Digital voltmeter using ICL7107
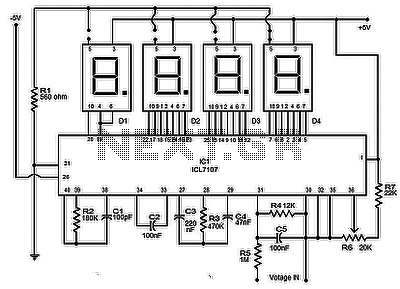
The circuit presented is a highly useful and accurate digital voltmeter featuring an LED display, utilizing the ICL7107 integrated circuit from Intersil. The ICL7107 is a high-performance, low-power, 3.5-digit analog-to-digital converter (ADC). This IC incorporates internal circuitry for seven-segment decoders, display drivers, a reference voltage source, and a clock. The power dissipation is less than 10mW, and the display stability is significantly high. The operation of this electronic circuit is straightforward. The voltage to be measured is converted into a digital equivalent by the ADC within the IC, which is then decoded into a seven-segment format for display. The ADC employed in the ICL7107 is of the dual-slope type. The process occurring within this ADC can be described as follows: for a fixed duration, the voltage to be measured is integrated to generate a ramp at the output of the integrator. Subsequently, a known reference voltage of opposite polarity is applied to the input of the integrator, allowing it to ramp until the output of the integrator reaches zero. The time required for the negative slope to reach zero is measured in terms of the IC's clock cycle and is proportional to the voltage being measured. In simpler terms, the input voltage is compared to an internal reference voltage, and the result is converted into a digital format. The resistor R2 and capacitor C1 are utilized to set the frequency of the IC's internal clock. Capacitor C2 serves to neutralize fluctuations in the internal reference voltage, enhancing the stability of the display. Resistor R4 regulates the range of the voltmeter. The rightmost three displays are connected to show all digits, while the leftmost display is configured to show only 1 and - signs. Pin 5 (representing the dot) is connected to ground solely for the third display, and its position must be adjusted when changing the voltmeter's range by modifying R4. (R4 = 1.2K provides a 0-20V range, while R4 = 12K offers a 0-200V range).
The digital voltmeter circuit utilizing the ICL7107 is designed for precision voltage measurements in various applications. The ICL7107's architecture allows for efficient conversion of analog signals to digital readings, ensuring high accuracy and low power consumption. The dual-slope ADC technique employed in this circuit is particularly advantageous for minimizing the effects of noise and fluctuations in the input voltage, as it averages the voltage over a period of time.
In terms of the circuit layout, the integration process begins when the voltage to be measured is applied to the integrator, producing a linear ramp voltage. This ramp is then reversed by applying a known reference voltage, which helps in determining the time taken for the ramp to return to zero. This time interval is crucial, as it is directly proportional to the input voltage. The internal clock frequency, determined by R2 and C1, plays a significant role in ensuring the accuracy of the timing measurements.
The display configuration is designed for clarity and ease of reading. The rightmost three seven-segment displays are responsible for displaying the full range of digits, while the leftmost display indicates the sign of the measured voltage. The adjustment of resistor R4 allows the user to select different measurement ranges, enhancing the versatility of the voltmeter for various applications.
Overall, the circuit is a robust solution for accurate voltage measurement, suitable for educational, industrial, and laboratory environments. Its design emphasizes stability, accuracy, and user-friendliness, making it an excellent choice for anyone needing a reliable digital voltmeter.The circuit given here is of a very useful and accurate digital voltmeter with LED display using the ICL7107 from Intersil. The ICL7107 is a high performance, low power, 3. 5 digit analog to digital converter. The IC includes internal circuitry for seven segment decoders, display drivers, reference voltage source and a clock.
The power dissipation is less than 10mW and the display stability is very high. The working of this electronic circuit is very simple. The voltage to be measured is converted into a digital equivalent by the ADC inside the IC and then this digital equivalent is decoded to the seven segment format and then displayed. The ADC used in ICL7107 is dual slope type ADC. The process taking place inside our ADC can be stated as follows. For a fixed period of time the voltage to be measured is integrated to obtain a ramp at the output of the integrator.
