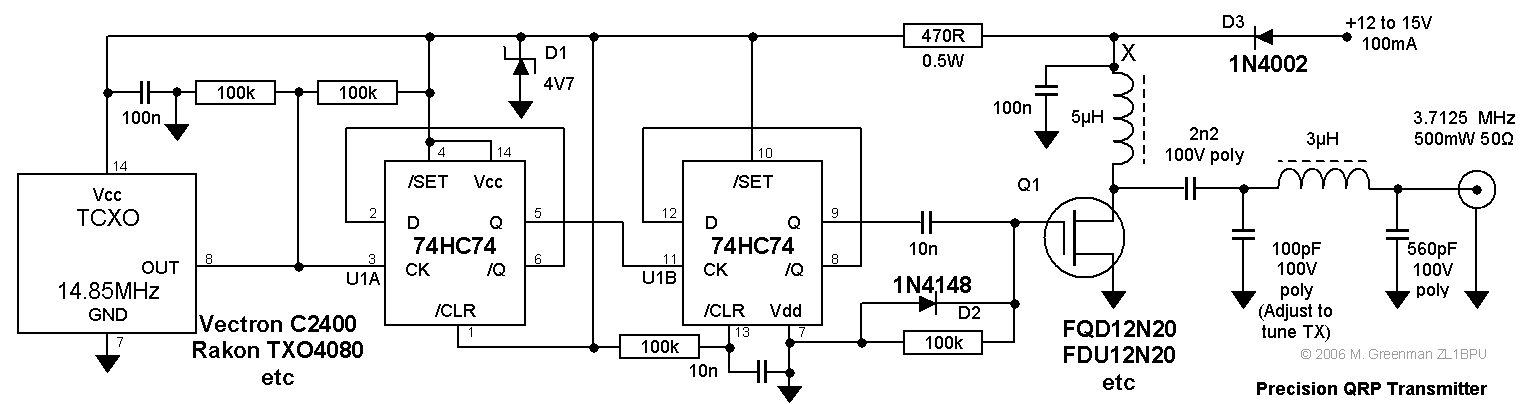
fm transmitter
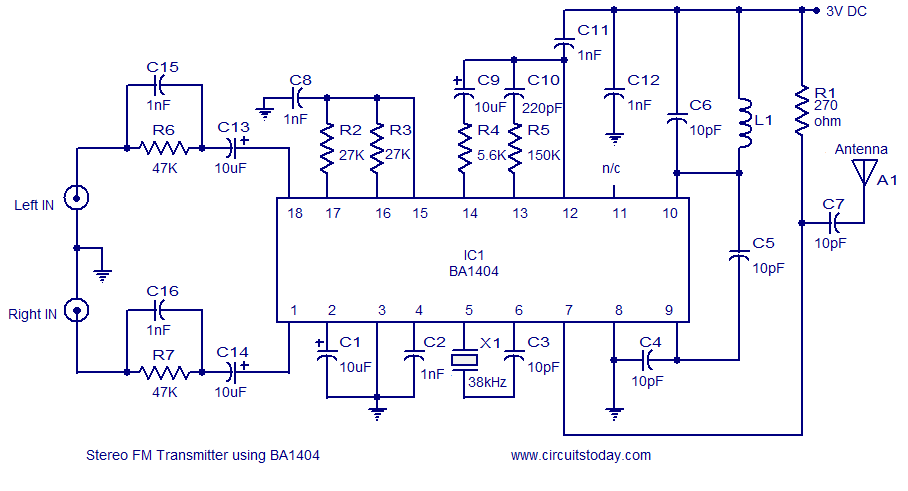
The first resistor on the left in the schematic is labeled as 68k. This value may change based on the microphone used. In this instance, a microphone from Digi-Key with a 1.5k output impedance was utilized, leading to the selection of a 1.5k resistor instead of the original 68k.
The circuit design incorporates a microphone with a specific output impedance, which is critical for ensuring optimal performance and signal integrity. The original schematic specifies a resistor value of 68k ohms, which is typically chosen to match the characteristics of certain microphones. However, in this implementation, a microphone with a lower output impedance of 1.5k ohms was selected. This necessitates the use of a 1.5k resistor to maintain proper impedance matching within the circuit.
Impedance matching is crucial in audio applications to minimize reflections and maximize power transfer between the microphone and subsequent stages of the circuit, such as amplifiers or signal processors. The choice of a 1.5k resistor in place of the 68k ensures that the microphone's output is effectively coupled to the input of the following stage, providing a balanced and clear audio signal.
In addition to the resistor, the schematic may include other components such as capacitors for AC coupling and power supply decoupling, which further enhance the performance of the microphone circuit. Proper layout and grounding techniques should also be considered to reduce noise and interference, ensuring high-quality audio capture.The first resistor on the left in the schematic says 68k. This will vary depending the the microphone. In our case we used a microphone from digikey with a 1. 5k output impedance, so we matched it with a 1. 5k resistor instead of using a 68k. 🔗 External reference
The circuit design incorporates a microphone with a specific output impedance, which is critical for ensuring optimal performance and signal integrity. The original schematic specifies a resistor value of 68k ohms, which is typically chosen to match the characteristics of certain microphones. However, in this implementation, a microphone with a lower output impedance of 1.5k ohms was selected. This necessitates the use of a 1.5k resistor to maintain proper impedance matching within the circuit.
Impedance matching is crucial in audio applications to minimize reflections and maximize power transfer between the microphone and subsequent stages of the circuit, such as amplifiers or signal processors. The choice of a 1.5k resistor in place of the 68k ensures that the microphone's output is effectively coupled to the input of the following stage, providing a balanced and clear audio signal.
In addition to the resistor, the schematic may include other components such as capacitors for AC coupling and power supply decoupling, which further enhance the performance of the microphone circuit. Proper layout and grounding techniques should also be considered to reduce noise and interference, ensuring high-quality audio capture.The first resistor on the left in the schematic says 68k. This will vary depending the the microphone. In our case we used a microphone from digikey with a 1. 5k output impedance, so we matched it with a 1. 5k resistor instead of using a 68k. 🔗 External reference