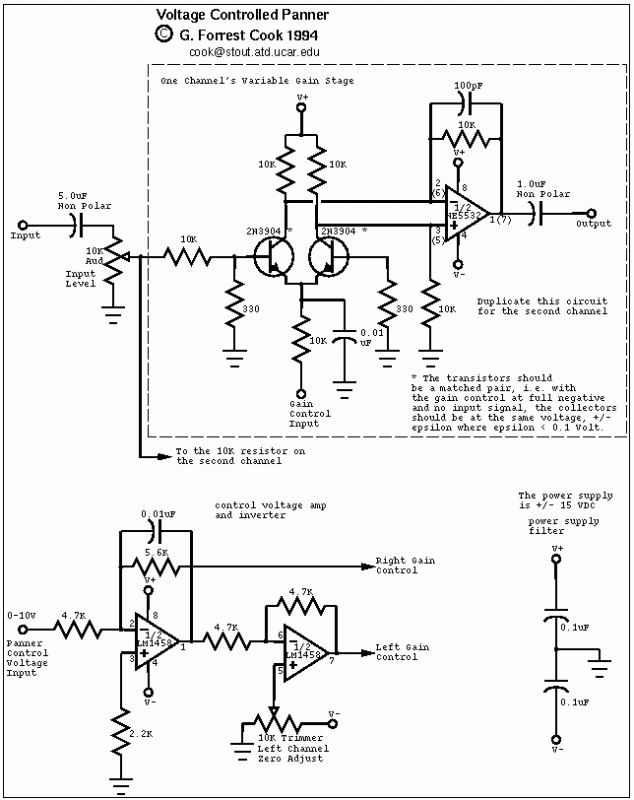
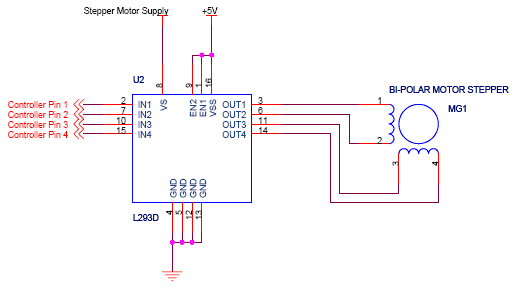
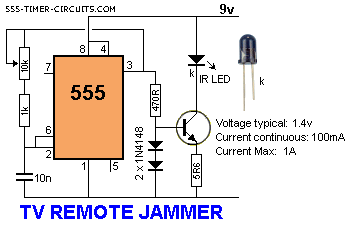
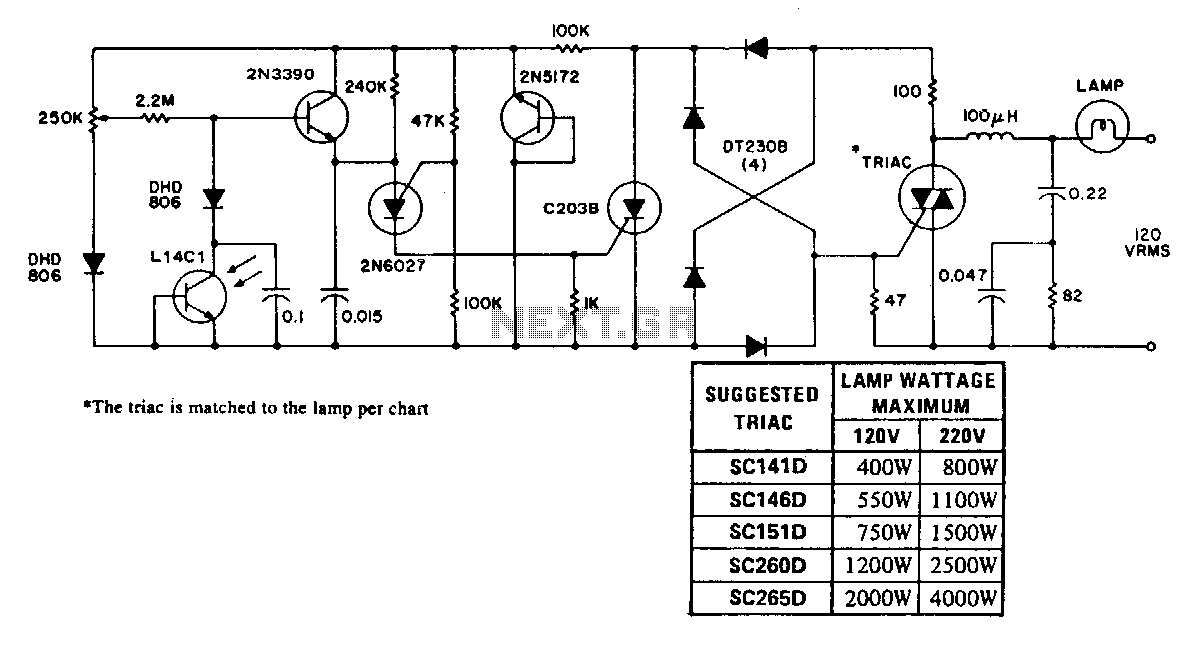
DC Control for Triacs
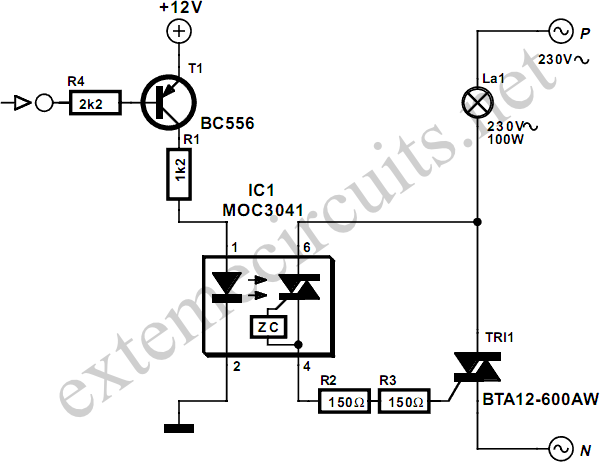
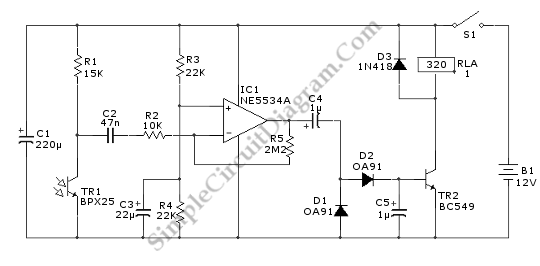
A relay is an effective solution for switching a mains voltage circuit, particularly in applications where long switching times and high currents are present. However, a...
A relay is an electromechanical switch that uses an electromagnetic coil to control the opening and closing of contacts in a circuit. In applications involving mains voltage, relays are essential for safely switching high currents without direct manual intervention. The basic operation of a relay involves energizing the coil, which generates a magnetic field that moves an armature. This movement either connects or disconnects the circuit, allowing or interrupting the flow of current.
For circuits requiring long switching times, relays provide a reliable mechanism due to their inherent design, which can handle the gradual changes in state without the risk of arcing or damage that might occur with solid-state devices. The contacts within the relay are designed to withstand high inrush currents, making them suitable for applications such as motor control, lighting systems, and heating elements.
When designing a circuit that incorporates a relay for switching mains voltage, it is crucial to select a relay rated for the specific voltage and current requirements of the application. Additionally, proper isolation techniques must be employed to ensure safety, including the use of fuses or circuit breakers to protect against overload conditions. The control side of the relay can be activated by a low-voltage signal, allowing for the integration of microcontrollers or other control systems without exposing them to high voltage levels.
Furthermore, consideration should be given to the relay's specifications, such as contact rating, coil voltage, and switching speed, to ensure optimal performance in the intended application. The layout of the circuit should also facilitate easy maintenance and troubleshooting, incorporating indicators such as LEDs to show the relay's status. Overall, relays are a vital component in circuits requiring the switching of mains voltages, providing a safe and effective means to control high-power devices.If a circuit is to switch a mains voltage, a relay is a simple solution in cases where switching times are long and high currents are involved. However, a.. 🔗 External reference
