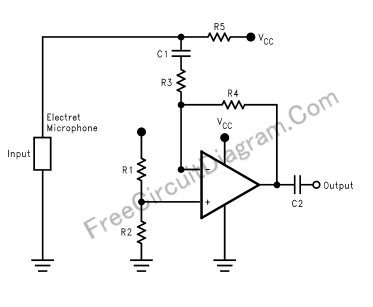
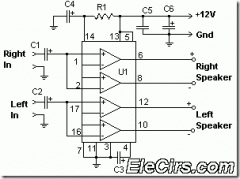
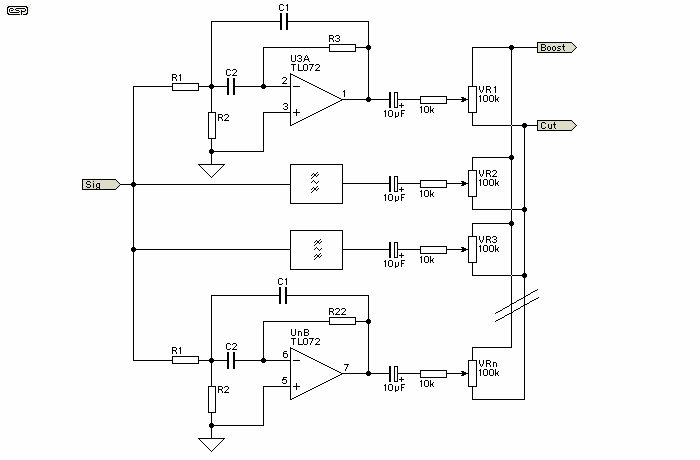
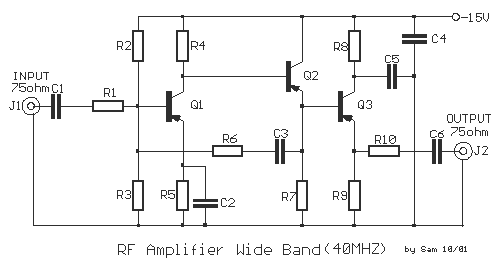
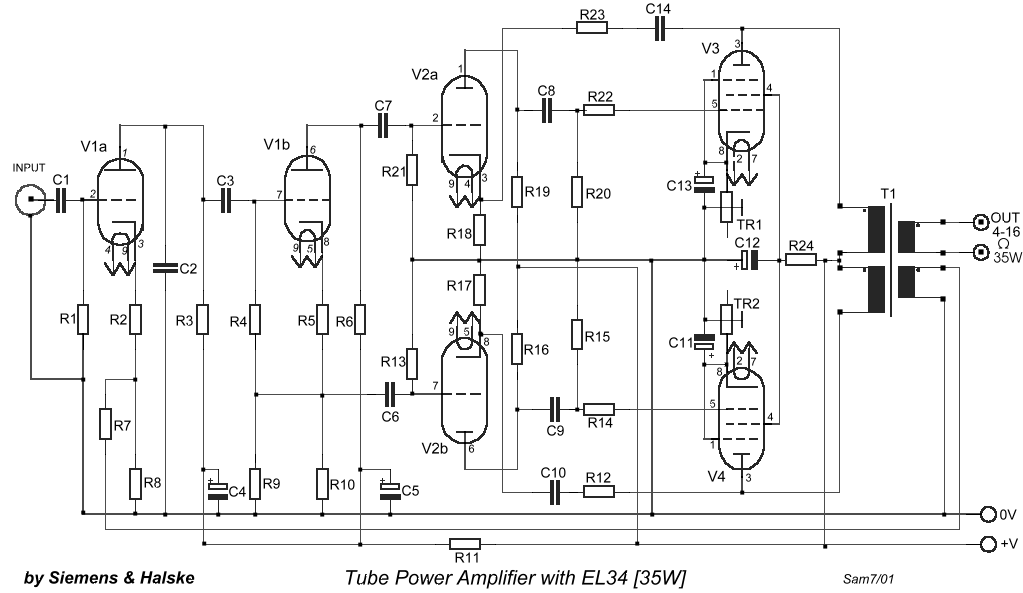
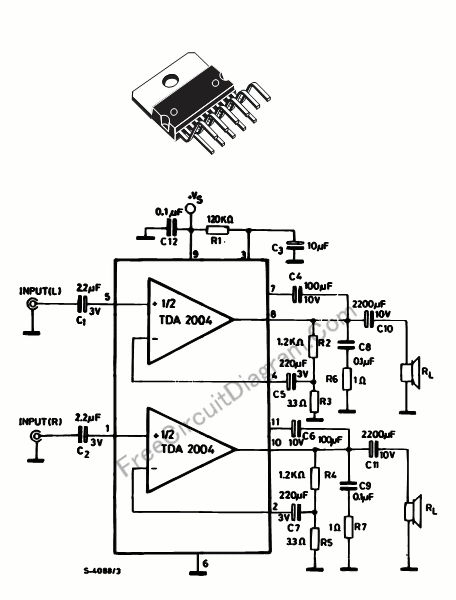
DC-Coupled Audio Amplifier

Designs for audio amplifiers with DC coupling to the load are not commonly seen today, despite their clear benefits. One advantage...
Audio amplifiers utilizing DC coupling to the load present several notable advantages in specific applications. DC coupling allows for a direct connection between stages of an amplifier without the need for coupling capacitors, which can introduce phase shifts and frequency response limitations. This configuration is particularly beneficial in low-frequency applications, such as in subwoofer amplification, where maintaining signal integrity across a wide frequency range is crucial.
In a typical DC-coupled audio amplifier design, the output stage directly drives the load, ensuring that the entire audio signal, including its DC component, is transmitted. This can result in improved transient response and better overall fidelity. Additionally, the absence of coupling capacitors reduces the risk of signal distortion that can occur due to capacitor leakage or frequency-dependent behavior.
However, implementing DC coupling requires careful consideration of biasing and power supply design. The amplifier must be designed to operate with a suitable quiescent current to ensure that the output stage remains linear across the intended signal range. Thermal stability is also a critical factor, as variations in temperature can affect the biasing conditions and potentially lead to distortion or clipping.
In summary, while DC-coupled audio amplifiers may not be prevalent in modern designs, they offer significant advantages in specific scenarios, particularly where low-frequency performance and signal integrity are paramount. Proper design and implementation can yield high-performance amplifiers capable of delivering exceptional audio quality.Designs for audio amplifiers with DC coupling to the load are not often encountered these days, even though they offer definite advantages. One advantage.. 🔗 External reference
