High-Power Car Audio Amplifier
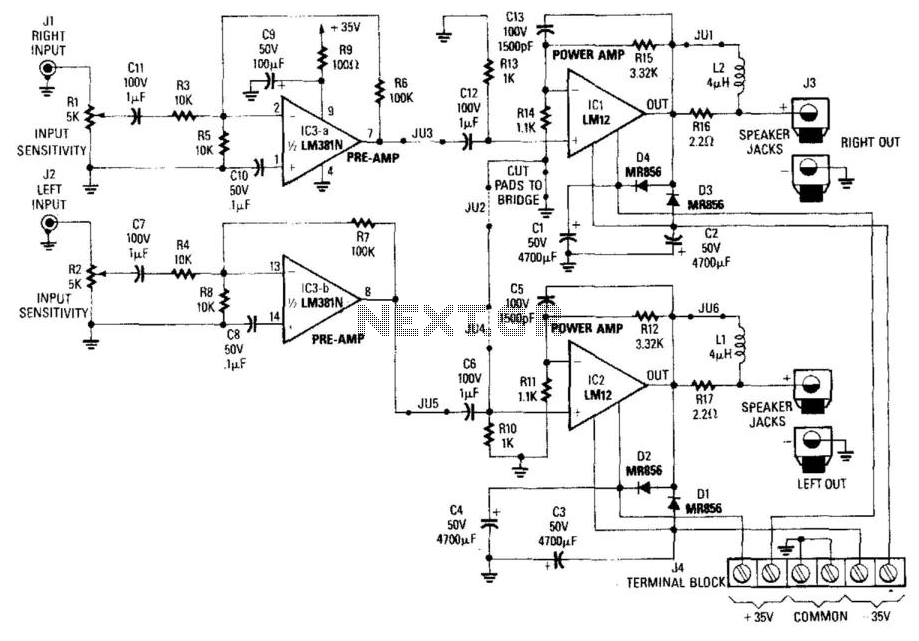
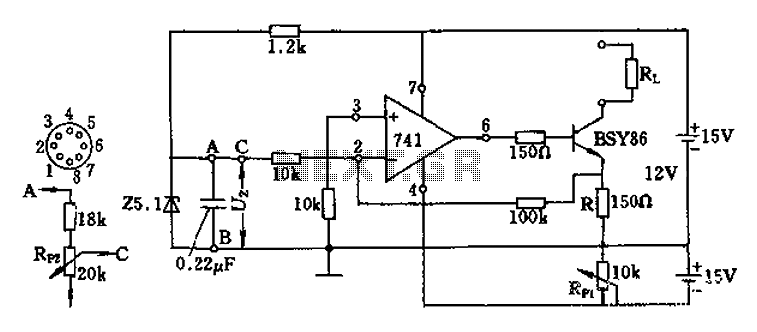
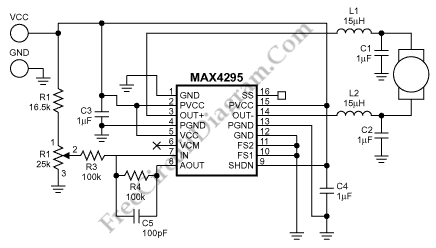
Note for bridge configuration: 1. Install jumpers JU2 and JU4. 2. Remove J1. 3. Remove RIO. 4. Replace R13 with a jumper wire. 5. Replace R15 with a 4.53 kΩ, 1% resistor. 6. Replace R14 with a 13 kΩ, 1% resistor. 7. Cut the foil between pads from RH and ground. 8. The input becomes the left channel input. 9. Take the output from the left output. 10. Take the output from the right output. This stereo amplifier will supply 60 W RMS into 8 ohms or 100 W RMS into 4 ohms. Notice that the LM12C1 requires a line level of about 300 mV. A ±35 V supply is required for full power output. Power can be obtained from a DC-DC converter.
