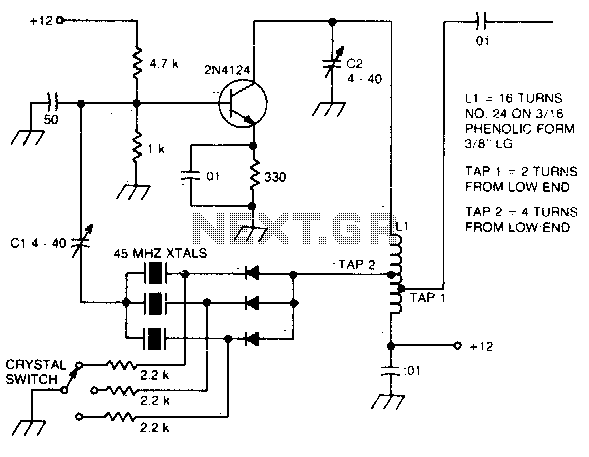
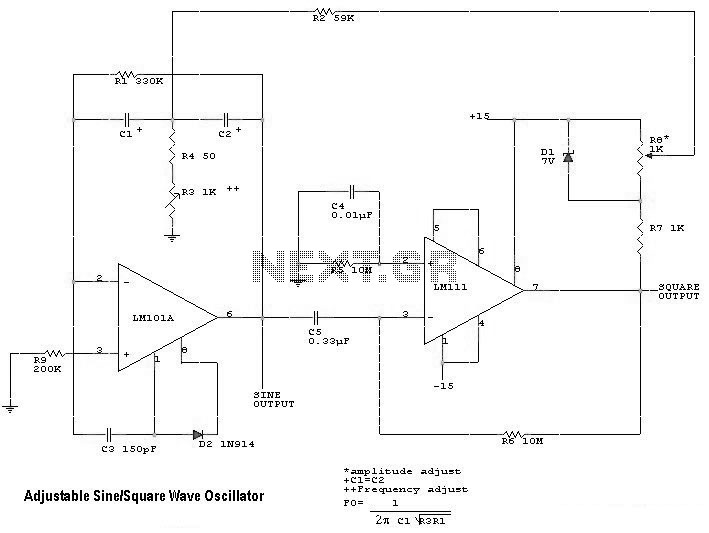
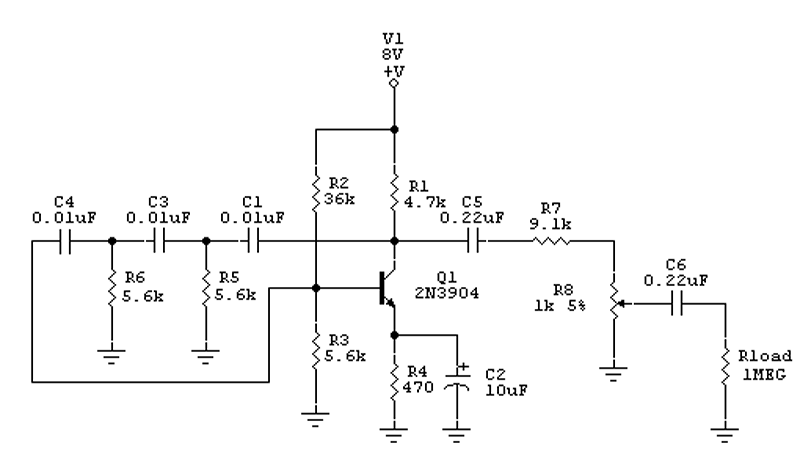
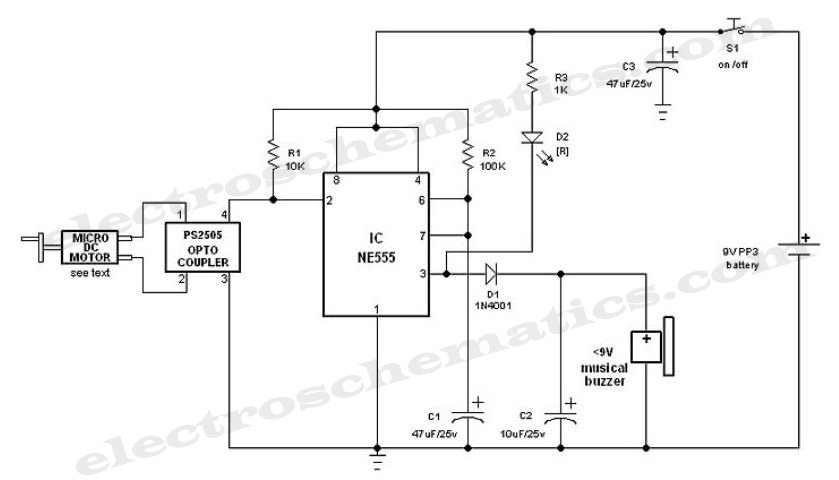
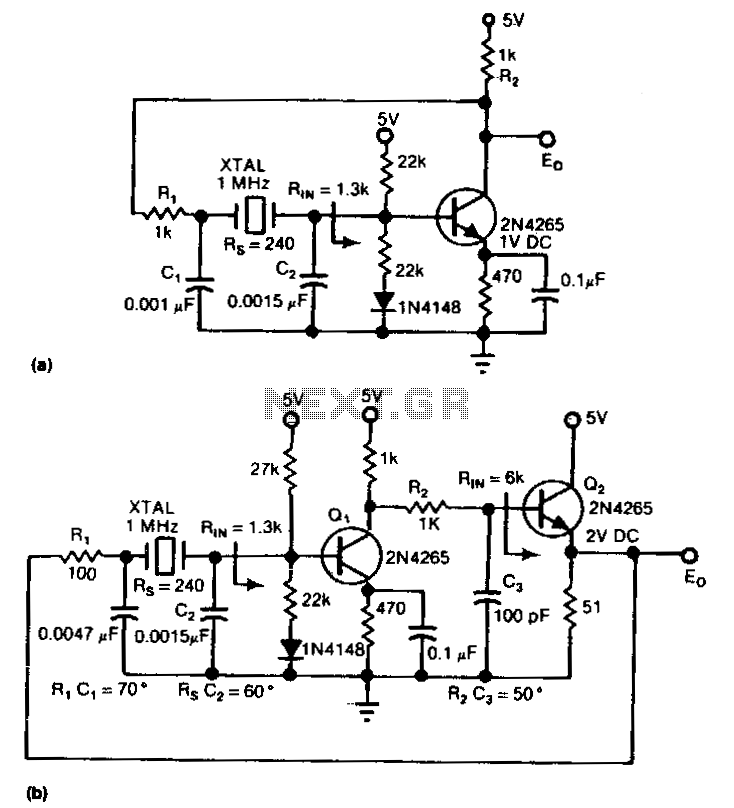
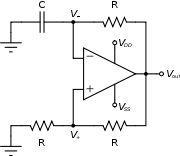
Electronic oscillator
An electronic circuit consists of individual electronic components such as resistors, transistors, capacitors, inductors, and diodes, which are interconnected by conductive wires or traces that allow electric current to flow. The sine wave or sinusoid is a mathematical function that represents a smooth, repetitive oscillation, commonly found in pure mathematics, physics, signal processing, electrical engineering, and various other fields. A square wave is a type of non-sinusoidal waveform typically encountered in electronics and signal processing, characterized by its regular and instantaneous alternation between two levels. These waveforms are prevalent in numerous electronic devices. Signals generated by oscillators, such as those broadcast by radio and television transmitters, are common examples. A television transmitter broadcasts electromagnetic signals to television receivers and can be either analog or digital. There are various types of transmitters based on system standards. A quartz clock utilizes an electronic oscillator regulated by a quartz crystal to maintain accurate time, producing a signal with a precise frequency, making quartz clocks significantly more accurate than mechanical clocks. Low-frequency oscillation denotes an electronic signal, generally below 20Hz, which creates rhythmic pulses or sweeps, often used to modulate synthesizers, delay lines, and other audio equipment for effects in electronic music production. In alternating current (AC), the electric charge movement periodically reverses direction, while in direct current (DC), the flow of electric charge remains unidirectional. The term "waveform" refers to the shape and form of a signal, which can be represented graphically, especially when direct visual observation of the wave is not possible. An inverter is an electrical device that converts direct current to alternating current, with the output AC adjustable in voltage and frequency through appropriate transformers, switching, and control circuits. In classical mechanics, a harmonic oscillator is a system that experiences a restoring force proportional to its displacement from equilibrium. A relaxation oscillator is based on the behavior of a physical system returning to equilibrium after disturbance, continuously dissipating internal energy. A linear circuit is defined as an electronic circuit where, for a sinusoidal input voltage of frequency f, the output remains sinusoidal at the same frequency. An electronic amplifier increases the power of a signal by drawing energy from a power supply, controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude. This process often involves positive feedback loops, where the output is fed back into the input through a filter. When first powered, the amplifier's output consists solely of noise, which travels around the loop and is filtered. In signal processing, a filter is a device or process that removes unwanted components or features from a signal, with filtering being a key aspect of signal processing that suppresses certain aspects of the signal.
An electronic circuit is fundamentally structured to facilitate the flow of electric current through interconnected components that perform specific functions. Resistors limit current, capacitors store and release energy, inductors store energy in a magnetic field, diodes allow current to flow in one direction, and transistors act as switches or amplifiers. The integration of these components enables the circuit to perform complex tasks, such as signal modulation and amplification.