Audio amplifiers utilizing DC coupling to the load present several notable advantages in specific applications. DC coupling allows for a direct connection between stages of an amplifier without the need for coupling capacitors, which can introduce phase shifts and frequency response limitations. This configuration is particularly beneficial in low-frequency applications, such as in subwoofer amplification, where maintaining signal integrity across a wide frequency range is crucial.
In a typical DC-coupled audio amplifier design, the output stage directly drives the load, ensuring that the entire audio signal, including its DC component, is transmitted. This can result in improved transient response and better overall fidelity. Additionally, the absence of coupling capacitors reduces the risk of signal distortion that can occur due to capacitor leakage or frequency-dependent behavior.
However, implementing DC coupling requires careful consideration of biasing and power supply design. The amplifier must be designed to operate with a suitable quiescent current to ensure that the output stage remains linear across the intended signal range. Thermal stability is also a critical factor, as variations in temperature can affect the biasing conditions and potentially lead to distortion or clipping.
In summary, while DC-coupled audio amplifiers may not be prevalent in modern designs, they offer significant advantages in specific scenarios, particularly where low-frequency performance and signal integrity are paramount. Proper design and implementation can yield high-performance amplifiers capable of delivering exceptional audio quality.Designs for audio amplifiers with DC coupling to the load are not often encountered these days, even though they offer definite advantages. One advantage.. 🔗 External reference