Headlight delay unit
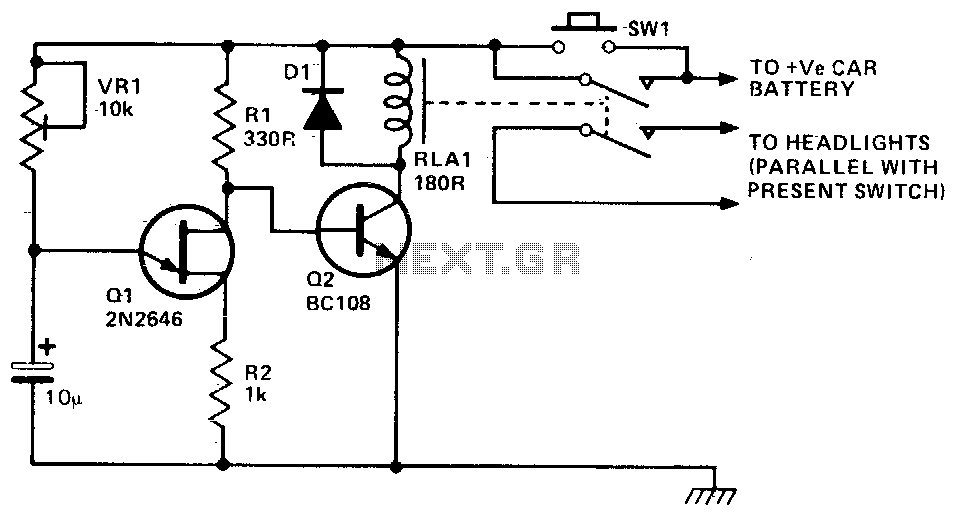
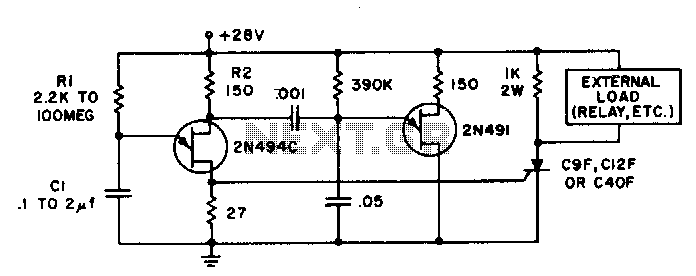
This circuit operates a car's headlights for a predetermined duration to illuminate the driveway or path after the driver has exited the vehicle. When the switch (SQ1) is activated, transistor Q2 is turned on, closing the relay and powering the car's headlights. Capacitor C1 begins to charge through variable resistor VR1 until transistor Q1 activates, which then turns off Q2. Subsequently, the relay opens, switching off both the headlights and the circuit. The delay is determined by the charging time of the capacitor, approximately one minute.
This circuit employs a simple timer mechanism utilizing a relay, transistors, and a capacitor to manage the operation of the car's headlights post-exit. The primary components include a relay for controlling the high-current headlights, and two transistors (Q1 and Q2) that function as electronic switches.
When the driver exits the vehicle and presses the switch SQ1, it triggers Q2, allowing current to flow through the relay coil. This energizes the relay, which closes its contacts and connects the car's headlights to the power supply, thereby illuminating the area. The use of a relay is crucial here, as it can handle the higher current required by the headlights without putting excessive load on the transistors.
Capacitor C1 plays a pivotal role in the timing aspect of the circuit. Initially, when SQ1 is pressed, C1 begins to charge through the variable resistor VR1, which allows for adjustment of the delay duration. The charging time of C1 determines how long the headlights remain on after the relay is activated. Once C1 reaches a certain voltage threshold, it activates Q1. This, in turn, turns off Q2, de-energizing the relay and opening its contacts, thus cutting power to the headlights.
The design allows for a customizable delay through the adjustment of VR1, making it adaptable to various user preferences. The circuit is efficient and reliable, providing a practical solution for enhancing safety and convenience when exiting a vehicle at night. Proper consideration should be given to the ratings of the components, particularly the relay and transistors, to ensure they can handle the expected load and operate within safe limits.This circuit will operate a car"s headlights for a predetermined time to light up the driveway or path after the driver has left the car. SQl is pushed and Q2 is turned on closing the relay and turning on the car"s headlights. Cl begins to charge through VR1 until Q1 turns on, turning Q2 off The relay will then open switching off both the lights and the unit. The delay is governed by the time taken for the capacitor to charge, which is about one minute.
This circuit employs a simple timer mechanism utilizing a relay, transistors, and a capacitor to manage the operation of the car's headlights post-exit. The primary components include a relay for controlling the high-current headlights, and two transistors (Q1 and Q2) that function as electronic switches.
When the driver exits the vehicle and presses the switch SQ1, it triggers Q2, allowing current to flow through the relay coil. This energizes the relay, which closes its contacts and connects the car's headlights to the power supply, thereby illuminating the area. The use of a relay is crucial here, as it can handle the higher current required by the headlights without putting excessive load on the transistors.
Capacitor C1 plays a pivotal role in the timing aspect of the circuit. Initially, when SQ1 is pressed, C1 begins to charge through the variable resistor VR1, which allows for adjustment of the delay duration. The charging time of C1 determines how long the headlights remain on after the relay is activated. Once C1 reaches a certain voltage threshold, it activates Q1. This, in turn, turns off Q2, de-energizing the relay and opening its contacts, thus cutting power to the headlights.
The design allows for a customizable delay through the adjustment of VR1, making it adaptable to various user preferences. The circuit is efficient and reliable, providing a practical solution for enhancing safety and convenience when exiting a vehicle at night. Proper consideration should be given to the ratings of the components, particularly the relay and transistors, to ensure they can handle the expected load and operate within safe limits.This circuit will operate a car"s headlights for a predetermined time to light up the driveway or path after the driver has left the car. SQl is pushed and Q2 is turned on closing the relay and turning on the car"s headlights. Cl begins to charge through VR1 until Q1 turns on, turning Q2 off The relay will then open switching off both the lights and the unit. The delay is governed by the time taken for the capacitor to charge, which is about one minute.