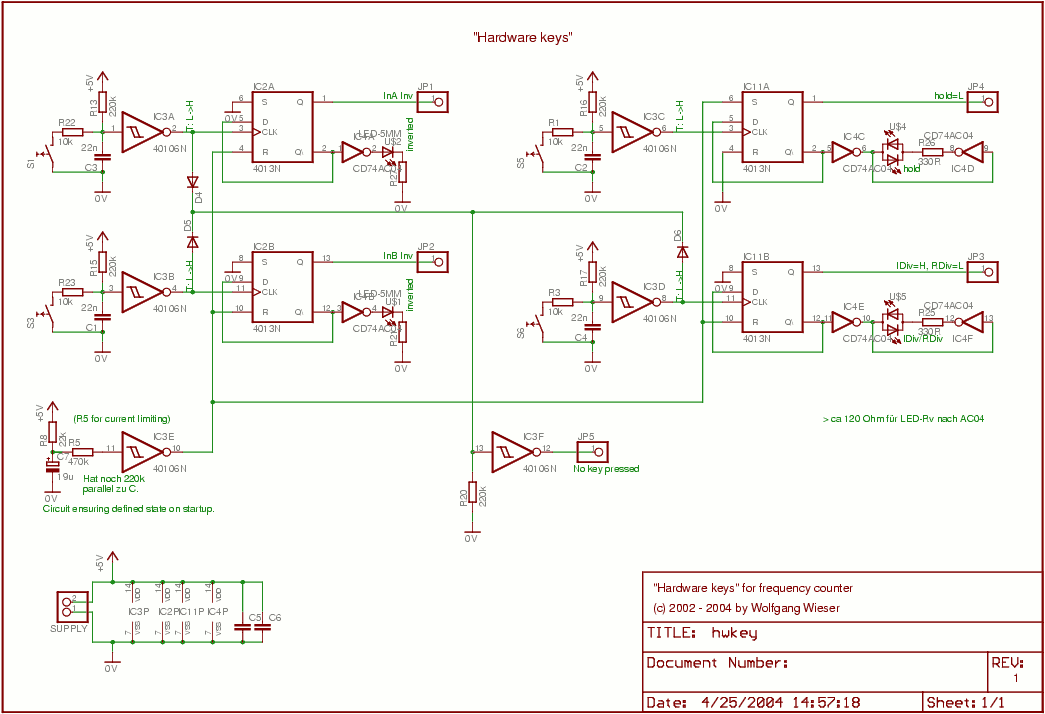
High voltage geiger counter supply
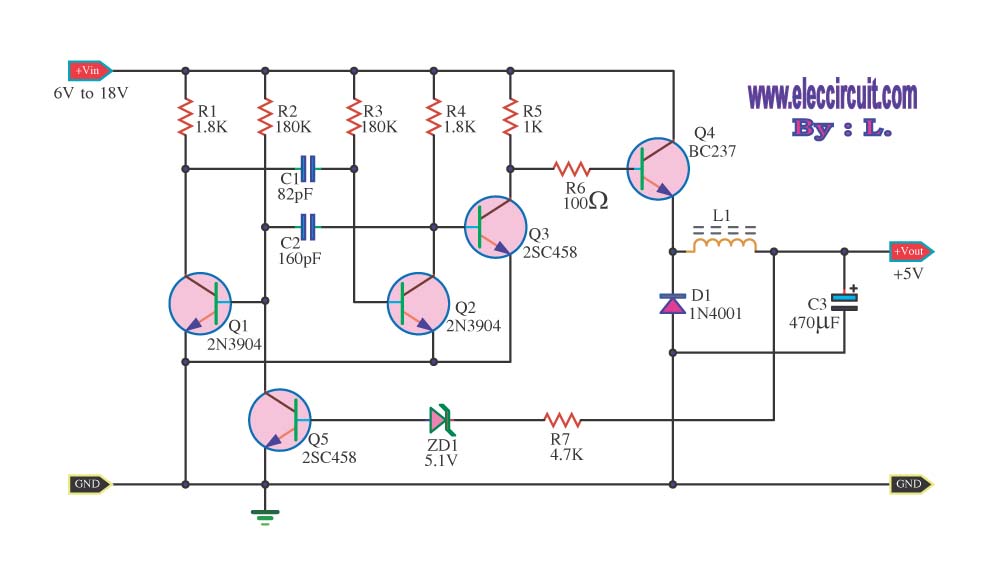
This circuit will generate approximately 300 volts DC at a very low current, sufficient for a GM tube. Caution is advised with the output.
The described circuit is a high-voltage DC power supply designed to provide approximately 300 volts, which is a typical requirement for Geiger-Müller (GM) tubes used in radiation detection applications. The circuit operates at a very low current, ensuring that the power output is adequate for the GM tube's operation without risking damage to the tube or the circuit itself.
The essential components of this circuit typically include a transformer, a rectifier, and a voltage regulation stage. The transformer steps up the input voltage to a higher AC voltage level before it is converted to DC. A full-wave rectifier configuration, often utilizing diodes, is employed to convert the AC output from the transformer into DC voltage.
To ensure the output voltage remains stable at 300 volts, a voltage regulation mechanism may be implemented. This could involve using zener diodes or a series of capacitors and resistors to filter and smooth the rectified voltage. Additionally, safety features such as a fuse or circuit breaker may be included to protect against overcurrent conditions.
It is crucial to handle this circuit with care due to the high voltage output, which poses a significant risk of electric shock. Proper insulation, secure connections, and the use of protective enclosures are recommended to minimize hazards during operation. Furthermore, users should be aware of the circuit's limitations, particularly the low current output, which may restrict its use to specific applications within the field of radiation detection.This circuit will generate about 300 volts dc—at a very low current, but enough for a GM tube. be careful with the output.
The described circuit is a high-voltage DC power supply designed to provide approximately 300 volts, which is a typical requirement for Geiger-Müller (GM) tubes used in radiation detection applications. The circuit operates at a very low current, ensuring that the power output is adequate for the GM tube's operation without risking damage to the tube or the circuit itself.
The essential components of this circuit typically include a transformer, a rectifier, and a voltage regulation stage. The transformer steps up the input voltage to a higher AC voltage level before it is converted to DC. A full-wave rectifier configuration, often utilizing diodes, is employed to convert the AC output from the transformer into DC voltage.
To ensure the output voltage remains stable at 300 volts, a voltage regulation mechanism may be implemented. This could involve using zener diodes or a series of capacitors and resistors to filter and smooth the rectified voltage. Additionally, safety features such as a fuse or circuit breaker may be included to protect against overcurrent conditions.
It is crucial to handle this circuit with care due to the high voltage output, which poses a significant risk of electric shock. Proper insulation, secure connections, and the use of protective enclosures are recommended to minimize hazards during operation. Furthermore, users should be aware of the circuit's limitations, particularly the low current output, which may restrict its use to specific applications within the field of radiation detection.This circuit will generate about 300 volts dc—at a very low current, but enough for a GM tube. be careful with the output.