DIY Circuit Car Battery Charger

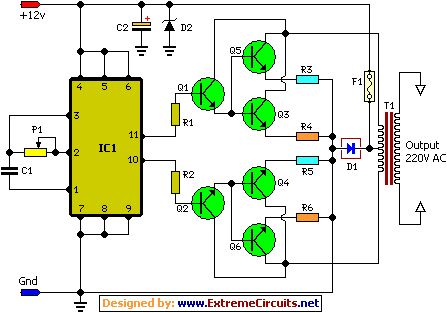
This simple circuit consists of a transformer, two diodes, a capacitor, and an ammeter. To charge a battery, connect the positive and negative terminals of the circuit to the corresponding terminals of the battery. When the battery is not charged, the ammeter reading indicates 1-3 amps. When the battery is fully charged, the ammeter reading drops to zero or nearly zero, after which the battery should be removed from the charger.
The circuit operates by utilizing the transformer to step down the AC voltage from the mains supply to a lower voltage suitable for charging the battery. The two diodes are configured in a bridge rectifier arrangement, allowing for full-wave rectification of the AC voltage. This conversion is essential for providing a steady DC output to the battery.
The capacitor serves to smooth out the rectified voltage, reducing ripple and providing a more stable charging voltage to the battery. This smoothing effect is crucial for the longevity of the battery, as it helps prevent over-voltage conditions that can lead to damage.
The ammeter is connected in series with the battery and serves as an indicator of the charging current. During the charging process, the ammeter will display a current of 1-3 amps, indicating that the battery is being charged. As the battery reaches its full charge state, the charging current will decrease, eventually dropping to zero or close to zero. This drop in current signifies that the battery is fully charged and should be disconnected from the charger to prevent overcharging, which could lead to battery damage or reduced lifespan.
Overall, this circuit is a straightforward and effective solution for charging batteries, providing essential indicators and protections to ensure safe and efficient operation.This very simple circuit uses a transformer, two diodes, a capacitor and an ammeter. To charge a battery just connect the + and terminals of the circuit to the corresponding terminals of the battery. When the battery is not charged, the ammeter reading shows 1-3 amps. When the battery is fully charged the ammeter reads Zero or nearly zero, af ter which the battery should be removed from the charger. 🔗 External reference
The circuit operates by utilizing the transformer to step down the AC voltage from the mains supply to a lower voltage suitable for charging the battery. The two diodes are configured in a bridge rectifier arrangement, allowing for full-wave rectification of the AC voltage. This conversion is essential for providing a steady DC output to the battery.
The capacitor serves to smooth out the rectified voltage, reducing ripple and providing a more stable charging voltage to the battery. This smoothing effect is crucial for the longevity of the battery, as it helps prevent over-voltage conditions that can lead to damage.
The ammeter is connected in series with the battery and serves as an indicator of the charging current. During the charging process, the ammeter will display a current of 1-3 amps, indicating that the battery is being charged. As the battery reaches its full charge state, the charging current will decrease, eventually dropping to zero or close to zero. This drop in current signifies that the battery is fully charged and should be disconnected from the charger to prevent overcharging, which could lead to battery damage or reduced lifespan.
Overall, this circuit is a straightforward and effective solution for charging batteries, providing essential indicators and protections to ensure safe and efficient operation.This very simple circuit uses a transformer, two diodes, a capacitor and an ammeter. To charge a battery just connect the + and terminals of the circuit to the corresponding terminals of the battery. When the battery is not charged, the ammeter reading shows 1-3 amps. When the battery is fully charged the ammeter reads Zero or nearly zero, af ter which the battery should be removed from the charger. 🔗 External reference