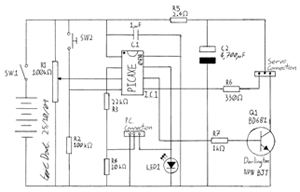
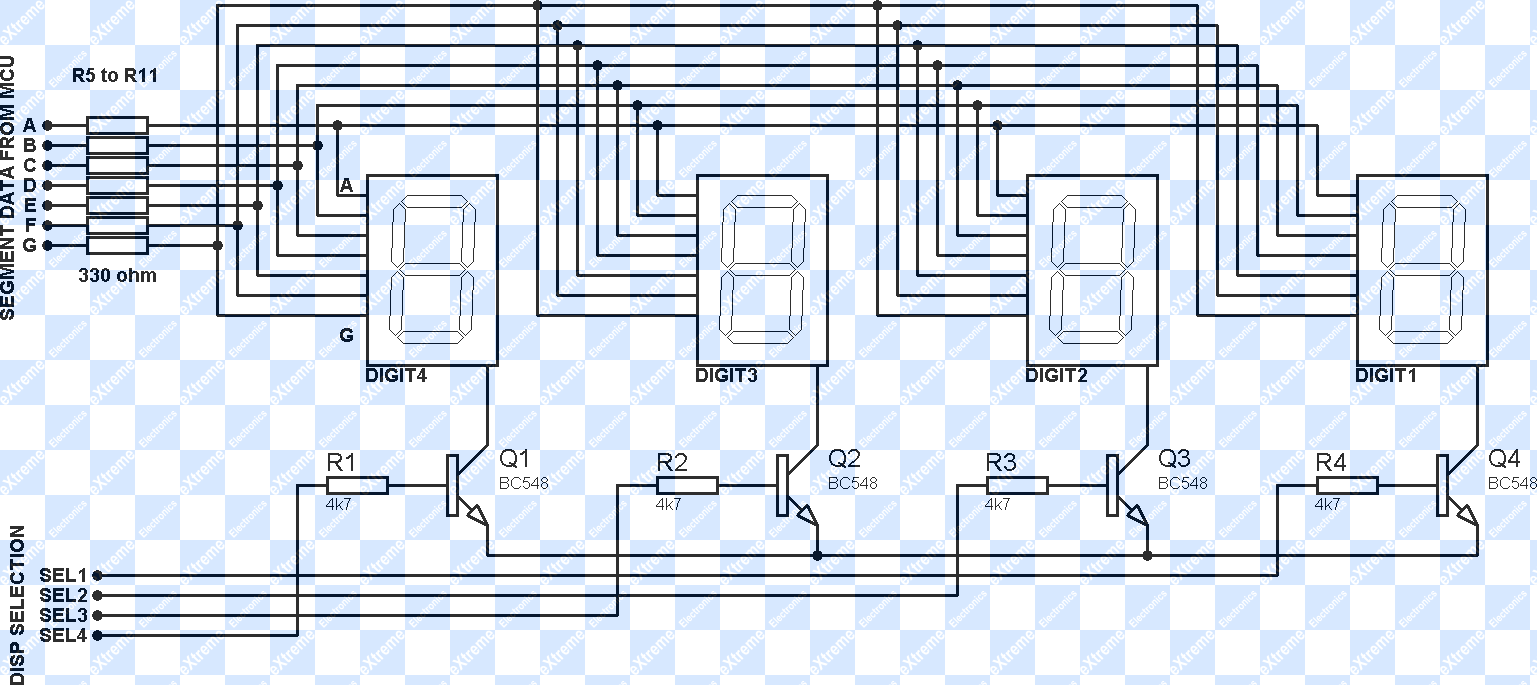
Flashing Led Controller
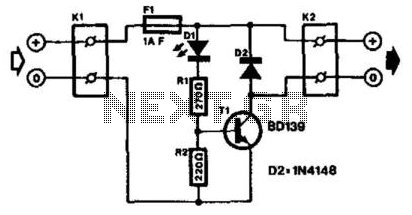
The LED with an integrated flasher is connected in series with the base-emitter junction of transistor T1. Consequently, the load connected to K2 is switched on and off in sync with the flash rate. This load can be a relay or a lamp. The maximum collector current of the transistor (BD139 = 750 mA) must not be exceeded. If this is insufficient, a power Darlington transistor can be employed, which can handle several amperes. The current drawn by the circuit under no-load conditions is 20 mA.
The described circuit utilizes an LED with an integrated flasher, which serves as a visual indicator while simultaneously controlling a load through a transistor switch. The LED is connected in series with the base-emitter junction of a bipolar junction transistor (BJT), specifically the BD139. This configuration allows the LED to modulate the transistor's operation, effectively switching the connected load on and off at a defined flash rate.
The load, which can either be a relay or a lamp, is connected to terminal K2. The operation of the load is directly influenced by the switching action of the transistor, which is driven by the LED's flashing. It is crucial to ensure that the collector current of the BD139 does not exceed its maximum rating of 750 mA. Should the application require a higher current capacity, a power Darlington transistor can be used as an alternative. Darlington transistors are known for their high current gain, allowing them to switch larger loads while maintaining a compact design.
Under no-load conditions, the circuit draws a current of 20 mA, which is relatively low, making it suitable for battery-operated devices or applications where power efficiency is essential. Proper consideration of the load's power requirements and the transistor's specifications will ensure reliable operation and longevity of the circuit. The LED with integrated flasher is connected in series with the base-emitter junction of transistor Tl. Thus, the l oad connected to K2 is switched on and off in rhythm with the flash rate. This load can be a relay or a lamp. The maximum collector current of the transistor (of the BD139 = 750 mA) must not be exceeded. If that is not sufficient, a power Darlington can be used, which will give some amperes. The current drawn by the circuit under no-load conditions amounts to 20 mA.
The described circuit utilizes an LED with an integrated flasher, which serves as a visual indicator while simultaneously controlling a load through a transistor switch. The LED is connected in series with the base-emitter junction of a bipolar junction transistor (BJT), specifically the BD139. This configuration allows the LED to modulate the transistor's operation, effectively switching the connected load on and off at a defined flash rate.
The load, which can either be a relay or a lamp, is connected to terminal K2. The operation of the load is directly influenced by the switching action of the transistor, which is driven by the LED's flashing. It is crucial to ensure that the collector current of the BD139 does not exceed its maximum rating of 750 mA. Should the application require a higher current capacity, a power Darlington transistor can be used as an alternative. Darlington transistors are known for their high current gain, allowing them to switch larger loads while maintaining a compact design.
Under no-load conditions, the circuit draws a current of 20 mA, which is relatively low, making it suitable for battery-operated devices or applications where power efficiency is essential. Proper consideration of the load's power requirements and the transistor's specifications will ensure reliable operation and longevity of the circuit. The LED with integrated flasher is connected in series with the base-emitter junction of transistor Tl. Thus, the l oad connected to K2 is switched on and off in rhythm with the flash rate. This load can be a relay or a lamp. The maximum collector current of the transistor (of the BD139 = 750 mA) must not be exceeded. If that is not sufficient, a power Darlington can be used, which will give some amperes. The current drawn by the circuit under no-load conditions amounts to 20 mA.