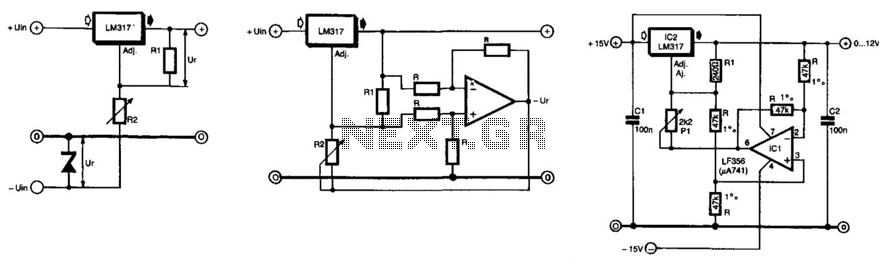
Electronic Thermostat Circuit
A diode, such as the IN4148, has a typical temperature coefficient of -2 mV/°C at a 1 mA diode current. Transistors Q1 and Q2 form a constant current source. Diode D1 serves as the temperature sensor. Integrated circuits ICl-a and ICl-b function as DC amplifiers, while ICl-c provides a temperature reference voltage supply. ICl-d operates as a comparator with variable hysteresis. Resistors R14, R15, and R16 are selected based on the desired thermostat range. Transistor Q3 acts as a relay driver (2N3904). The relay used should be capable of handling the load current, or an optoisolator and triac combination may be utilized.
The described circuit employs an IN4148 diode, which is characterized by its negative temperature coefficient, making it suitable for temperature sensing applications. The constant current source formed by transistors Q1 and Q2 ensures that the current flowing through the diode remains stable, allowing for accurate temperature readings. The output voltage from the diode, which varies with temperature, is amplified by the DC amplifiers ICl-a and ICl-b. The temperature reference voltage supplied by ICl-c is critical for establishing a baseline against which the temperature sensor's output can be compared.
ICl-d, functioning as a comparator, compares the amplified voltage from the temperature sensor against the reference voltage. The variable hysteresis implemented in the comparator helps to prevent oscillations in the output, ensuring stable operation when the temperature approaches the setpoint. The resistors R14, R15, and R16 are integral to setting the thresholds for the thermostat, allowing for customization based on the specific temperature range required for the application.
The relay driver Q3, utilizing a 2N3904 transistor, is responsible for activating the relay, which can control larger loads. It is essential that the relay is rated to handle the current requirements of the load it controls. Alternatively, for applications requiring electrical isolation and protection, an optoisolator paired with a triac can be employed, providing a robust solution for interfacing with high-power loads while maintaining safety and circuit integrity. This circuit design is particularly useful in temperature control systems, such as thermostats, where precise temperature regulation is necessary. A diode, such as a IN4148, has a typical -2m V/C temperature coefficient at a 1 mA diode current. Ql and Q2 form a constant current source. D1 is the temperature sensor. ICl-a and -b are dc amplifiers, with ICl-c a temperature reference voltage supply. ICl-d is a comparator with variable hysteresis. R14, R15, and R16 are chosen depending on the thermostat range desired. Q3 is a relay driver (2N3904). The relay used should handle the load current or an optoisolator triac combination can be used.
The described circuit employs an IN4148 diode, which is characterized by its negative temperature coefficient, making it suitable for temperature sensing applications. The constant current source formed by transistors Q1 and Q2 ensures that the current flowing through the diode remains stable, allowing for accurate temperature readings. The output voltage from the diode, which varies with temperature, is amplified by the DC amplifiers ICl-a and ICl-b. The temperature reference voltage supplied by ICl-c is critical for establishing a baseline against which the temperature sensor's output can be compared.
ICl-d, functioning as a comparator, compares the amplified voltage from the temperature sensor against the reference voltage. The variable hysteresis implemented in the comparator helps to prevent oscillations in the output, ensuring stable operation when the temperature approaches the setpoint. The resistors R14, R15, and R16 are integral to setting the thresholds for the thermostat, allowing for customization based on the specific temperature range required for the application.
The relay driver Q3, utilizing a 2N3904 transistor, is responsible for activating the relay, which can control larger loads. It is essential that the relay is rated to handle the current requirements of the load it controls. Alternatively, for applications requiring electrical isolation and protection, an optoisolator paired with a triac can be employed, providing a robust solution for interfacing with high-power loads while maintaining safety and circuit integrity. This circuit design is particularly useful in temperature control systems, such as thermostats, where precise temperature regulation is necessary. A diode, such as a IN4148, has a typical -2m V/C temperature coefficient at a 1 mA diode current. Ql and Q2 form a constant current source. D1 is the temperature sensor. ICl-a and -b are dc amplifiers, with ICl-c a temperature reference voltage supply. ICl-d is a comparator with variable hysteresis. R14, R15, and R16 are chosen depending on the thermostat range desired. Q3 is a relay driver (2N3904). The relay used should handle the load current or an optoisolator triac combination can be used.