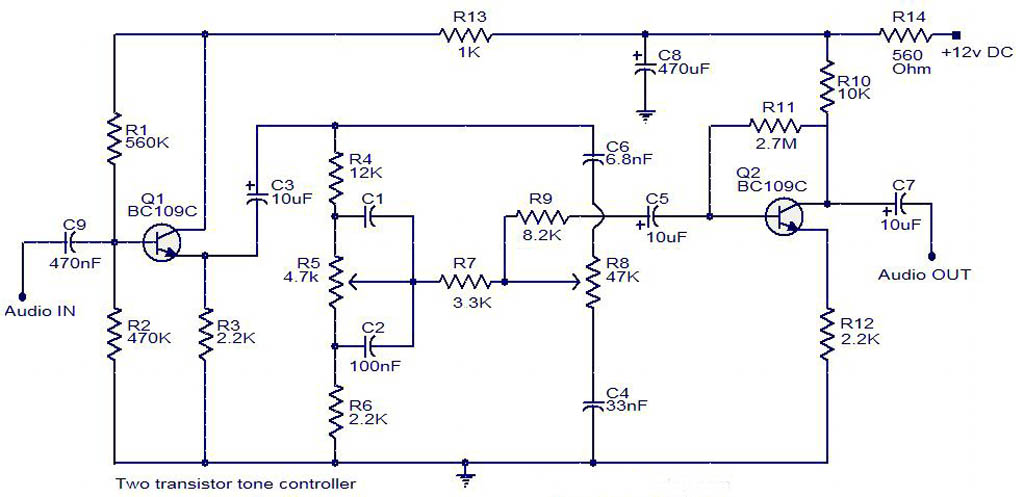
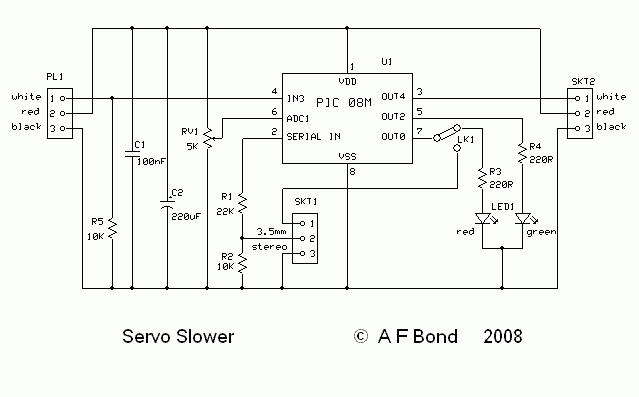
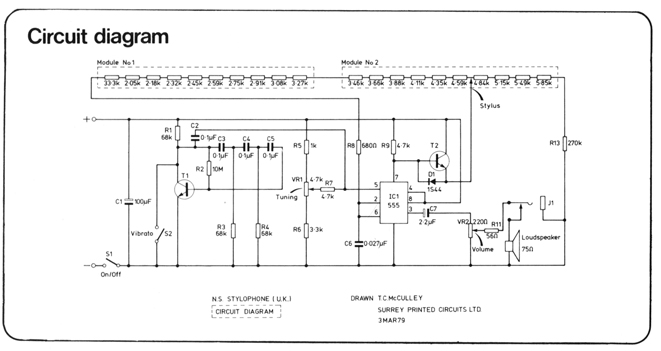
Control circuit keeps dc motor running at constant speed

The purpose of this circuit is to maintain a permanent magnet DC motor at a constant speed, which is set externally. This is achieved by monitoring the current flowing through and the voltage across the motor's brushes.
The schematic for this circuit typically includes a feedback loop that incorporates a speed sensor, such as a tachometer, which provides real-time feedback on the motor's speed. The output from the tachometer is compared to a reference voltage that corresponds to the desired speed setting. This comparison is usually performed using an operational amplifier configured as a differential amplifier.
The output of the operational amplifier is then used to control a PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signal that drives a power transistor or MOSFET. This transistor acts as a switch to control the voltage applied to the motor. By adjusting the duty cycle of the PWM signal, the effective voltage and current supplied to the motor can be varied, thus controlling its speed.
Additional components may include a current sensing resistor placed in series with the motor, allowing for the measurement of the motor's current. This current feedback can be used to implement current limiting or protection features to prevent damage to the motor during stall conditions or overload situations.
Filtering capacitors may also be included in the circuit to smooth out any voltage spikes or noise, ensuring stable operation. Diodes are typically placed in parallel with the motor to protect against back EMF generated when the motor is turned off or when it operates under dynamic conditions.
Overall, this circuit design effectively ensures that the DC motor operates at the desired speed, providing reliable performance in various applications where speed control is critical.The aim of this circuit is to keep the permanent magnet dc motor running at a constant speed, set externally. To do this, the current through, and the voltage across, the brushes of the motor are monitored 🔗 External reference
The schematic for this circuit typically includes a feedback loop that incorporates a speed sensor, such as a tachometer, which provides real-time feedback on the motor's speed. The output from the tachometer is compared to a reference voltage that corresponds to the desired speed setting. This comparison is usually performed using an operational amplifier configured as a differential amplifier.
The output of the operational amplifier is then used to control a PWM (Pulse Width Modulation) signal that drives a power transistor or MOSFET. This transistor acts as a switch to control the voltage applied to the motor. By adjusting the duty cycle of the PWM signal, the effective voltage and current supplied to the motor can be varied, thus controlling its speed.
Additional components may include a current sensing resistor placed in series with the motor, allowing for the measurement of the motor's current. This current feedback can be used to implement current limiting or protection features to prevent damage to the motor during stall conditions or overload situations.
Filtering capacitors may also be included in the circuit to smooth out any voltage spikes or noise, ensuring stable operation. Diodes are typically placed in parallel with the motor to protect against back EMF generated when the motor is turned off or when it operates under dynamic conditions.
Overall, this circuit design effectively ensures that the DC motor operates at the desired speed, providing reliable performance in various applications where speed control is critical.The aim of this circuit is to keep the permanent magnet dc motor running at a constant speed, set externally. To do this, the current through, and the voltage across, the brushes of the motor are monitored 🔗 External reference