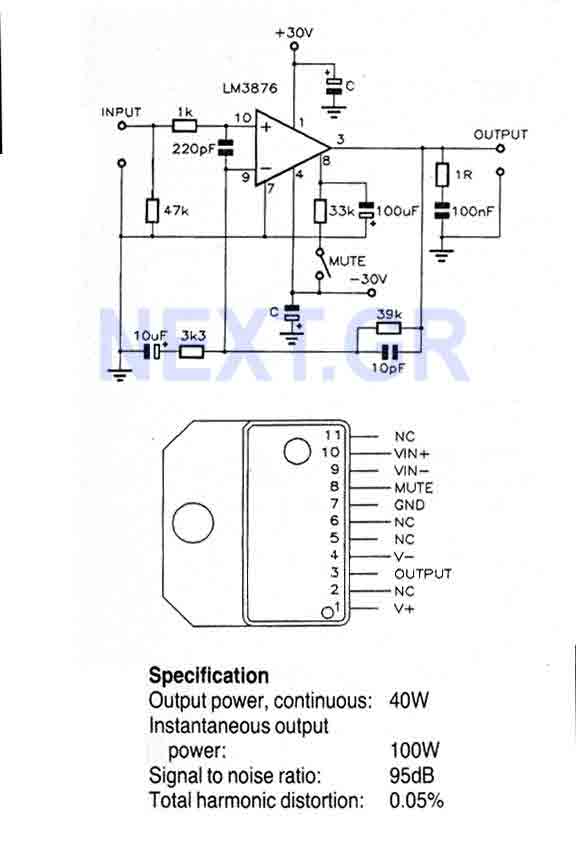
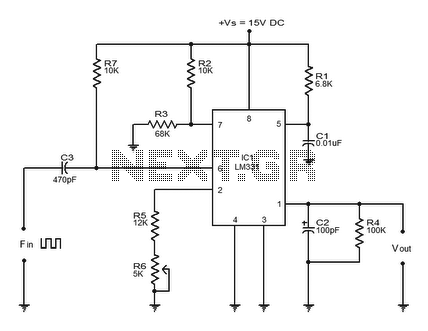
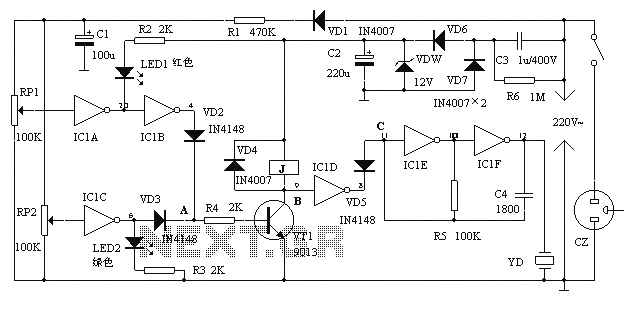
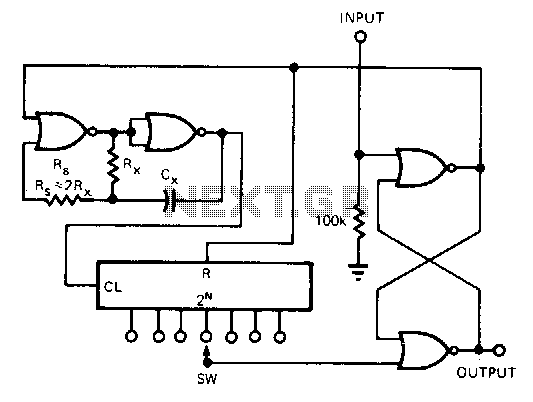
Fixed Voltage Power Supply
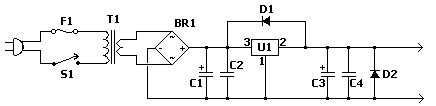
The fixed voltage power supply is useful in applications where an adjustable output is not required. This supply is simple, but very flexible as the voltage it outputs is dependent only on the regulator and transformer you choose. The maximum output current is 1.5A.
A fixed voltage power supply typically consists of several key components: a transformer, a rectifier, a filter capacitor, and a voltage regulator. The transformer steps down the input AC voltage to a lower AC voltage suitable for the desired output. The selection of the transformer is critical, as it determines the output voltage level based on the turns ratio.
Following the transformer, the rectifier converts the AC voltage to pulsating DC. A full-wave bridge rectifier is commonly used, as it provides better efficiency and smoother output compared to a half-wave rectifier. The rectifier consists of four diodes arranged in a bridge configuration, allowing current to flow through the load during both halves of the AC cycle.
The output from the rectifier is not suitable for most applications due to its ripple voltage. Therefore, a filter capacitor is employed to smooth out the pulsating DC voltage. The value of the capacitor is chosen based on the load current and the acceptable ripple voltage. Larger capacitance results in lower ripple but may increase the physical size and cost of the power supply.
The final stage is the voltage regulator, which ensures that the output voltage remains constant despite variations in load current or input voltage. Linear voltage regulators, such as the LM7812 for a 12V output, are often used for their simplicity and low noise. The regulator's output voltage is determined by its design, and the maximum output current is typically specified by the manufacturer—in this case, 1.5A.
Overall, this fixed voltage power supply design is straightforward and reliable, making it suitable for various applications where a constant voltage is essential.The fixed voltage power supply is useful in applications where an adjustable output is not required. This supply is simple, but very flexable as the voltage it outputs is dependant only on the regulator and transformer you choose. The maximum output current is 1.5A. 🔗 External reference
A fixed voltage power supply typically consists of several key components: a transformer, a rectifier, a filter capacitor, and a voltage regulator. The transformer steps down the input AC voltage to a lower AC voltage suitable for the desired output. The selection of the transformer is critical, as it determines the output voltage level based on the turns ratio.
Following the transformer, the rectifier converts the AC voltage to pulsating DC. A full-wave bridge rectifier is commonly used, as it provides better efficiency and smoother output compared to a half-wave rectifier. The rectifier consists of four diodes arranged in a bridge configuration, allowing current to flow through the load during both halves of the AC cycle.
The output from the rectifier is not suitable for most applications due to its ripple voltage. Therefore, a filter capacitor is employed to smooth out the pulsating DC voltage. The value of the capacitor is chosen based on the load current and the acceptable ripple voltage. Larger capacitance results in lower ripple but may increase the physical size and cost of the power supply.
The final stage is the voltage regulator, which ensures that the output voltage remains constant despite variations in load current or input voltage. Linear voltage regulators, such as the LM7812 for a 12V output, are often used for their simplicity and low noise. The regulator's output voltage is determined by its design, and the maximum output current is typically specified by the manufacturer—in this case, 1.5A.
Overall, this fixed voltage power supply design is straightforward and reliable, making it suitable for various applications where a constant voltage is essential.The fixed voltage power supply is useful in applications where an adjustable output is not required. This supply is simple, but very flexable as the voltage it outputs is dependant only on the regulator and transformer you choose. The maximum output current is 1.5A. 🔗 External reference