Waveforms such as sine waves and square waves are critical in defining the behavior of signals within electronic circuits. Sine waves are essential for representing alternating current and other periodic signals due to their smooth oscillation, while square waves are commonly used in digital circuits and timing applications because of their distinct high and low states.
Television transmitters exemplify the practical application of these concepts, broadcasting signals that are modulated to carry audio and video information. The transition from analog to digital transmission has further enhanced the efficiency and quality of signal delivery, utilizing advanced modulation techniques to optimize bandwidth usage.
Quartz clocks illustrate the precision achievable in electronic timing applications through the use of crystal oscillators. The frequency stability provided by quartz crystals is crucial in various applications, from timekeeping to frequency synthesis in communication systems.
The role of oscillators in generating low-frequency signals is particularly relevant in audio applications, where they contribute to sound synthesis and effects processing. The ability to manipulate these signals through filters and amplifiers allows for the creation of diverse audio effects, essential in modern music production.
Inverters play a vital role in converting DC to AC, enabling the integration of renewable energy sources into the power grid and providing AC power for household appliances. The design of inverters must account for various parameters, including voltage, frequency, and power factor, to ensure compatibility with the load and efficiency in energy conversion.
Harmonic and relaxation oscillators are fundamental concepts in both electronics and physics, providing insight into system dynamics and energy dissipation. The principles governing these oscillators are applied in various technologies, including signal generators, timers, and control systems.
Overall, the interplay between these components and concepts forms the foundation of modern electronic circuit design, facilitating the development of sophisticated devices that enhance daily life and drive technological advancement.An electronic circuit is composed of individual electronic components, such as resistors, transistors, capacitors, inductors and diodes, connected by conductive wires or traces through which electric current can flow. The sine wave or sinusoid is a mathematical function that describes a smooth repetitive oscillation. It occurs often in pure mathem atics, as well as physics, signal processing, electrical engineering and many other fields. A square wave is a kind of non-sinusoidal waveform, most typically encountered in electronics and signal processing. An ideal square wave alternates regularly and instantaneously between two levels. . They are widely used in innumerable electronic devices. Common examples of signals generated by oscillators include signals broadcast by radioand television transmitter A television transmitter is a device which broadcasts an electromagnetic signal to the television receivers.
Television transmitters may be analog or digital. - Types of transmitters :There are many types of transmitters depending on* The system standard. A quartz clock is a clock that uses an electronic oscillator that is regulated by a quartz crystal to keep time. This crystal oscillator creates a signal with very precise frequency, so that quartz clocks are at least an order of magnitude more accurate than good mechanical clocks.
Low-frequency oscillation is an electronic signal, which is usually below 20Hz and creates a rhythmic pulse or sweep. This pulse or sweep is often used to modulate synthesizers, delay lines and other audio equipment in order to create effects used in the production of electronic music.
Audio. In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current, the flow of electric charge is only in one direction. Waveform means the shape and form of a signal such as a wave moving in a physical medium or an abstract representation. In many cases the medium in which the wave is being propagated does not permit a direct visual image of the form.
In these cases, the term `waveform` refers to the shape of a graph. An inverter is an electrical device that converts direct current to alternating current ; the converted AC can be at any required voltage and frequency with the use of appropriate transformers, switching, and control circuits. In classical mechanics, a harmonic oscillator is a system that, when displaced from its equilibrium position, experiences a restoring force, F, proportional to the displacement, x: vec F = -k vec x , where k is a positive constant.
A relaxation oscillator is an oscillator based upon the behavior of a physical system`s return to equilibrium after being disturbed. That is, a dynamical system within the oscillator continuously dissipates its internal energy. A linear circuit is an electronic circuit in which, for a sinusoidal input voltage of frequency f, any output of the circuit is also sinusoidal with frequency f.
An electronic amplifier is a device for increasing the power of a signal. It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude. connected in a positive feedback loopwith its output fed back into its input through a filter. When the power supply to the amplifier is first switched on, the amplifier`s output consists only of noise.
The noise travels around the loop and is filtered In signal processing, a filter is a device or process that removes from a signal some unwanted component or feature. Filtering is a class of signal processing, the defining feature of filters being the complete or partial suppression of some aspect of the signal.
The sine wave or sinusoid is a mathematical function that describes a smooth repetitive oscillation. It occurs often in pure mathematics, as well as physics, signal processing, electrical engineering and many other fields. An inductor is a passive 🔗 External reference
An electronic circuit is fundamentally structured to facilitate the flow of electric current through interconnected components that perform specific functions. Resistors limit current, capacitors store and release energy, inductors store energy in a magnetic field, diodes allow current to flow in one direction, and transistors act as switches or amplifiers. The integration of these components enables the circuit to perform complex tasks, such as signal modulation and amplification.
