DIGITAL ENTRY LOCK
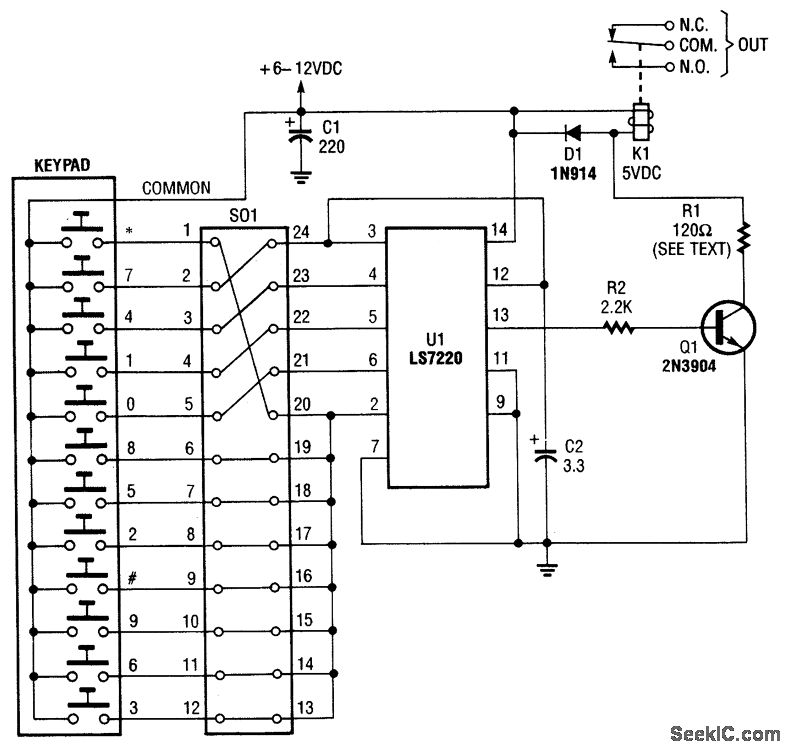
A keypad is used to input a four-digit access code, which can be programmed using jumpers on a 24-pin plug-in header and socket. The component U1 is an LST220, responsible for detecting the sequential four-digit data input. Upon entering the correct code on the keyboard, pin 13 of U1 goes high, triggering Q1 and K1. K1 then activates an external electric lock solenoid.
The circuit design features a keypad interface for user input, allowing for secure access control through a four-digit code. The keypad connects to a 24-pin header, where jumpers can be configured to set the desired access code. The LST220 (U1) serves as the core logic component, interpreting the signals from the keypad. It is designed to recognize a specific sequence of four digits, ensuring that only authorized users can gain access.
When the correct code is entered, a high signal is generated at pin 13 of U1. This signal is utilized to drive a transistor (Q1), which acts as a switch to control the current flow to the relay (K1). The relay is responsible for activating an external electric lock solenoid, thereby unlocking the door or access point.
The circuit should also include necessary debouncing mechanisms for the keypad to prevent false triggering due to mechanical noise when keys are pressed. Additional components such as resistors and capacitors may be used to stabilize the power supply to U1 and ensure reliable operation. Optional features could include LED indicators to provide visual feedback when the correct code is entered or audible alerts for incorrect entries.
Overall, this electronic schematic provides a straightforward and effective method for implementing a secure access control system using a keypad and relay mechanism.A keypad enters a four-digit access code, which is programmed via jumpers on a 24-pin plug-in header and socket. U1 is an LST220, which detects a four-digit sequential data input. When the correct data is entered into the keyboard, pin 13 of U1 goes high, which activates Q1 and K1.
K1 drives an external electric lock solenoid, etc. 🔗 External reference
The circuit design features a keypad interface for user input, allowing for secure access control through a four-digit code. The keypad connects to a 24-pin header, where jumpers can be configured to set the desired access code. The LST220 (U1) serves as the core logic component, interpreting the signals from the keypad. It is designed to recognize a specific sequence of four digits, ensuring that only authorized users can gain access.
When the correct code is entered, a high signal is generated at pin 13 of U1. This signal is utilized to drive a transistor (Q1), which acts as a switch to control the current flow to the relay (K1). The relay is responsible for activating an external electric lock solenoid, thereby unlocking the door or access point.
The circuit should also include necessary debouncing mechanisms for the keypad to prevent false triggering due to mechanical noise when keys are pressed. Additional components such as resistors and capacitors may be used to stabilize the power supply to U1 and ensure reliable operation. Optional features could include LED indicators to provide visual feedback when the correct code is entered or audible alerts for incorrect entries.
Overall, this electronic schematic provides a straightforward and effective method for implementing a secure access control system using a keypad and relay mechanism.A keypad enters a four-digit access code, which is programmed via jumpers on a 24-pin plug-in header and socket. U1 is an LST220, which detects a four-digit sequential data input. When the correct data is entered into the keyboard, pin 13 of U1 goes high, which activates Q1 and K1.
K1 drives an external electric lock solenoid, etc. 🔗 External reference