contsant voltage current limited charger
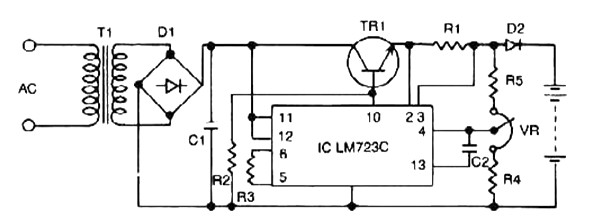
Constant Voltage Current Limited Charger power supply. Refer to the page for an explanation regarding the associated circuit diagram.
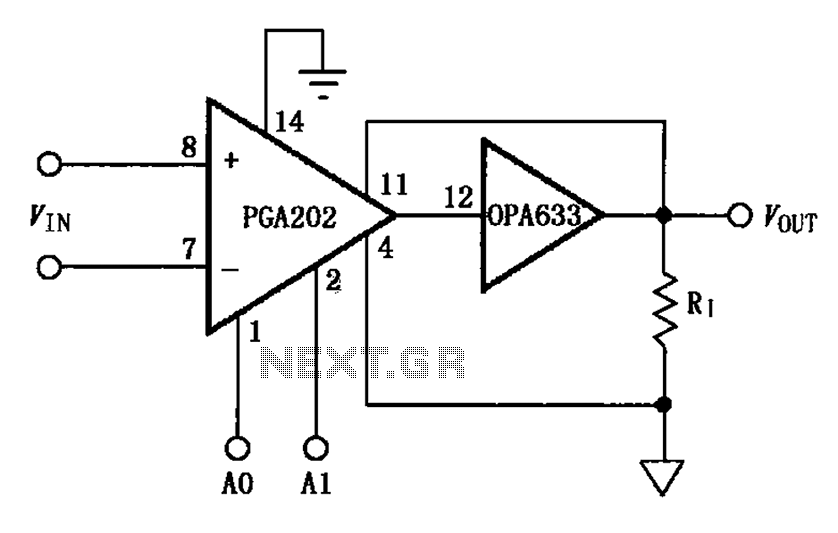
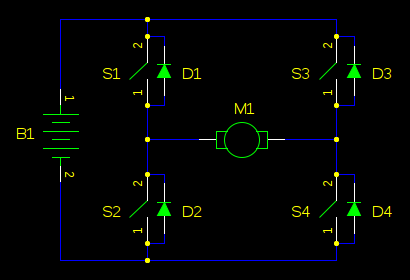
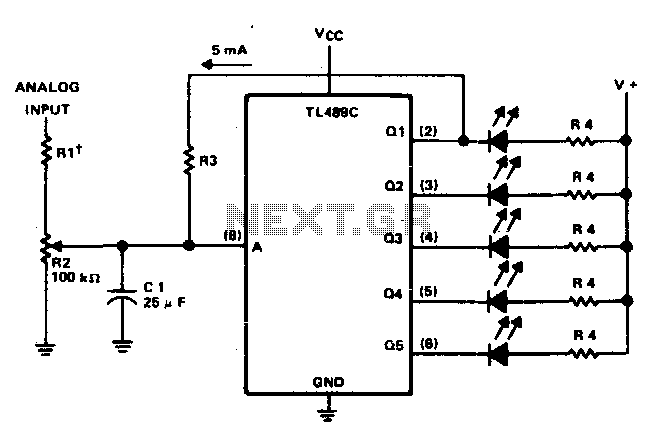
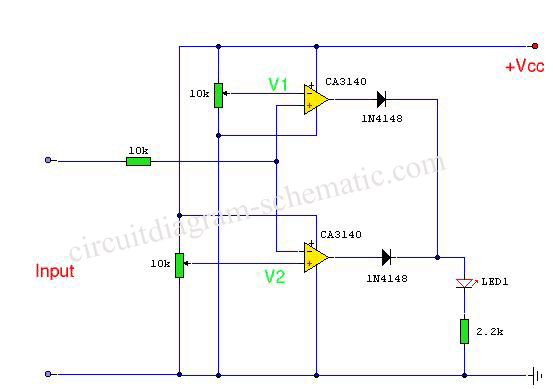
The Constant Voltage Current Limited Charger power supply is designed to provide a stable output voltage while limiting the current to protect the connected load. This type of charger is particularly useful for applications where batteries or sensitive electronic components require a controlled charging environment to prevent damage from overcurrent conditions.
The circuit typically consists of a voltage regulation stage, which maintains a constant output voltage, and a current limiting mechanism that restricts the maximum output current. Common components used in this type of circuit include operational amplifiers, voltage reference diodes, and power transistors.
The operational amplifier is configured to compare the output voltage with a reference voltage. When the output voltage exceeds the set point, the operational amplifier adjusts the gate of a power transistor, reducing the output voltage to maintain the desired constant level. The current limiting feature is generally implemented using a shunt resistor in series with the load. A second operational amplifier monitors the voltage across this resistor; if it exceeds a predetermined threshold, the circuit will reduce the output voltage to limit the current flowing through the load.
This charger is suitable for various applications, including lead-acid, lithium-ion, and nickel-metal hydride batteries, ensuring safe and efficient charging while extending battery life. Proper heat dissipation measures, such as heat sinks or thermal cutoffs, should also be included in the design to prevent overheating of components during operation.
In summary, the Constant Voltage Current Limited Charger power supply is an essential component for safely charging batteries and sensitive electronic devices, ensuring that both voltage and current levels remain within specified limits.Constant Voltage Current Limited Charger power supply. Go to that page to read the explanation about above power supply related circuit diagram. 🔗 External reference
The Constant Voltage Current Limited Charger power supply is designed to provide a stable output voltage while limiting the current to protect the connected load. This type of charger is particularly useful for applications where batteries or sensitive electronic components require a controlled charging environment to prevent damage from overcurrent conditions.
The circuit typically consists of a voltage regulation stage, which maintains a constant output voltage, and a current limiting mechanism that restricts the maximum output current. Common components used in this type of circuit include operational amplifiers, voltage reference diodes, and power transistors.
The operational amplifier is configured to compare the output voltage with a reference voltage. When the output voltage exceeds the set point, the operational amplifier adjusts the gate of a power transistor, reducing the output voltage to maintain the desired constant level. The current limiting feature is generally implemented using a shunt resistor in series with the load. A second operational amplifier monitors the voltage across this resistor; if it exceeds a predetermined threshold, the circuit will reduce the output voltage to limit the current flowing through the load.
This charger is suitable for various applications, including lead-acid, lithium-ion, and nickel-metal hydride batteries, ensuring safe and efficient charging while extending battery life. Proper heat dissipation measures, such as heat sinks or thermal cutoffs, should also be included in the design to prevent overheating of components during operation.
In summary, the Constant Voltage Current Limited Charger power supply is an essential component for safely charging batteries and sensitive electronic devices, ensuring that both voltage and current levels remain within specified limits.Constant Voltage Current Limited Charger power supply. Go to that page to read the explanation about above power supply related circuit diagram. 🔗 External reference