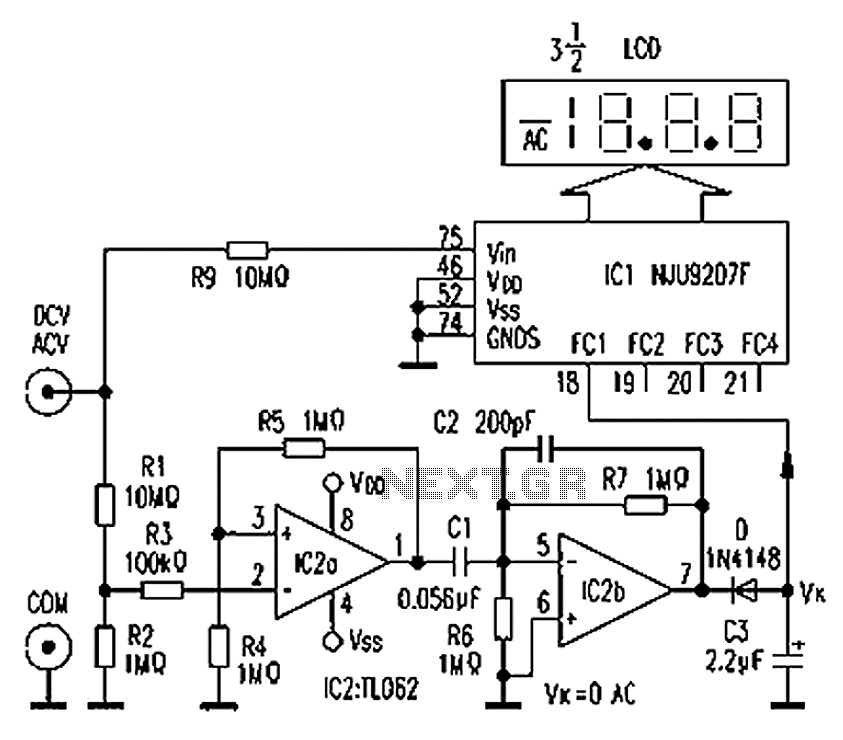
F/V Converter for Tachometer Bar Graph Display
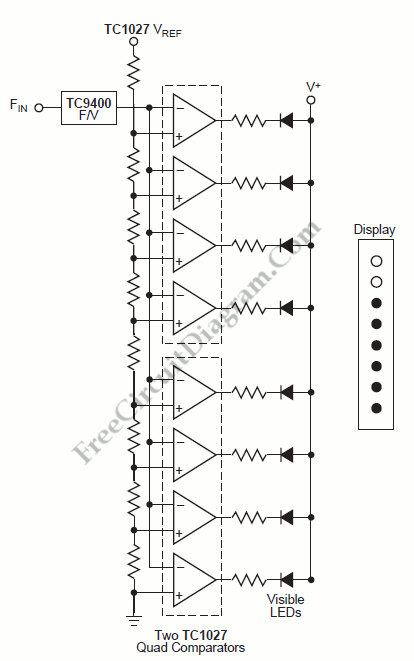
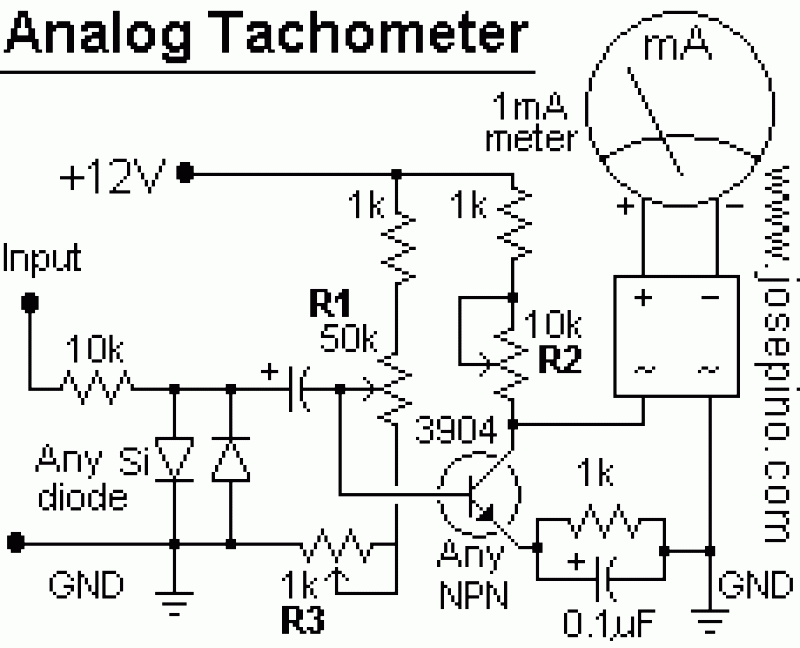
A tachometer can be constructed using the TC9400 in frequency-to-voltage (F/V) mode to convert frequency information (RPM) into a linearly proportional voltage. This voltage can then be compared to one of several comparators (in this example, using eight). The corresponding LED will illuminate and remain lit as long as the voltage exceeds the trip point of the comparator. This configuration will provide a bar-graph-type display, where the height of the bar is proportional to the RPM.