Waveforms such as sine waves and square waves are critical in defining the behavior of signals within electronic circuits. Sine waves are essential for representing alternating current and other periodic signals due to their smooth oscillation, while square waves are commonly used in digital circuits and timing applications because of their distinct high and low states.
Television transmitters exemplify the practical application of these concepts, broadcasting signals that are modulated to carry audio and video information. The transition from analog to digital transmission has further enhanced the efficiency and quality of signal delivery, utilizing advanced modulation techniques to optimize bandwidth usage.
Quartz clocks illustrate the precision achievable in electronic timing applications through the use of crystal oscillators. The frequency stability provided by quartz crystals is crucial in various applications, from timekeeping to frequency synthesis in communication systems.
The role of oscillators in generating low-frequency signals is particularly relevant in audio applications, where they contribute to sound synthesis and effects processing. The ability to manipulate these signals through filters and amplifiers allows for the creation of diverse audio effects, essential in modern music production.
Inverters play a vital role in converting DC to AC, enabling the integration of renewable energy sources into the power grid and providing AC power for household appliances. The design of inverters must account for various parameters, including voltage, frequency, and power factor, to ensure compatibility with the load and efficiency in energy conversion.
Harmonic and relaxation oscillators are fundamental concepts in both electronics and physics, providing insight into system dynamics and energy dissipation. The principles governing these oscillators are applied in various technologies, including signal generators, timers, and control systems.
Overall, the interplay between these components and concepts forms the foundation of modern electronic circuit design, facilitating the development of sophisticated devices that enhance daily life and drive technological advancement.An electronic circuit is composed of individual electronic components, such as resistors, transistors, capacitors, inductors and diodes, connected by conductive wires or traces through which electric current can flow. The sine wave or sinusoid is a mathematical function that describes a smooth repetitive oscillation. It occurs often in pure mathem atics, as well as physics, signal processing, electrical engineering and many other fields. A square wave is a kind of non-sinusoidal waveform, most typically encountered in electronics and signal processing. An ideal square wave alternates regularly and instantaneously between two levels. . They are widely used in innumerable electronic devices. Common examples of signals generated by oscillators include signals broadcast by radioand television transmitter A television transmitter is a device which broadcasts an electromagnetic signal to the television receivers.
Television transmitters may be analog or digital. - Types of transmitters :There are many types of transmitters depending on* The system standard. A quartz clock is a clock that uses an electronic oscillator that is regulated by a quartz crystal to keep time. This crystal oscillator creates a signal with very precise frequency, so that quartz clocks are at least an order of magnitude more accurate than good mechanical clocks.
Low-frequency oscillation is an electronic signal, which is usually below 20Hz and creates a rhythmic pulse or sweep. This pulse or sweep is often used to modulate synthesizers, delay lines and other audio equipment in order to create effects used in the production of electronic music.
Audio. In alternating current the movement of electric charge periodically reverses direction. In direct current, the flow of electric charge is only in one direction. Waveform means the shape and form of a signal such as a wave moving in a physical medium or an abstract representation. In many cases the medium in which the wave is being propagated does not permit a direct visual image of the form.
In these cases, the term `waveform` refers to the shape of a graph. An inverter is an electrical device that converts direct current to alternating current ; the converted AC can be at any required voltage and frequency with the use of appropriate transformers, switching, and control circuits. In classical mechanics, a harmonic oscillator is a system that, when displaced from its equilibrium position, experiences a restoring force, F, proportional to the displacement, x: vec F = -k vec x , where k is a positive constant.
A relaxation oscillator is an oscillator based upon the behavior of a physical system`s return to equilibrium after being disturbed. That is, a dynamical system within the oscillator continuously dissipates its internal energy. A linear circuit is an electronic circuit in which, for a sinusoidal input voltage of frequency f, any output of the circuit is also sinusoidal with frequency f.
An electronic amplifier is a device for increasing the power of a signal. It does this by taking energy from a power supply and controlling the output to match the input signal shape but with a larger amplitude. connected in a positive feedback loopwith its output fed back into its input through a filter. When the power supply to the amplifier is first switched on, the amplifier`s output consists only of noise.
The noise travels around the loop and is filtered In signal processing, a filter is a device or process that removes from a signal some unwanted component or feature. Filtering is a class of signal processing, the defining feature of filters being the complete or partial suppression of some aspect of the signal.
The sine wave or sinusoid is a mathematical function that describes a smooth repetitive oscillation. It occurs often in pure mathematics, as well as physics, signal processing, electrical engineering and many other fields. An inductor is a passive 🔗 External reference