The circuit described pertains to a stereo amplifier with a bridge configuration. The setup requires specific modifications to optimize performance and ensure proper functionality. The installation of jumpers JU2 and JU4 is necessary to enable the bridge mode, which enhances the amplifier's power output capabilities. The removal of J1 and RIO is a crucial step in configuring the circuit for bridge operation.
Resistor modifications include replacing R13 with a jumper wire, which effectively bypasses that component, and substituting R15 with a 4.53 kΩ, 1% tolerance resistor. Additionally, R14 should be replaced with a 13 kΩ, 1% tolerance resistor, ensuring precise resistance values are maintained for stability and performance. The instruction to cut the foil between the pads from RH and ground is essential for isolating the circuit paths, preventing unintended connections that could lead to performance degradation.
The input configuration transforms into the left channel input, which is critical for stereo sound separation. Outputs from both the left and right channels are specified, allowing for a balanced audio performance. This amplifier is capable of delivering 60 W RMS into an 8-ohm load and 100 W RMS into a 4-ohm load, making it suitable for various audio applications.
The LM12C1 operational amplifier requires a line level input of approximately 300 mV for optimal performance. For full power output, a dual polarity supply of ±35 V is necessary. This power supply can be obtained using a DC-DC converter, which can efficiently convert available voltage levels to meet the amplifier's requirements. Overall, this configuration and the specified components ensure robust audio amplification suited for high-fidelity applications. NOTE: FOR BRIDGE CONFIGURATION: t install jumpers ju2 and ju4 2.remove j 1)3 3.remove rio 4replace r13 with jumper wire 5replace ri5 with 4.53k ohm 1% 6. replace r14 with 1 13k ohm 1% 7 cut foil between pads from rh and ground 8.input becomes left channel input 9.take ( output from left output 10 takf output from right output This stereo amp will supply 60 W rms into 8 or 100 W rms into 4 . Notice that the LM12C1 line level (about 300 mV) into 5 . A ±35-V supply is required for full power output. Power can be obtained from a dc-dc converter.
The circuit described pertains to a stereo amplifier with a bridge configuration. The setup requires specific modifications to optimize performance and ensure proper functionality. The installation of jumpers JU2 and JU4 is necessary to enable the bridge mode, which enhances the amplifier's power output capabilities. The removal of J1 and RIO is a crucial step in configuring the circuit for bridge operation.
Resistor modifications include replacing R13 with a jumper wire, which effectively bypasses that component, and substituting R15 with a 4.53 kΩ, 1% tolerance resistor. Additionally, R14 should be replaced with a 13 kΩ, 1% tolerance resistor, ensuring precise resistance values are maintained for stability and performance. The instruction to cut the foil between the pads from RH and ground is essential for isolating the circuit paths, preventing unintended connections that could lead to performance degradation.
The input configuration transforms into the left channel input, which is critical for stereo sound separation. Outputs from both the left and right channels are specified, allowing for a balanced audio performance. This amplifier is capable of delivering 60 W RMS into an 8-ohm load and 100 W RMS into a 4-ohm load, making it suitable for various audio applications.
The LM12C1 operational amplifier requires a line level input of approximately 300 mV for optimal performance. For full power output, a dual polarity supply of ±35 V is necessary. This power supply can be obtained using a DC-DC converter, which can efficiently convert available voltage levels to meet the amplifier's requirements. Overall, this configuration and the specified components ensure robust audio amplification suited for high-fidelity applications. NOTE: FOR BRIDGE CONFIGURATION: t install jumpers ju2 and ju4 2.remove j 1)3 3.remove rio 4replace r13 with jumper wire 5replace ri5 with 4.53k ohm 1% 6. replace r14 with 1 13k ohm 1% 7 cut foil between pads from rh and ground 8.input becomes left channel input 9.take ( output from left output 10 takf output from right output This stereo amp will supply 60 W rms into 8 or 100 W rms into 4 . Notice that the LM12C1 line level (about 300 mV) into 5 . A ±35-V supply is required for full power output. Power can be obtained from a dc-dc converter.