The TC9400 is a versatile integrated circuit designed for frequency-to-voltage conversion, making it suitable for tachometer applications. In this setup, the input frequency, representing the rotational speed of a motor or similar device, is fed into the TC9400. The circuit converts this frequency into a DC voltage that is directly proportional to the input frequency.
The output voltage from the TC9400 is then routed to a series of comparators. Each comparator is set to a specific voltage threshold, which corresponds to a certain RPM level. In this example, eight comparators are utilized, allowing for a range of RPM thresholds to be monitored. When the output voltage from the TC9400 exceeds the threshold voltage of a comparator, the corresponding LED indicator is activated. The arrangement of the LEDs creates a visual representation akin to a bar graph, where the number of illuminated LEDs indicates the current RPM level.
This design not only provides a clear visual display of RPM but also allows for quick interpretation of the data. The proportional relationship between the voltage output and RPM ensures that users can easily gauge the performance of the monitored device. Such a tachometer can be beneficial in various applications, including motor speed monitoring, automotive diagnostics, and industrial equipment control.
Overall, the combination of the TC9400 with comparators and LEDs offers a robust solution for RPM measurement, enabling effective monitoring and control of rotational speed in various electronic systems.We can construct a tachometer using the TC9400 in the F/V mode to convert the frequency information (RPM) into a linearly proportional voltage. Then we can compare this voltage to one of n comparators (on this example using 8). The respective LED lights up and will continue to stay lit as long as the voltage exceeds the trip point when he volta
ge exceed the trip point of comparator. This will give us a bar-graph-type display. The height of this bar is proportional to RPM. We aim to transmit more information by carrying articles. Please send us an E-mail to wanghuali@hqew. net within 15 days if we are involved in the problems of article content, copyright or other problems. We will delete it soon. 🔗 External reference
The TC9400 is a versatile integrated circuit designed for frequency-to-voltage conversion, making it suitable for tachometer applications. In this setup, the input frequency, representing the rotational speed of a motor or similar device, is fed into the TC9400. The circuit converts this frequency into a DC voltage that is directly proportional to the input frequency.
The output voltage from the TC9400 is then routed to a series of comparators. Each comparator is set to a specific voltage threshold, which corresponds to a certain RPM level. In this example, eight comparators are utilized, allowing for a range of RPM thresholds to be monitored. When the output voltage from the TC9400 exceeds the threshold voltage of a comparator, the corresponding LED indicator is activated. The arrangement of the LEDs creates a visual representation akin to a bar graph, where the number of illuminated LEDs indicates the current RPM level.
This design not only provides a clear visual display of RPM but also allows for quick interpretation of the data. The proportional relationship between the voltage output and RPM ensures that users can easily gauge the performance of the monitored device. Such a tachometer can be beneficial in various applications, including motor speed monitoring, automotive diagnostics, and industrial equipment control.
Overall, the combination of the TC9400 with comparators and LEDs offers a robust solution for RPM measurement, enabling effective monitoring and control of rotational speed in various electronic systems.We can construct a tachometer using the TC9400 in the F/V mode to convert the frequency information (RPM) into a linearly proportional voltage. Then we can compare this voltage to one of n comparators (on this example using 8). The respective LED lights up and will continue to stay lit as long as the voltage exceeds the trip point when he volta
ge exceed the trip point of comparator. This will give us a bar-graph-type display. The height of this bar is proportional to RPM. We aim to transmit more information by carrying articles. Please send us an E-mail to wanghuali@hqew. net within 15 days if we are involved in the problems of article content, copyright or other problems. We will delete it soon. 🔗 External reference