Four-Input Minimum Maximum Selector Circuit
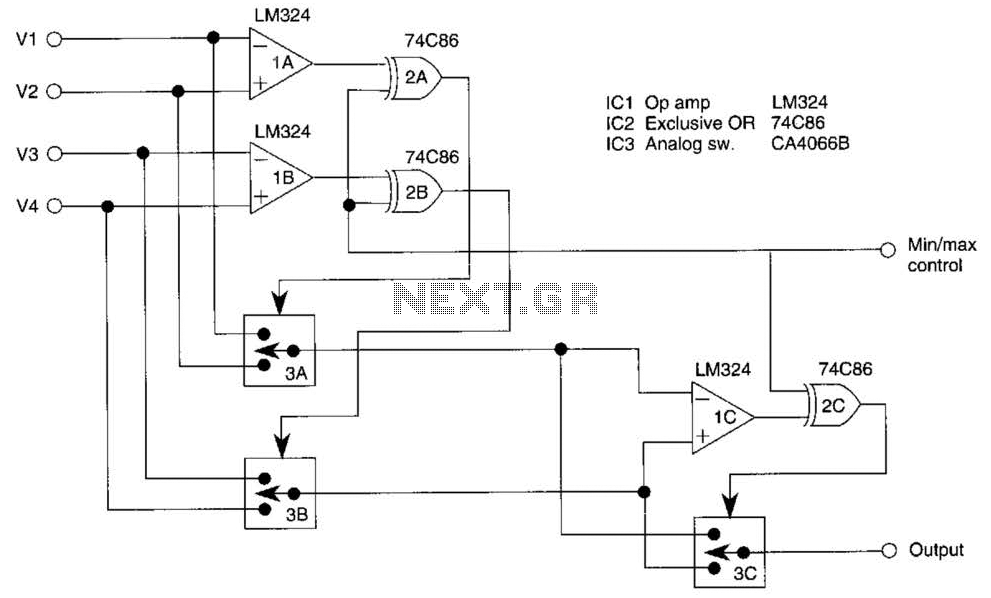
This circuit outputs the maximum or minimum of four input voltages, V1, V2, V3, and V4. Each of these input voltages ranges from 0 to 5 V. The output of the circuit is the maximum of V1, V2, V3, and V4 when the control voltage input is 5 V (logical 1). Conversely, the output is the minimum of V1, V2, V3, and V4 when the control input is 0 V. By cascading multiple such units, it is possible to select the maximum or minimum of 3N + 1 input voltages. Therefore, if k represents the number of input voltages, [(/k + 1)/3] units are required.
This circuit operates as a voltage selector, utilizing a combination of comparators and multiplexers to determine either the maximum or minimum value among the provided inputs. The four input voltages, V1 through V4, are fed into a series of operational amplifiers configured as comparators. These comparators compare the input voltages against each other and produce a binary output indicating which voltage is higher or lower based on the control voltage.
When the control voltage is set to 5 V, the circuit prioritizes finding the maximum voltage. This is achieved through the use of a priority encoder, which selects the highest voltage from the inputs. The output is then sent to a buffer to ensure that the signal can drive subsequent stages without degradation.
In the case where the control voltage is 0 V, the circuit switches its function to find the minimum voltage. This is accomplished by inverting the logic of the comparators or by using additional circuitry to ensure that the lowest voltage is selected and outputted.
The cascading capability of the circuit allows for the extension of its functionality. By connecting multiple units, it becomes feasible to handle a larger number of input voltages, adhering to the formula of 3N + 1, where N is the number of cascaded units. This modular approach enables flexibility in design, accommodating various applications where maximum or minimum voltage selection is critical, such as in analog signal processing, sensor data handling, or automated control systems.
In practical implementations, careful consideration must be given to the power supply, grounding, and layout of the circuit to minimize noise and ensure stability. Additionally, the selection of components such as operational amplifiers and multiplexers should be done based on their specifications to maintain performance across the desired voltage range. This circuit outputs the maximum (or the minimum) of the four input voltages Vv V2, V3, and V4. Each of these input voltages is in the range 0 to 5 V. The output of the unit is the maximum of Vv V2, V3, and V4 if the control voltage input is 5 V (i.e., logical 1). The output is the minimum of Vv V2, V3, and V4 if the control input is zero. By cascading TV such units, one can select the maximum (or the minimum) of 3N + 1 input voltages. Thus if k is the number of input voltages, we need [(/c+l)/3] units.
This circuit operates as a voltage selector, utilizing a combination of comparators and multiplexers to determine either the maximum or minimum value among the provided inputs. The four input voltages, V1 through V4, are fed into a series of operational amplifiers configured as comparators. These comparators compare the input voltages against each other and produce a binary output indicating which voltage is higher or lower based on the control voltage.
When the control voltage is set to 5 V, the circuit prioritizes finding the maximum voltage. This is achieved through the use of a priority encoder, which selects the highest voltage from the inputs. The output is then sent to a buffer to ensure that the signal can drive subsequent stages without degradation.
In the case where the control voltage is 0 V, the circuit switches its function to find the minimum voltage. This is accomplished by inverting the logic of the comparators or by using additional circuitry to ensure that the lowest voltage is selected and outputted.
The cascading capability of the circuit allows for the extension of its functionality. By connecting multiple units, it becomes feasible to handle a larger number of input voltages, adhering to the formula of 3N + 1, where N is the number of cascaded units. This modular approach enables flexibility in design, accommodating various applications where maximum or minimum voltage selection is critical, such as in analog signal processing, sensor data handling, or automated control systems.
In practical implementations, careful consideration must be given to the power supply, grounding, and layout of the circuit to minimize noise and ensure stability. Additionally, the selection of components such as operational amplifiers and multiplexers should be done based on their specifications to maintain performance across the desired voltage range. This circuit outputs the maximum (or the minimum) of the four input voltages Vv V2, V3, and V4. Each of these input voltages is in the range 0 to 5 V. The output of the unit is the maximum of Vv V2, V3, and V4 if the control voltage input is 5 V (i.e., logical 1). The output is the minimum of Vv V2, V3, and V4 if the control input is zero. By cascading TV such units, one can select the maximum (or the minimum) of 3N + 1 input voltages. Thus if k is the number of input voltages, we need [(/c+l)/3] units.