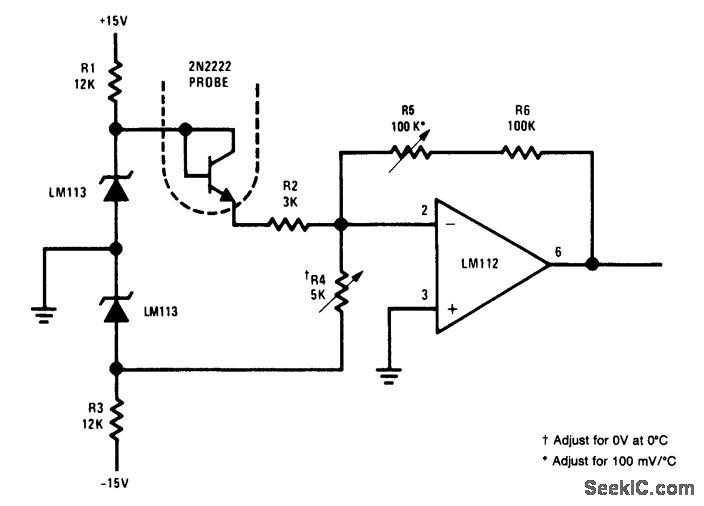
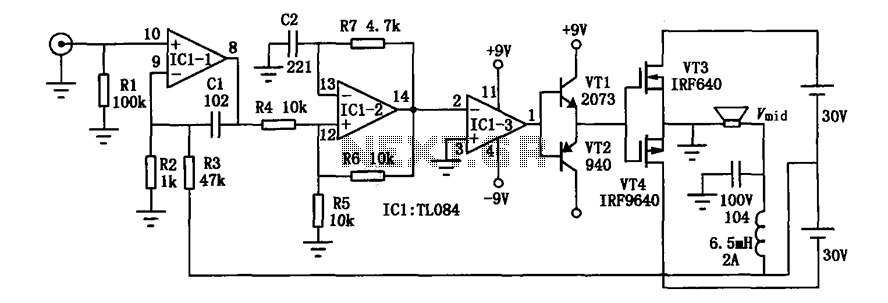
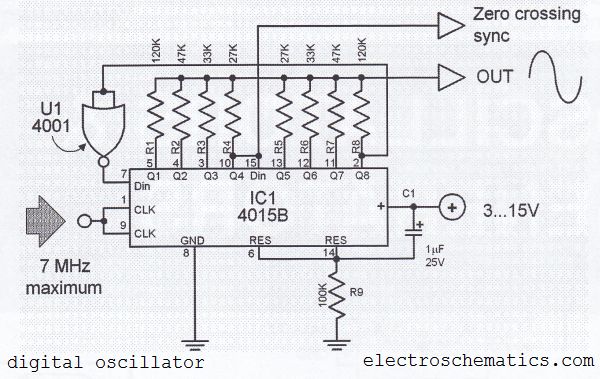
Digital thermometer with zero adjust
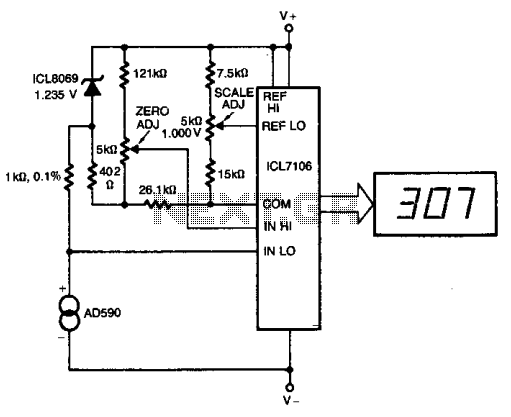
The ICL8069 brings the input within the common-mode range, while the 5 k ohm pots trim any offset at 218° (-55°C) and set the scale factor. This circuit allows for zero adjustment as well as slope adjustment.
The ICL8069 is a precision instrumentation amplifier designed to operate effectively within specified common-mode voltage ranges, making it suitable for various sensor applications. The device's architecture allows it to amplify small differential signals while rejecting common-mode noise, ensuring high accuracy in measurements.
In this circuit, two 5 k ohm potentiometers are utilized for fine-tuning the output. The first potentiometer is dedicated to offset adjustment, allowing the user to eliminate any inherent voltage offset that may affect the accuracy of the measurement at low temperatures, specifically at -55°C. This adjustment is critical for applications requiring precise readings, as any offset can lead to significant errors in the output signal.
The second potentiometer is used for slope adjustment, which enables the user to calibrate the gain of the amplifier circuit. This feature ensures that the output signal accurately reflects the input signal's amplitude, allowing for precise scaling of the measurements. By adjusting the slope, the user can tailor the amplifier's response to match the specific requirements of the application, ensuring that the output remains linear across the operating range.
Overall, the ICL8069 circuit with its adjustable components provides a robust solution for applications that require high precision and flexibility in signal processing. The combination of common-mode range capability, offset trimming, and slope adjustment makes this circuit suitable for a variety of sensor interfaces and measurement systems. The ICL8069 brings the input within the common-mode range, while the 5 k ohm pots trim any offset at 218° (-55°C), and set the scale factor. This circuit allows "zero adjustment" as well as slope adjustment.
The ICL8069 is a precision instrumentation amplifier designed to operate effectively within specified common-mode voltage ranges, making it suitable for various sensor applications. The device's architecture allows it to amplify small differential signals while rejecting common-mode noise, ensuring high accuracy in measurements.
In this circuit, two 5 k ohm potentiometers are utilized for fine-tuning the output. The first potentiometer is dedicated to offset adjustment, allowing the user to eliminate any inherent voltage offset that may affect the accuracy of the measurement at low temperatures, specifically at -55°C. This adjustment is critical for applications requiring precise readings, as any offset can lead to significant errors in the output signal.
The second potentiometer is used for slope adjustment, which enables the user to calibrate the gain of the amplifier circuit. This feature ensures that the output signal accurately reflects the input signal's amplitude, allowing for precise scaling of the measurements. By adjusting the slope, the user can tailor the amplifier's response to match the specific requirements of the application, ensuring that the output remains linear across the operating range.
Overall, the ICL8069 circuit with its adjustable components provides a robust solution for applications that require high precision and flexibility in signal processing. The combination of common-mode range capability, offset trimming, and slope adjustment makes this circuit suitable for a variety of sensor interfaces and measurement systems. The ICL8069 brings the input within the common-mode range, while the 5 k ohm pots trim any offset at 218° (-55°C), and set the scale factor. This circuit allows "zero adjustment" as well as slope adjustment.