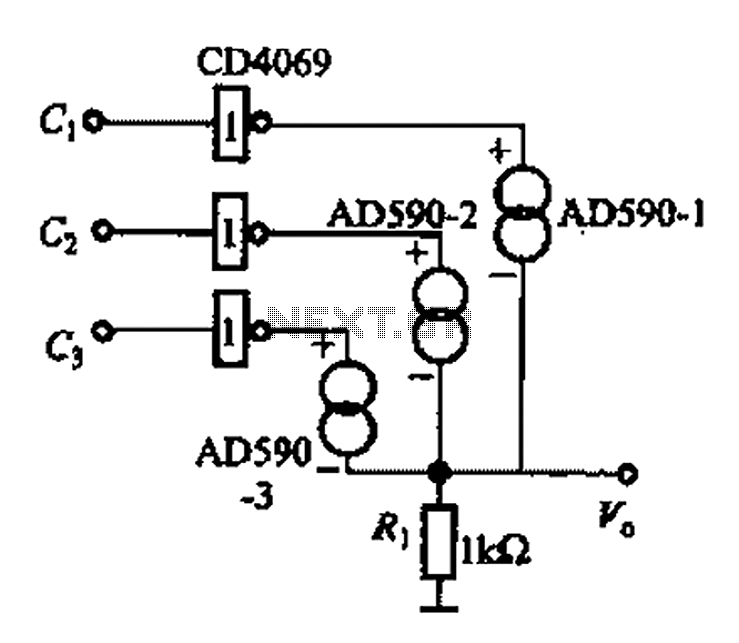
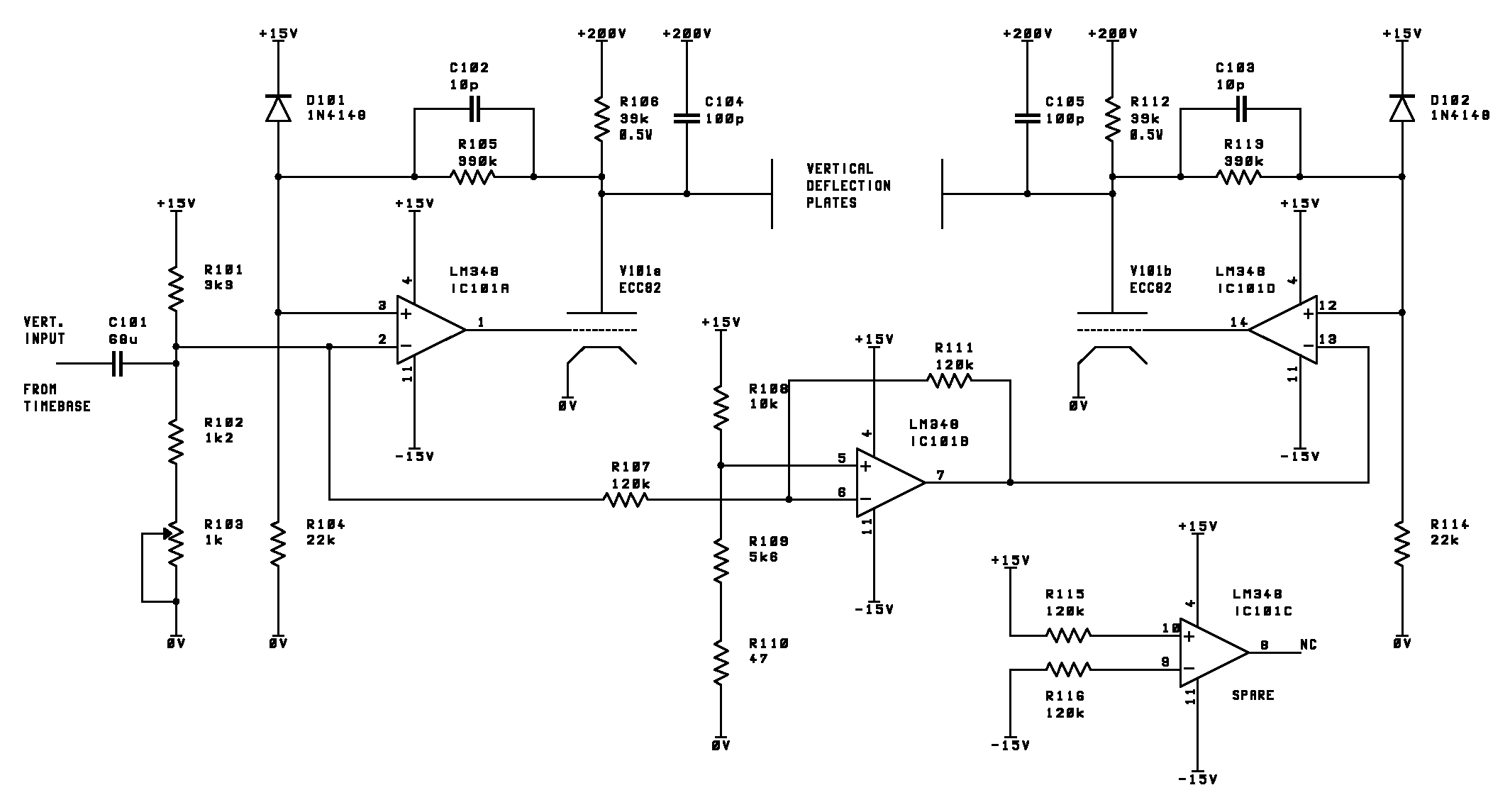
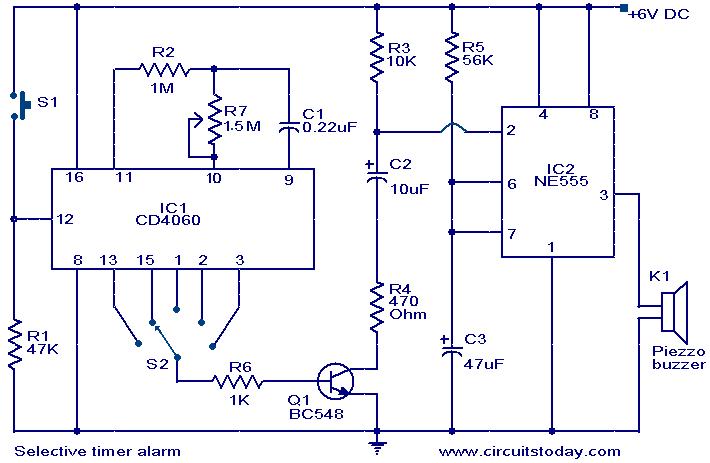
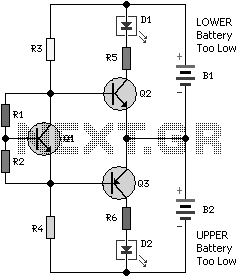
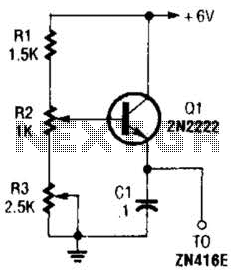
simple short circuit detection

This circuit is appropriate for any scenario where over-current protection is necessary. An example from the model train hobbyist community illustrates its importance. Experienced model train enthusiasts understand that locating the source of a short circuit can be quite challenging. While it may be relatively straightforward to identify issues on a small model railway with a single locomotive, larger layouts complicate matters significantly. In such cases, all locomotives come to a halt during a short circuit, requiring the operator to inspect each one individually to determine the cause of the failure.
This over-current protection circuit can be implemented using a combination of current sensing components, a comparator, and a relay or circuit breaker. The design typically includes a shunt resistor positioned in series with the load to measure the current flowing through the circuit. The voltage drop across this resistor is proportional to the current, allowing for real-time monitoring.
A comparator is employed to compare the voltage across the shunt resistor with a predefined threshold voltage, which corresponds to the maximum allowable current for the system. If the current exceeds this threshold, the comparator output changes state, triggering a relay or a circuit breaker to disconnect the load and prevent damage from over-current conditions.
In model train applications, the circuit can be finely tuned to accommodate the specific current ratings of various locomotives and accessories. This precision ensures that the protection mechanism activates only when necessary, allowing for optimal performance and minimizing unnecessary interruptions.
The circuit can be enhanced with features such as LED indicators to provide visual feedback regarding the operational status and fault conditions. Additionally, a reset mechanism can be integrated, allowing the user to easily restore functionality after resolving the short circuit issue.
