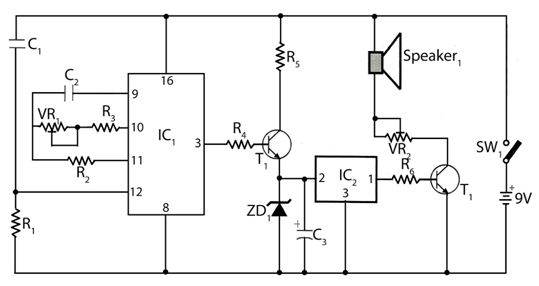
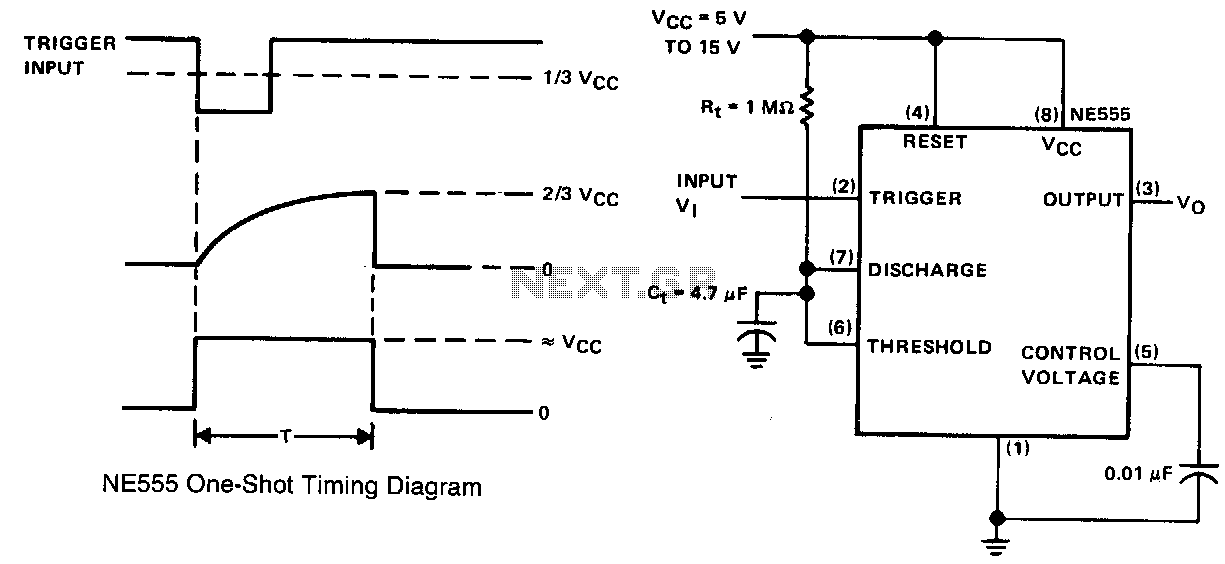
Driving 72 leds with 555 timer
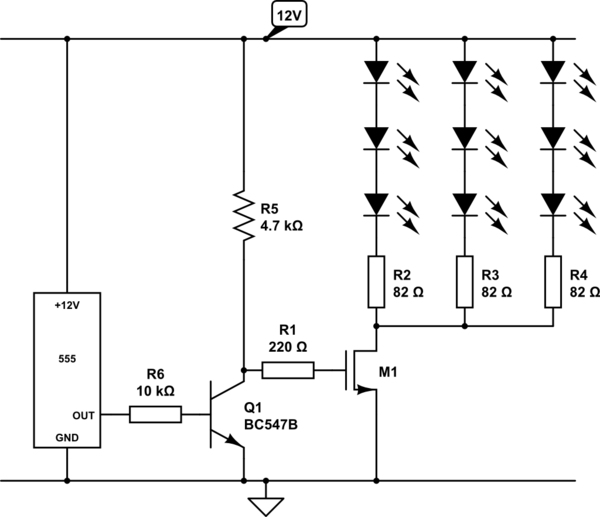
Create a circuit using a 555 timer to operate 72 LEDs simultaneously. A circuit has already been constructed, but there are concerns regarding its safety and longevity. A picture of the circuit is provided for review, and assistance is requested to determine if additional components are necessary. Instructions for adding these components should also be included.
The proposed circuit utilizes a 555 timer in astable mode to drive 72 LEDs concurrently. The 555 timer is a versatile integrated circuit capable of generating precise timing sequences and is commonly used in various applications, including LED drivers.
To ensure the circuit operates safely and effectively, a few critical considerations must be addressed. First, the power supply voltage should be compatible with the 555 timer and the forward voltage ratings of the LEDs. Typically, a 5V to 15V supply is suitable for the 555 timer, while the LEDs may require a lower voltage, generally around 2V to 3V depending on their color and type.
