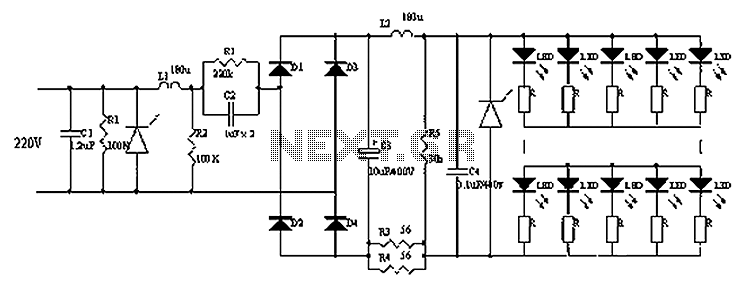
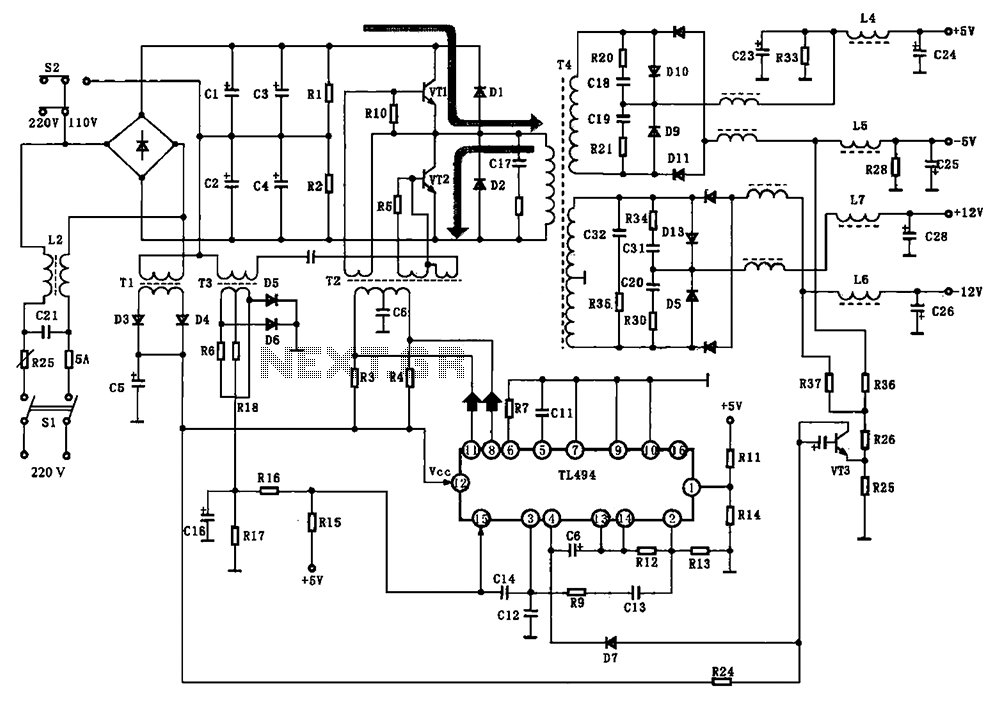
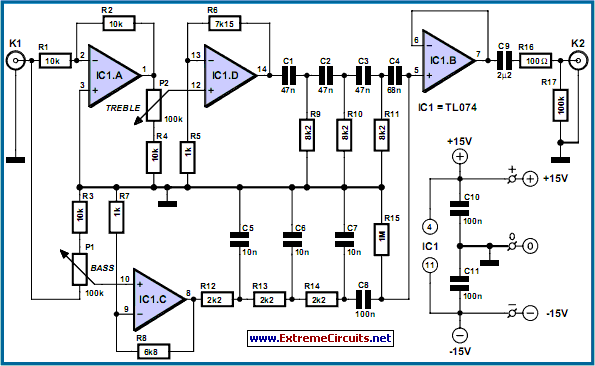
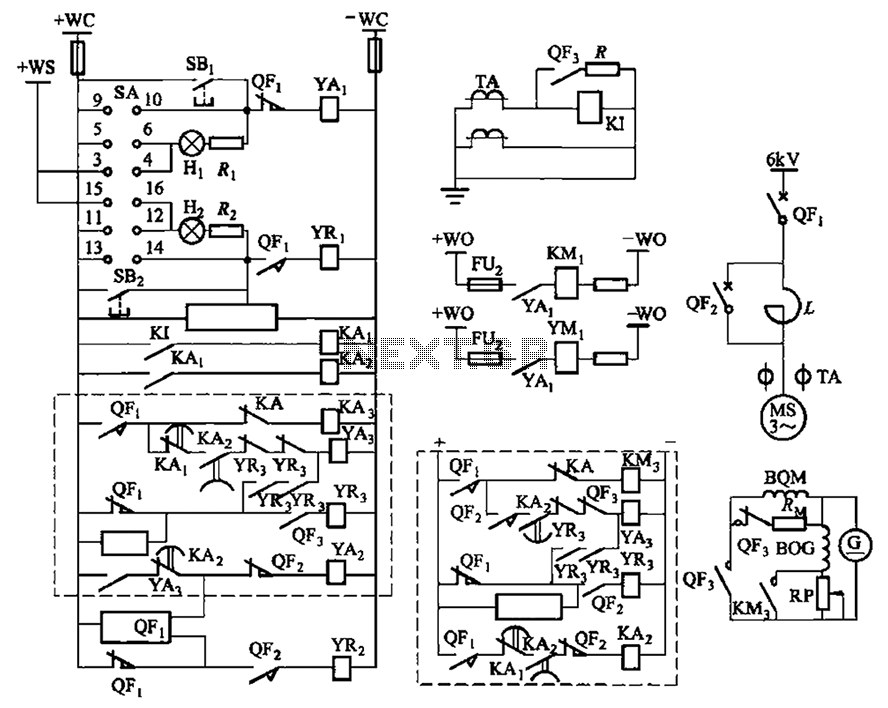
Flashing Light Circuit with Transistors
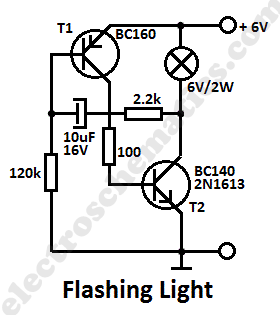
This simple flashing light circuit operates at 6 volts and 0.5A, exhibiting low current consumption when the light bulb is turned off. The frequency of the flashing is predetermined.
The circuit consists of a power supply, typically a battery or a DC adapter providing 6 volts, which feeds into a control mechanism that regulates the flashing of the light bulb. The primary components of this circuit include a timer IC, such as the 555 timer, configured in astable mode to generate a square wave output. This output is used to drive a transistor, which acts as a switch to control the light bulb.
When the circuit is powered, the 555 timer oscillates between its high and low states, causing the transistor to turn on and off rapidly. This switching action results in the light bulb flashing at a specific frequency, which can be adjusted by changing the resistor and capacitor values connected to the timer IC. The low current consumption when the light bulb is off is achieved by ensuring that the circuit enters a low-power state during the off phase, which minimizes power usage.
Additional components may include a diode for reverse polarity protection, ensuring that the circuit is not damaged if the power supply is connected incorrectly. A capacitor can also be placed across the power supply to filter out any noise, providing a stable voltage to the circuit. The entire assembly can be mounted on a PCB for ease of use and reliability, allowing for various applications such as decorative lighting, indicators, or signaling devices.This simple flashing light circuit is powered with 6 volts/0.5A and has a low current consumption when the light bulb is off. The flashing frequency is set.. 🔗 External reference
The circuit consists of a power supply, typically a battery or a DC adapter providing 6 volts, which feeds into a control mechanism that regulates the flashing of the light bulb. The primary components of this circuit include a timer IC, such as the 555 timer, configured in astable mode to generate a square wave output. This output is used to drive a transistor, which acts as a switch to control the light bulb.
When the circuit is powered, the 555 timer oscillates between its high and low states, causing the transistor to turn on and off rapidly. This switching action results in the light bulb flashing at a specific frequency, which can be adjusted by changing the resistor and capacitor values connected to the timer IC. The low current consumption when the light bulb is off is achieved by ensuring that the circuit enters a low-power state during the off phase, which minimizes power usage.
Additional components may include a diode for reverse polarity protection, ensuring that the circuit is not damaged if the power supply is connected incorrectly. A capacitor can also be placed across the power supply to filter out any noise, providing a stable voltage to the circuit. The entire assembly can be mounted on a PCB for ease of use and reliability, allowing for various applications such as decorative lighting, indicators, or signaling devices.This simple flashing light circuit is powered with 6 volts/0.5A and has a low current consumption when the light bulb is off. The flashing frequency is set.. 🔗 External reference