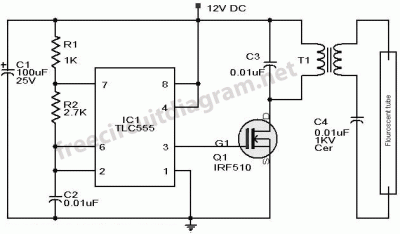
Electronic Pest Killing Lamp

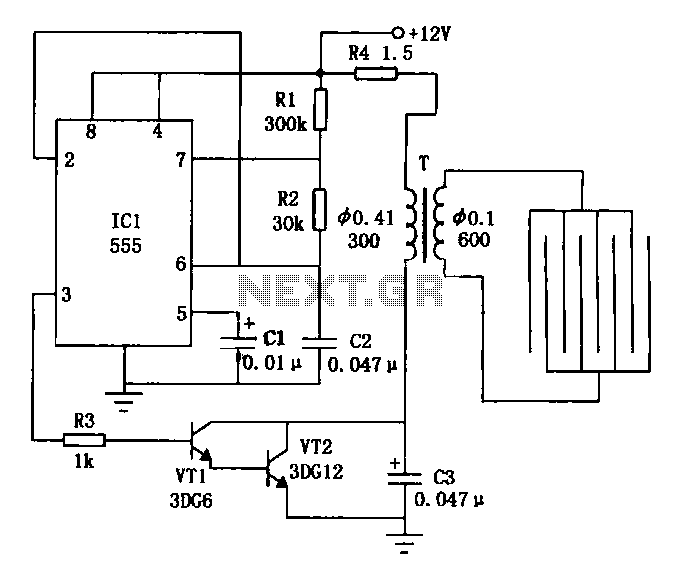
Working Principle: The circuit, as illustrated in figure 4-187, is composed of three main components: the power circuit, the pulse oscillator, and the high voltage generator. The power circuit includes components S, FU, TI, VD1-VD4, C1, C3, IC1, R1, and VL. The pulse oscillator is made up of IC1, R2, R3, RP1, and C2. The high voltage generator consists of V1, V2, RP2, RP3, R4, R5, and T2. EL represents the trap lamp, and C5 is...
The described circuit operates through a systematic integration of its components, each serving a specific function to achieve the desired output. The power circuit is responsible for supplying the necessary voltage and current to the entire system. It incorporates a switch (S) for control, a fuse (FU) for protection against overcurrent conditions, and a transformer (TI) to step up or step down the voltage as required. The diodes (VD1-VD4) are configured for rectification, ensuring that the output is suitable for the following stages. Capacitors C1 and C3 filter the output to smooth out any voltage fluctuations, while IC1 serves as a control element, possibly functioning as a voltage regulator or an operational amplifier, depending on the circuit requirements. Resistor R1 limits the current to protect sensitive components, and VL indicates a load or visual indicator.
The pulse oscillator generates the necessary timing signals for the circuit's operation. It utilizes IC1, which may be a timer or oscillator IC, along with resistors R2 and R3 that set the frequency of oscillation. Potentiometer RP1 allows for adjustable frequency settings, providing flexibility in the circuit's operation. Capacitor C2 is crucial for determining the timing characteristics of the oscillator, influencing the pulse width and frequency.
The high voltage generator is designed to produce the elevated voltages required for the operation of the trap lamp (EL). This section includes two voltage sources (V1 and V2), which may be configured in series or parallel depending on the design requirements. Resistors RP2, RP3, R4, and R5 are used to control the voltage levels and current flow within this section, ensuring safety and efficiency. Transformer T2 is likely employed to step up the voltage to the required high levels for the trap lamp operation, enabling effective illumination.
Overall, this circuit is a well-structured assembly of components designed to perform a specific function, with each part contributing to the efficient generation and management of electrical energy.Working Principle: As seen in the figure 4-187, the circuit consists of power circuit, pulse oscillator and high voltage generator. The power circuit consists of S,FU,TI,VD1-VD4,C1,C3,IC1,R1 and VL. The pulse oscillator consists of IC1,R2,R3,RP1 and C2. The high voltage generator consists of V1,V2,RP2,RP3,R4,R5,T2. EL is the trap lamp and C5 is.. 🔗 External reference
The described circuit operates through a systematic integration of its components, each serving a specific function to achieve the desired output. The power circuit is responsible for supplying the necessary voltage and current to the entire system. It incorporates a switch (S) for control, a fuse (FU) for protection against overcurrent conditions, and a transformer (TI) to step up or step down the voltage as required. The diodes (VD1-VD4) are configured for rectification, ensuring that the output is suitable for the following stages. Capacitors C1 and C3 filter the output to smooth out any voltage fluctuations, while IC1 serves as a control element, possibly functioning as a voltage regulator or an operational amplifier, depending on the circuit requirements. Resistor R1 limits the current to protect sensitive components, and VL indicates a load or visual indicator.
The pulse oscillator generates the necessary timing signals for the circuit's operation. It utilizes IC1, which may be a timer or oscillator IC, along with resistors R2 and R3 that set the frequency of oscillation. Potentiometer RP1 allows for adjustable frequency settings, providing flexibility in the circuit's operation. Capacitor C2 is crucial for determining the timing characteristics of the oscillator, influencing the pulse width and frequency.
The high voltage generator is designed to produce the elevated voltages required for the operation of the trap lamp (EL). This section includes two voltage sources (V1 and V2), which may be configured in series or parallel depending on the design requirements. Resistors RP2, RP3, R4, and R5 are used to control the voltage levels and current flow within this section, ensuring safety and efficiency. Transformer T2 is likely employed to step up the voltage to the required high levels for the trap lamp operation, enabling effective illumination.
Overall, this circuit is a well-structured assembly of components designed to perform a specific function, with each part contributing to the efficient generation and management of electrical energy.Working Principle: As seen in the figure 4-187, the circuit consists of power circuit, pulse oscillator and high voltage generator. The power circuit consists of S,FU,TI,VD1-VD4,C1,C3,IC1,R1 and VL. The pulse oscillator consists of IC1,R2,R3,RP1 and C2. The high voltage generator consists of V1,V2,RP2,RP3,R4,R5,T2. EL is the trap lamp and C5 is.. 🔗 External reference