High Voltage Converter Circuit
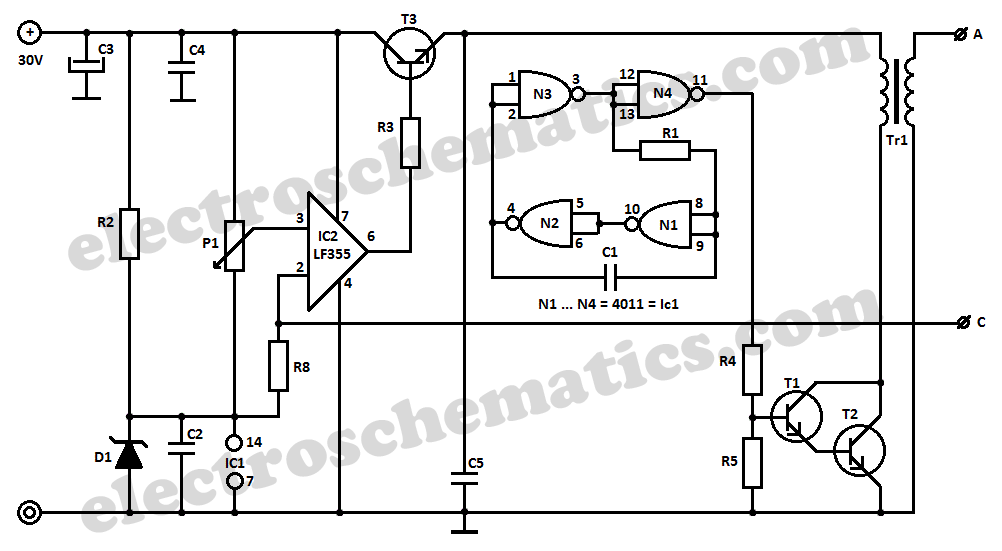
This high voltage converter circuit operates from a 30-volt power supply and can output a voltage ranging from 0 to 3 kV in version 1 or from 0 to 10 kV in version 2.
The high voltage converter circuit is designed to efficiently step up the input voltage from a standard 30-volt power supply to significantly higher output levels, specifically 0 to 3 kV for version 1 and 0 to 10 kV for version 2. The circuit typically employs a transformer-based architecture or a switched-mode power supply (SMPS) topology to achieve this voltage conversion.
In version 1, the output voltage is regulated using a feedback mechanism that monitors the output and adjusts the duty cycle of the switching element, ensuring stable operation across varying load conditions. The transformer in this version is designed to handle high voltages and is insulated appropriately to prevent arcing or breakdown.
Version 2, capable of delivering up to 10 kV, may utilize a more robust transformer with enhanced insulation and possibly additional stages of voltage multiplication to achieve the higher output. Safety features are critical in this version, including over-voltage protection, current limiting, and thermal shutdown mechanisms to prevent damage to the circuit or connected loads.
The circuit may also incorporate additional components such as high-voltage capacitors, diodes rated for high voltage, and adequate filtering to smooth the output voltage and reduce ripple. Proper layout and grounding techniques are essential to minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI) and ensure the safety and reliability of the high voltage output.
This converter circuit finds applications in various fields, including industrial equipment, scientific research, and medical devices, where high voltage is required for specific processes such as particle acceleration, x-ray generation, or electrostatic applications.Starting from a 30 volt power supply this high voltage converter circuit can deliver a voltage between 0 to 3 kV (version 1) or from 0 to 10 kV (version 2).. 🔗 External reference
The high voltage converter circuit is designed to efficiently step up the input voltage from a standard 30-volt power supply to significantly higher output levels, specifically 0 to 3 kV for version 1 and 0 to 10 kV for version 2. The circuit typically employs a transformer-based architecture or a switched-mode power supply (SMPS) topology to achieve this voltage conversion.
In version 1, the output voltage is regulated using a feedback mechanism that monitors the output and adjusts the duty cycle of the switching element, ensuring stable operation across varying load conditions. The transformer in this version is designed to handle high voltages and is insulated appropriately to prevent arcing or breakdown.
Version 2, capable of delivering up to 10 kV, may utilize a more robust transformer with enhanced insulation and possibly additional stages of voltage multiplication to achieve the higher output. Safety features are critical in this version, including over-voltage protection, current limiting, and thermal shutdown mechanisms to prevent damage to the circuit or connected loads.
The circuit may also incorporate additional components such as high-voltage capacitors, diodes rated for high voltage, and adequate filtering to smooth the output voltage and reduce ripple. Proper layout and grounding techniques are essential to minimize electromagnetic interference (EMI) and ensure the safety and reliability of the high voltage output.
This converter circuit finds applications in various fields, including industrial equipment, scientific research, and medical devices, where high voltage is required for specific processes such as particle acceleration, x-ray generation, or electrostatic applications.Starting from a 30 volt power supply this high voltage converter circuit can deliver a voltage between 0 to 3 kV (version 1) or from 0 to 10 kV (version 2).. 🔗 External reference