A relay is an electromechanical switch that uses an electromagnetic coil to control the opening and closing of contacts in a circuit. In applications involving mains voltage, relays are essential for safely switching high currents without direct manual intervention. The basic operation of a relay involves energizing the coil, which generates a magnetic field that moves an armature. This movement either connects or disconnects the circuit, allowing or interrupting the flow of current.
For circuits requiring long switching times, relays provide a reliable mechanism due to their inherent design, which can handle the gradual changes in state without the risk of arcing or damage that might occur with solid-state devices. The contacts within the relay are designed to withstand high inrush currents, making them suitable for applications such as motor control, lighting systems, and heating elements.
When designing a circuit that incorporates a relay for switching mains voltage, it is crucial to select a relay rated for the specific voltage and current requirements of the application. Additionally, proper isolation techniques must be employed to ensure safety, including the use of fuses or circuit breakers to protect against overload conditions. The control side of the relay can be activated by a low-voltage signal, allowing for the integration of microcontrollers or other control systems without exposing them to high voltage levels.
Furthermore, consideration should be given to the relay's specifications, such as contact rating, coil voltage, and switching speed, to ensure optimal performance in the intended application. The layout of the circuit should also facilitate easy maintenance and troubleshooting, incorporating indicators such as LEDs to show the relay's status. Overall, relays are a vital component in circuits requiring the switching of mains voltages, providing a safe and effective means to control high-power devices.If a circuit is to switch a mains voltage, a relay is a simple solution in cases where switching times are long and high currents are involved. However, a.. 🔗 External reference