Then a known reference voltage of opposite polarity is applied to the input of the integrator and allowed to ramp until the output of integrator becomes zero. The time taken for the negative slope to reach zero is measured in terms of the IC`s clock cycle and it will be proportional to the voltage under measurement.
In simple words, the input voltage is compared to an internal reference voltage and the result is converted in a digital format. The resistor R2 and C1 are used to set the frequency of IC`s internal clock. Capacitor C2 neutralizes the fluctuations in the internal reference voltage and increases the stability of the display.
R4 controls the range of the voltmeter. Right most three displays are connected so that they can display all digits. The left most display is so connected that it can display only 1 and -. The pin5(representing the dot) is connected to ground only for the third display and its position needs to be changed when you change the range of the volt meter by altering R4. (R4=1. 2K gives 0-20V range, R4=12K gives 0-200V range ). 🔗 External reference
The digital voltmeter circuit utilizing the ICL7107 is designed for precision voltage measurements in various applications. The ICL7107's architecture allows for efficient conversion of analog signals to digital readings, ensuring high accuracy and low power consumption. The dual-slope ADC technique employed in this circuit is particularly advantageous for minimizing the effects of noise and fluctuations in the input voltage, as it averages the voltage over a period of time.
In terms of the circuit layout, the integration process begins when the voltage to be measured is applied to the integrator, producing a linear ramp voltage. This ramp is then reversed by applying a known reference voltage, which helps in determining the time taken for the ramp to return to zero. This time interval is crucial, as it is directly proportional to the input voltage. The internal clock frequency, determined by R2 and C1, plays a significant role in ensuring the accuracy of the timing measurements.
The display configuration is designed for clarity and ease of reading. The rightmost three seven-segment displays are responsible for displaying the full range of digits, while the leftmost display indicates the sign of the measured voltage. The adjustment of resistor R4 allows the user to select different measurement ranges, enhancing the versatility of the voltmeter for various applications.
Overall, the circuit is a robust solution for accurate voltage measurement, suitable for educational, industrial, and laboratory environments. Its design emphasizes stability, accuracy, and user-friendliness, making it an excellent choice for anyone needing a reliable digital voltmeter.The circuit given here is of a very useful and accurate digital voltmeter with LED display using the ICL7107 from Intersil. The ICL7107 is a high performance, low power, 3. 5 digit analog to digital converter. The IC includes internal circuitry for seven segment decoders, display drivers, reference voltage source and a clock.
The power dissipation is less than 10mW and the display stability is very high. The working of this electronic circuit is very simple. The voltage to be measured is converted into a digital equivalent by the ADC inside the IC and then this digital equivalent is decoded to the seven segment format and then displayed. The ADC used in ICL7107 is dual slope type ADC. The process taking place inside our ADC can be stated as follows. For a fixed period of time the voltage to be measured is integrated to obtain a ramp at the output of the integrator.
Then a known reference voltage of opposite polarity is applied to the input of the integrator and allowed to ramp until the output of integrator becomes zero. The time taken for the negative slope to reach zero is measured in terms of the IC`s clock cycle and it will be proportional to the voltage under measurement.
In simple words, the input voltage is compared to an internal reference voltage and the result is converted in a digital format. The resistor R2 and C1 are used to set the frequency of IC`s internal clock. Capacitor C2 neutralizes the fluctuations in the internal reference voltage and increases the stability of the display.
R4 controls the range of the voltmeter. Right most three displays are connected so that they can display all digits. The left most display is so connected that it can display only 1 and -. The pin5(representing the dot) is connected to ground only for the third display and its position needs to be changed when you change the range of the volt meter by altering R4. (R4=1. 2K gives 0-20V range, R4=12K gives 0-200V range ). 🔗 External reference