Overall, this over-current protection circuit serves as a vital component in maintaining the reliability and safety of model train layouts, ensuring that enthusiasts can enjoy their hobby without the constant worry of damaging their equipment due to unforeseen electrical faults.This circuit is suitable in every situation where over-current protection is required. Here we give an example from the model train world. Every seasoned model train enthusiast knows that there is nothing worse than having to find the cause of a short-circuit. On a small model railway with one locomotive it is obviously fairly easy, but on large layouts all locomotives stand still when there is a short and then you have to check each one in turn to find the culprit..
🔗 External reference
This over-current protection circuit can be implemented using a combination of current sensing components, a comparator, and a relay or circuit breaker. The design typically includes a shunt resistor positioned in series with the load to measure the current flowing through the circuit. The voltage drop across this resistor is proportional to the current, allowing for real-time monitoring.
A comparator is employed to compare the voltage across the shunt resistor with a predefined threshold voltage, which corresponds to the maximum allowable current for the system. If the current exceeds this threshold, the comparator output changes state, triggering a relay or a circuit breaker to disconnect the load and prevent damage from over-current conditions.
In model train applications, the circuit can be finely tuned to accommodate the specific current ratings of various locomotives and accessories. This precision ensures that the protection mechanism activates only when necessary, allowing for optimal performance and minimizing unnecessary interruptions.
The circuit can be enhanced with features such as LED indicators to provide visual feedback regarding the operational status and fault conditions. Additionally, a reset mechanism can be integrated, allowing the user to easily restore functionality after resolving the short circuit issue.
Overall, this over-current protection circuit serves as a vital component in maintaining the reliability and safety of model train layouts, ensuring that enthusiasts can enjoy their hobby without the constant worry of damaging their equipment due to unforeseen electrical faults.This circuit is suitable in every situation where over-current protection is required. Here we give an example from the model train world. Every seasoned model train enthusiast knows that there is nothing worse than having to find the cause of a short-circuit. On a small model railway with one locomotive it is obviously fairly easy, but on large layouts all locomotives stand still when there is a short and then you have to check each one in turn to find the culprit..
🔗 External reference