The circuit can be designed as follows:
1. **555 Timer Configuration**: Connect the 555 timer in astable mode. This involves connecting pins 2 and 6 together, with a resistor (R1) connected from pin 7 to the supply voltage and another resistor (R2) from pin 7 to pin 6. A capacitor (C1) should be connected from pin 6 to ground. The values of R1, R2, and C1 will determine the frequency of the output signal, which should be set to a frequency that allows the LEDs to appear continuously lit rather than blinking.
2. **LED Connection**: Connect the anodes of the LEDs to the output pin (pin 3) of the 555 timer. Connect the cathodes of the LEDs to ground. To ensure that the LEDs operate safely, it is advisable to include current-limiting resistors in series with each LED. The resistor value can be calculated using Ohm’s Law: R = (V_supply - V_LED) / I_LED, where V_supply is the supply voltage, V_LED is the forward voltage of the LED, and I_LED is the desired current through the LED (typically around 20mA for standard LEDs).
3. **Power Considerations**: When driving a large number of LEDs, it is essential to ensure that the total current does not exceed the current rating of the 555 timer. If the total current exceeds the rating, consider using a transistor or MOSFET as a switch to drive the LEDs, allowing the timer to control the gate of the transistor, which in turn will handle the higher current for the LEDs.
4. **Heat Management**: With 72 LEDs, heat dissipation may become an issue. Ensure that the components, especially the 555 timer and any transistors used, are rated for the expected power dissipation. Heat sinks may be necessary for higher power applications.
5. **Testing and Validation**: Once the circuit is assembled, it is crucial to test the circuit with a multimeter to ensure proper voltage levels and current flow through the LEDs. Observe the operation for an extended period to confirm reliability and thermal performance.
By addressing these considerations, the circuit can be optimized for safety and longevity while effectively driving the 72 LEDs.Make a circuit with a 555 timer to run 72 LEDs all at the same time. I have already made a circuit, but am not sure If it will work safe and long or not. I am putting the picture of the circuit and I want anybody who can help to look at it and see if it needs some extra components. Please add them on the circuit or explain instructions to add. 🔗 External reference
The proposed circuit utilizes a 555 timer in astable mode to drive 72 LEDs concurrently. The 555 timer is a versatile integrated circuit capable of generating precise timing sequences and is commonly used in various applications, including LED drivers.
To ensure the circuit operates safely and effectively, a few critical considerations must be addressed. First, the power supply voltage should be compatible with the 555 timer and the forward voltage ratings of the LEDs. Typically, a 5V to 15V supply is suitable for the 555 timer, while the LEDs may require a lower voltage, generally around 2V to 3V depending on their color and type.
The circuit can be designed as follows:
1. **555 Timer Configuration**: Connect the 555 timer in astable mode. This involves connecting pins 2 and 6 together, with a resistor (R1) connected from pin 7 to the supply voltage and another resistor (R2) from pin 7 to pin 6. A capacitor (C1) should be connected from pin 6 to ground. The values of R1, R2, and C1 will determine the frequency of the output signal, which should be set to a frequency that allows the LEDs to appear continuously lit rather than blinking.
2. **LED Connection**: Connect the anodes of the LEDs to the output pin (pin 3) of the 555 timer. Connect the cathodes of the LEDs to ground. To ensure that the LEDs operate safely, it is advisable to include current-limiting resistors in series with each LED. The resistor value can be calculated using Ohm’s Law: R = (V_supply - V_LED) / I_LED, where V_supply is the supply voltage, V_LED is the forward voltage of the LED, and I_LED is the desired current through the LED (typically around 20mA for standard LEDs).
3. **Power Considerations**: When driving a large number of LEDs, it is essential to ensure that the total current does not exceed the current rating of the 555 timer. If the total current exceeds the rating, consider using a transistor or MOSFET as a switch to drive the LEDs, allowing the timer to control the gate of the transistor, which in turn will handle the higher current for the LEDs.
4. **Heat Management**: With 72 LEDs, heat dissipation may become an issue. Ensure that the components, especially the 555 timer and any transistors used, are rated for the expected power dissipation. Heat sinks may be necessary for higher power applications.
5. **Testing and Validation**: Once the circuit is assembled, it is crucial to test the circuit with a multimeter to ensure proper voltage levels and current flow through the LEDs. Observe the operation for an extended period to confirm reliability and thermal performance.
By addressing these considerations, the circuit can be optimized for safety and longevity while effectively driving the 72 LEDs.Make a circuit with a 555 timer to run 72 LEDs all at the same time. I have already made a circuit, but am not sure If it will work safe and long or not. I am putting the picture of the circuit and I want anybody who can help to look at it and see if it needs some extra components. Please add them on the circuit or explain instructions to add. 🔗 External reference