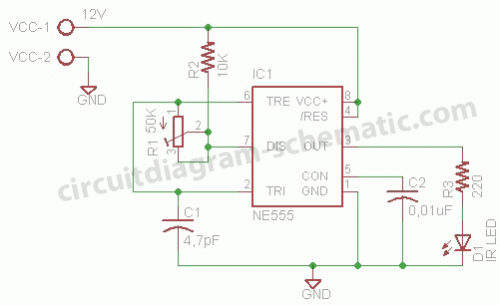
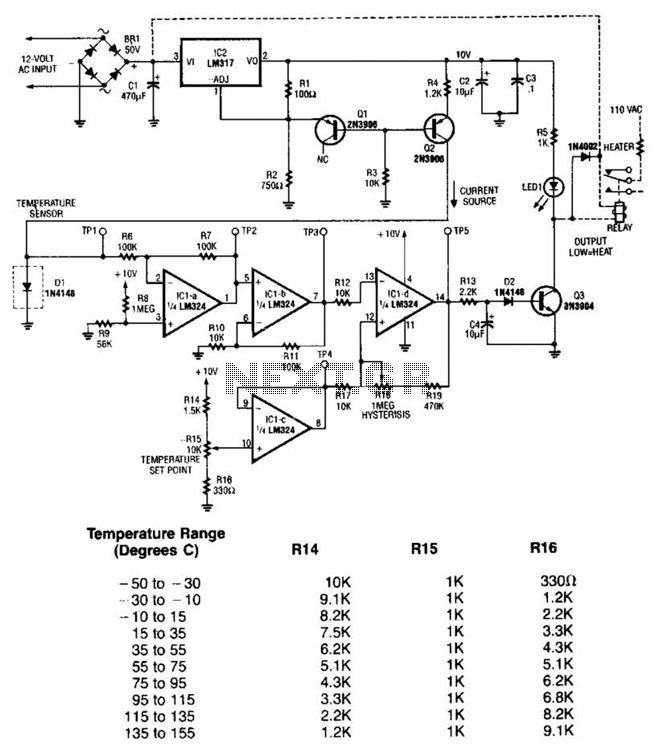
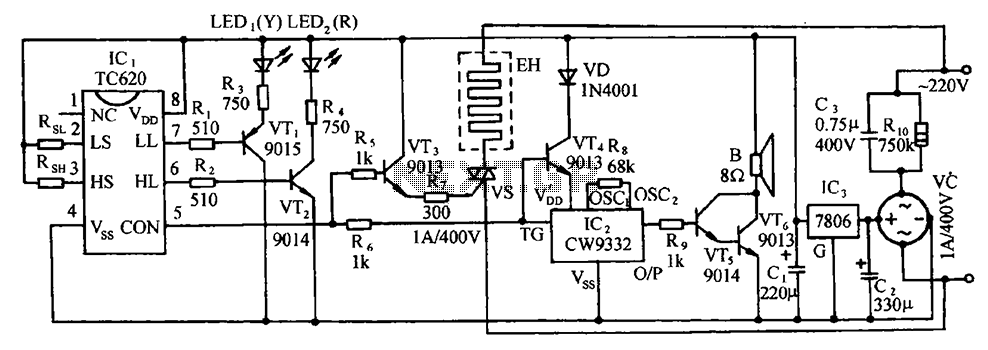
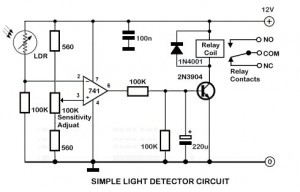
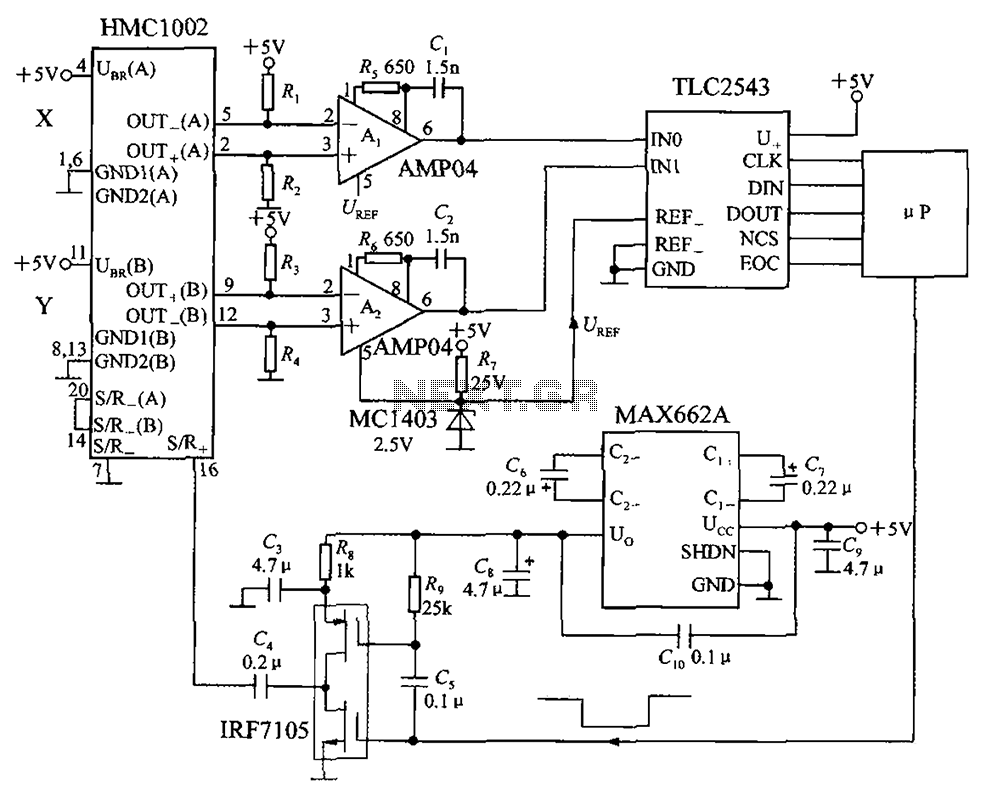
Fluid Sensor Limiter with MC14093B
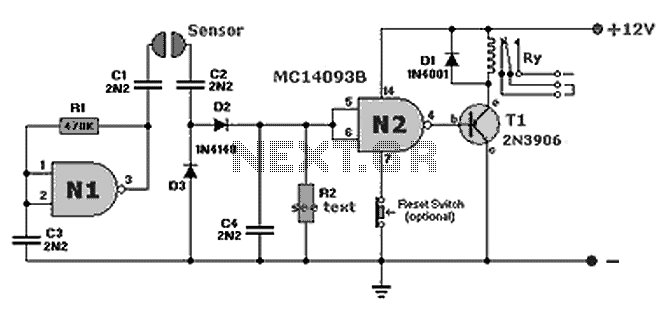
A compact fluid (water) sensor circuit that activates a relay for various applications. Additionally, a printed circuit board (PCB) is not necessary due to the small size of the circuit.
The fluid sensor circuit is designed to detect the presence of water and control a relay based on the sensor's output. This configuration is particularly useful in applications such as automatic irrigation systems, leak detection, and other scenarios where monitoring the presence of water is critical.
The core components of the circuit include a water sensor, a relay module, and a power supply. The water sensor typically consists of two conductive probes that detect the presence of water by measuring the conductivity between them. When water bridges the gap between the probes, the sensor outputs a signal that triggers the relay.
The relay serves as an electromechanical switch, allowing the circuit to control higher voltage devices, such as pumps or alarms, without exposing the low-voltage sensor directly to high currents. The relay coil is energized when the sensor detects water, closing the switch and activating the connected load.
Given the circuit's compact nature, it can be assembled on a small perfboard or directly soldered onto a minimal footprint, eliminating the need for a full PCB. This approach not only reduces material costs but also simplifies the assembly process, making it accessible for hobbyists and engineers alike.
For optimal performance, it is essential to ensure proper power supply ratings and to select a relay that can handle the load requirements of the application. Additionally, incorporating protective elements such as diodes across the relay coil can prevent back EMF from damaging the sensor or other components.
