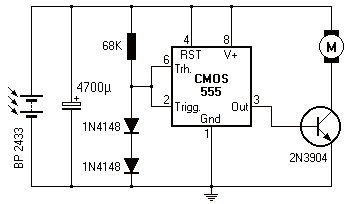
Gasoline engine tachometer
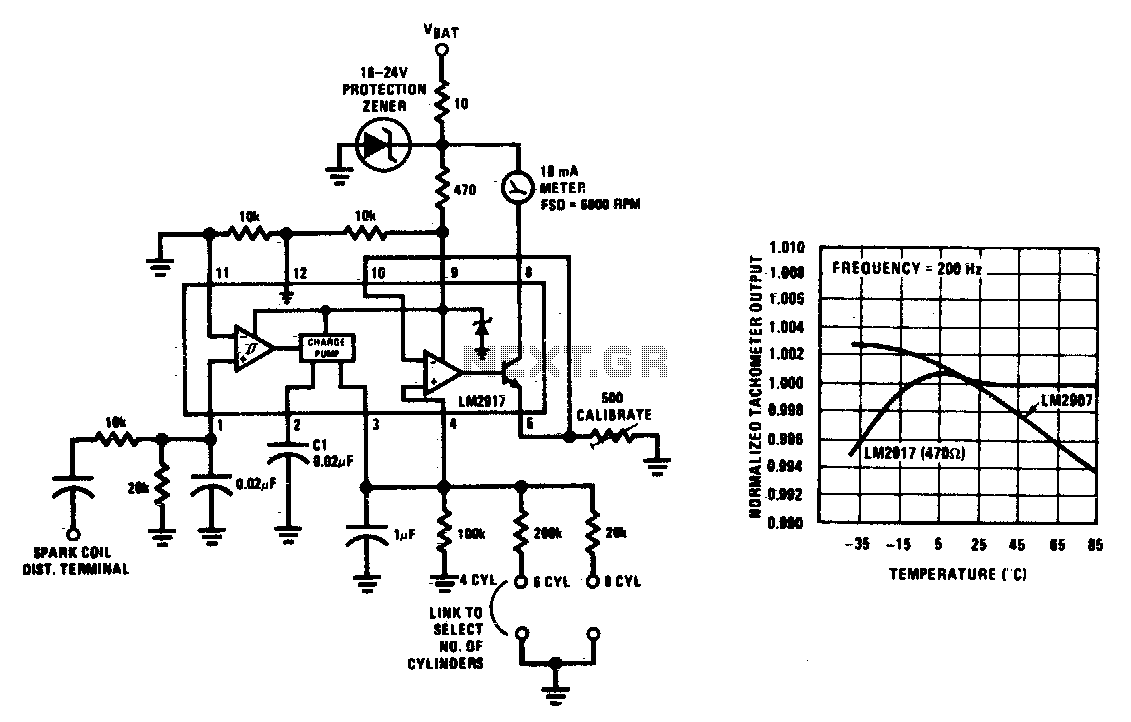
This tachometer can be configured for any number of cylinders by connecting the appropriate timing resistor as illustrated. A 500-ohm trim resistor can be utilized for final calibration. Additionally, a protection circuit consisting of a 10-ohm resistor and a Zener diode is included as a safety measure against transients commonly found in automobiles.
The tachometer circuit is designed to accurately measure the rotational speed of an engine, providing critical information for performance monitoring and diagnostics. The configuration allows for flexibility in the number of engine cylinders, which is essential for compatibility with various vehicle types. By selecting the correct timing resistor, the tachometer can be tailored to the specific engine configuration, ensuring precise readings.
The inclusion of a 500-ohm trim resistor serves as a calibration tool, allowing for fine-tuning of the output signal. This adjustment is crucial for achieving accurate RPM readings, as variations in engine characteristics can affect the tachometer's performance. The calibration process typically involves adjusting the trim resistor while monitoring the output to match the expected RPM values.
Furthermore, the protection circuit enhances the reliability of the tachometer by safeguarding it against electrical transients. The 10-ohm resistor limits the current flowing through the circuit, while the Zener diode provides a voltage clamping mechanism. This combination protects sensitive components from voltage spikes that can occur in automotive environments, thereby extending the lifespan and functionality of the tachometer.
Overall, this tachometer design integrates flexibility, precision calibration, and robust protection features, making it suitable for various automotive applications.This tachometer can be set up for any number of cylinders by linking the appropriate timing resistor as illustrated. A 500 ohm trim resistor can be used to set up final calibration A protection circuit composed of a 10 ohm resistor and a zener diode is also shown as a safety precaution against the transients which are to be found in automobiles.
The tachometer circuit is designed to accurately measure the rotational speed of an engine, providing critical information for performance monitoring and diagnostics. The configuration allows for flexibility in the number of engine cylinders, which is essential for compatibility with various vehicle types. By selecting the correct timing resistor, the tachometer can be tailored to the specific engine configuration, ensuring precise readings.
The inclusion of a 500-ohm trim resistor serves as a calibration tool, allowing for fine-tuning of the output signal. This adjustment is crucial for achieving accurate RPM readings, as variations in engine characteristics can affect the tachometer's performance. The calibration process typically involves adjusting the trim resistor while monitoring the output to match the expected RPM values.
Furthermore, the protection circuit enhances the reliability of the tachometer by safeguarding it against electrical transients. The 10-ohm resistor limits the current flowing through the circuit, while the Zener diode provides a voltage clamping mechanism. This combination protects sensitive components from voltage spikes that can occur in automotive environments, thereby extending the lifespan and functionality of the tachometer.
Overall, this tachometer design integrates flexibility, precision calibration, and robust protection features, making it suitable for various automotive applications.This tachometer can be set up for any number of cylinders by linking the appropriate timing resistor as illustrated. A 500 ohm trim resistor can be used to set up final calibration A protection circuit composed of a 10 ohm resistor and a zener diode is also shown as a safety precaution against the transients which are to be found in automobiles.