Dimmer Circuit
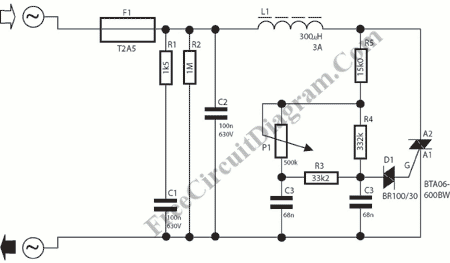
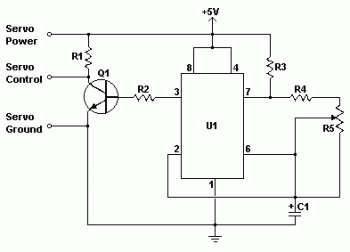
A light dimmer circuit is utilized to adjust the brightness of a lamp to various levels. This dimmer circuit is designed specifically for incandescent lamps, and it is not suitable for use with fluorescent lamps.
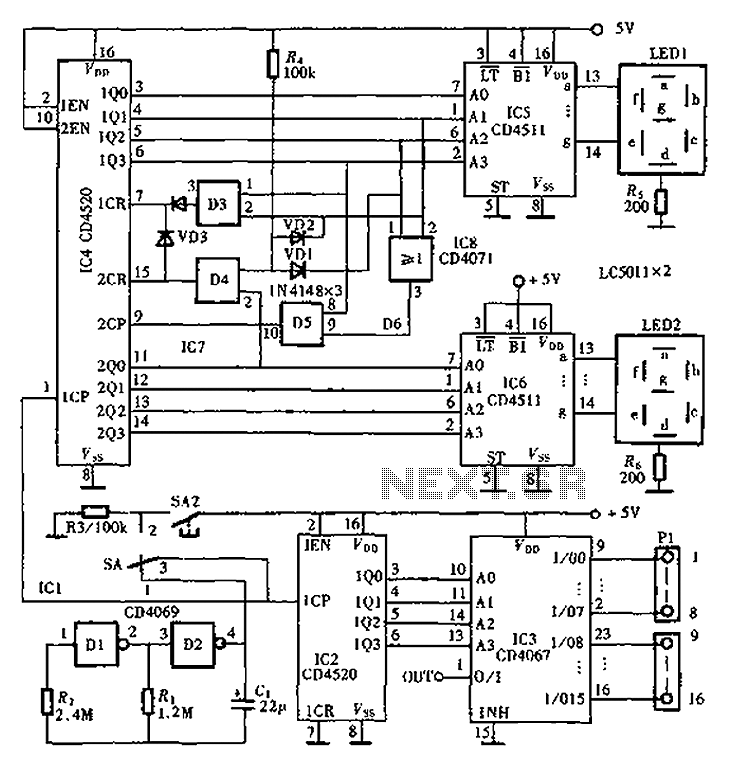
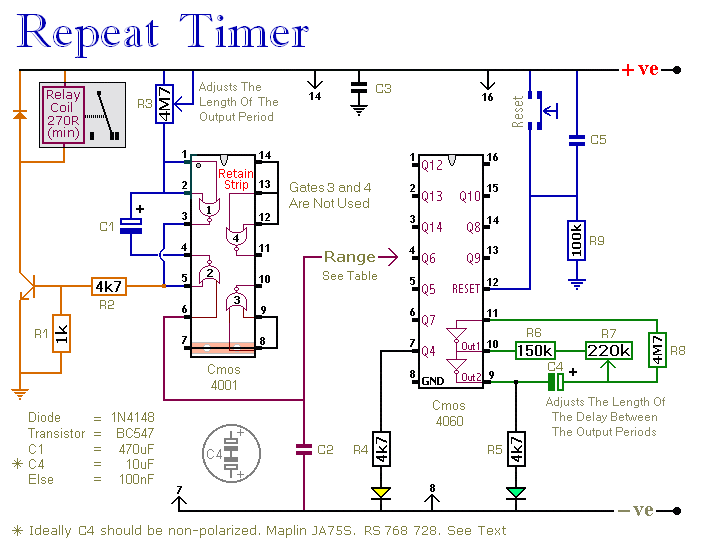
The light dimmer circuit typically employs a triac or a similar semiconductor device to control the power delivered to the incandescent lamp. The operation of the circuit relies on phase control, where the triac is triggered at a specific point in the AC waveform. This allows the circuit to effectively reduce the average power delivered to the lamp, resulting in a dimming effect.
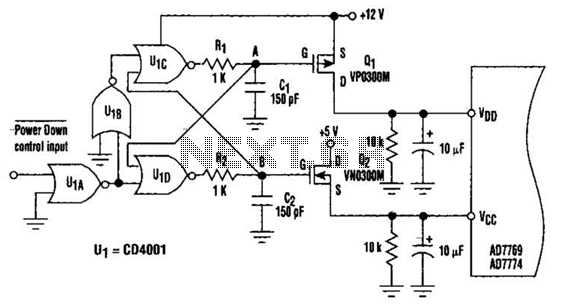
Key components of a standard light dimmer circuit include a variable resistor or potentiometer, which is used to adjust the phase angle at which the triac is triggered. The circuit may also incorporate an opto-isolator for safety, providing electrical isolation between the control circuit and the high-voltage AC line.
When the variable resistor is adjusted, it changes the timing of the triac's gate signal, thereby modifying the conduction angle of the AC waveform. This results in a change in the brightness of the incandescent lamp. The circuit should be designed to handle the maximum current and voltage ratings of the lamp to ensure safe operation.
In summary, the light dimmer circuit is an essential device for controlling the brightness of incandescent lamps through phase control techniques, making it a valuable addition to residential and commercial lighting systems.Light dimmer circuit is used to control the lamp for arbitrary brightness. This dimmer circuit work for incandescent lamp, not a fluorescent one.? The dimmer. 🔗 External reference
The light dimmer circuit typically employs a triac or a similar semiconductor device to control the power delivered to the incandescent lamp. The operation of the circuit relies on phase control, where the triac is triggered at a specific point in the AC waveform. This allows the circuit to effectively reduce the average power delivered to the lamp, resulting in a dimming effect.
Key components of a standard light dimmer circuit include a variable resistor or potentiometer, which is used to adjust the phase angle at which the triac is triggered. The circuit may also incorporate an opto-isolator for safety, providing electrical isolation between the control circuit and the high-voltage AC line.
When the variable resistor is adjusted, it changes the timing of the triac's gate signal, thereby modifying the conduction angle of the AC waveform. This results in a change in the brightness of the incandescent lamp. The circuit should be designed to handle the maximum current and voltage ratings of the lamp to ensure safe operation.
In summary, the light dimmer circuit is an essential device for controlling the brightness of incandescent lamps through phase control techniques, making it a valuable addition to residential and commercial lighting systems.Light dimmer circuit is used to control the lamp for arbitrary brightness. This dimmer circuit work for incandescent lamp, not a fluorescent one.? The dimmer. 🔗 External reference