In summary, this fluid sensor circuit is an efficient solution for water detection and control, providing versatility in various applications while maintaining a compact and cost-effective design.A nice and small Fluid (water) sensor circuit that drives a relay for every use that comes to your head :) You do not need pcb because the circuit is to small. 🔗 External reference
The fluid sensor circuit is designed to detect the presence of water and control a relay based on the sensor's output. This configuration is particularly useful in applications such as automatic irrigation systems, leak detection, and other scenarios where monitoring the presence of water is critical.
The core components of the circuit include a water sensor, a relay module, and a power supply. The water sensor typically consists of two conductive probes that detect the presence of water by measuring the conductivity between them. When water bridges the gap between the probes, the sensor outputs a signal that triggers the relay.
The relay serves as an electromechanical switch, allowing the circuit to control higher voltage devices, such as pumps or alarms, without exposing the low-voltage sensor directly to high currents. The relay coil is energized when the sensor detects water, closing the switch and activating the connected load.
Given the circuit's compact nature, it can be assembled on a small perfboard or directly soldered onto a minimal footprint, eliminating the need for a full PCB. This approach not only reduces material costs but also simplifies the assembly process, making it accessible for hobbyists and engineers alike.
For optimal performance, it is essential to ensure proper power supply ratings and to select a relay that can handle the load requirements of the application. Additionally, incorporating protective elements such as diodes across the relay coil can prevent back EMF from damaging the sensor or other components.
In summary, this fluid sensor circuit is an efficient solution for water detection and control, providing versatility in various applications while maintaining a compact and cost-effective design.A nice and small Fluid (water) sensor circuit that drives a relay for every use that comes to your head :) You do not need pcb because the circuit is to small. 🔗 External reference