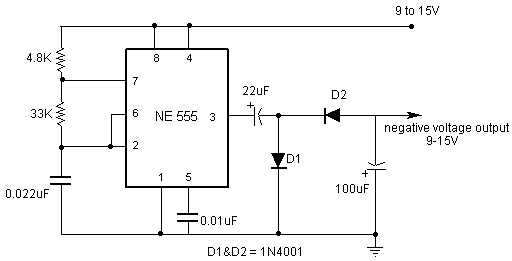
DC-AC Inverter Convert 12V DC Voltage to 110/220V AC Voltage
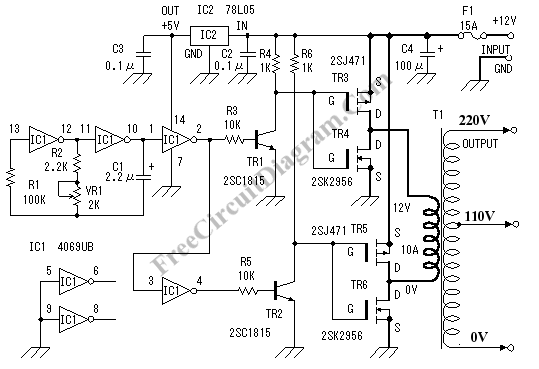
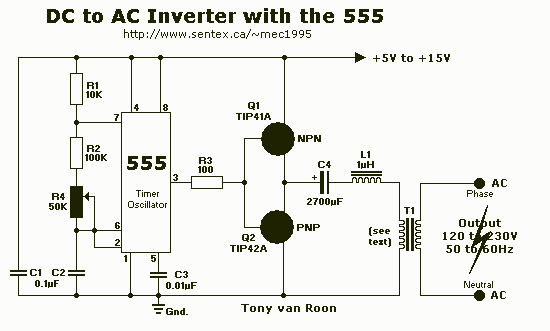
The DC to AC inverter circuit illustrated in the schematic is a straightforward design that produces a square wave output, which is sufficient to power various devices. The schematic diagram of the inverter circuit features a MOSFET configured as a bridge, allowing current to flow alternately through the primary windings of the transformer. The most costly component of this DC-AC inverter circuit is the transformer, as it must accommodate high currents of up to 10 Amps. This 12V inverter circuit can power any device with a maximum consumption of 120 Watts.
The described DC to AC inverter circuit employs a basic square wave generation technique, which is effective for a range of applications despite its simplicity. The configuration utilizes a bridge of MOSFETs that alternates the direction of current through the primary winding of the transformer, thus generating an alternating current (AC) output from a direct current (DC) source.
The transformer plays a crucial role in stepping up the voltage to the desired level while also isolating the load from the power source for safety. It is essential that the transformer is rated to handle the maximum current of 10 Amps to prevent overheating or damage during operation. The selection of the transformer should consider both the current rating and the power rating, ensuring it can handle loads up to 120 Watts efficiently.
In practical applications, this inverter circuit can be used to power various electronic devices, including small appliances, lights, and other equipment that operates on AC voltage. The square wave output may not be suitable for devices that require a pure sine wave for optimal performance; however, it is adequate for resistive loads and many inductive loads.
It is also important to incorporate adequate heat sinking for the MOSFETs to manage thermal performance, especially under maximum load conditions. Additionally, implementing filtering capacitors at the output can help reduce voltage spikes and improve the quality of the AC waveform, making it more suitable for sensitive electronic devices. Overall, this inverter circuit exemplifies a cost-effective solution for converting DC to AC power for various applications.The DC to AC inverter circuit shown in the schematic here is very simple circuit since it produce square wave, but it`s enough to power many devices. Here is the schematic diagram of the inverter circuit: The MOSFET is configured as bridge, so the current will flow alternatively in through the primary windings of the transformer.
The most expensiv e part of this dc-ac inverter circuit is the transformer, since it must handle high current up to 10 Amps. You can power any device up to 120 Watts using this 12V inverter circuit. 🔗 External reference
The described DC to AC inverter circuit employs a basic square wave generation technique, which is effective for a range of applications despite its simplicity. The configuration utilizes a bridge of MOSFETs that alternates the direction of current through the primary winding of the transformer, thus generating an alternating current (AC) output from a direct current (DC) source.
The transformer plays a crucial role in stepping up the voltage to the desired level while also isolating the load from the power source for safety. It is essential that the transformer is rated to handle the maximum current of 10 Amps to prevent overheating or damage during operation. The selection of the transformer should consider both the current rating and the power rating, ensuring it can handle loads up to 120 Watts efficiently.
In practical applications, this inverter circuit can be used to power various electronic devices, including small appliances, lights, and other equipment that operates on AC voltage. The square wave output may not be suitable for devices that require a pure sine wave for optimal performance; however, it is adequate for resistive loads and many inductive loads.
It is also important to incorporate adequate heat sinking for the MOSFETs to manage thermal performance, especially under maximum load conditions. Additionally, implementing filtering capacitors at the output can help reduce voltage spikes and improve the quality of the AC waveform, making it more suitable for sensitive electronic devices. Overall, this inverter circuit exemplifies a cost-effective solution for converting DC to AC power for various applications.The DC to AC inverter circuit shown in the schematic here is very simple circuit since it produce square wave, but it`s enough to power many devices. Here is the schematic diagram of the inverter circuit: The MOSFET is configured as bridge, so the current will flow alternatively in through the primary windings of the transformer.
The most expensiv e part of this dc-ac inverter circuit is the transformer, since it must handle high current up to 10 Amps. You can power any device up to 120 Watts using this 12V inverter circuit. 🔗 External reference