High Voltage Solid State Flyback Driver
Fully illustrated and schematized plans for a high-performance, easy-to-build transistorized high voltage flyback driver.
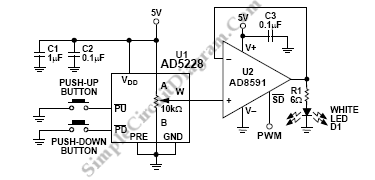
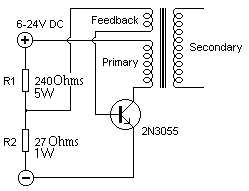
The high voltage flyback driver circuit is designed to efficiently convert low voltage DC into high voltage pulses suitable for driving flyback transformers. The circuit typically utilizes a transistor as the main switching element, which is responsible for rapidly turning the current on and off in the primary winding of the flyback transformer.
To construct this circuit, essential components include a high-voltage flyback transformer, a suitable N-channel MOSFET or BJT transistor, resistors for current limiting, capacitors for filtering, and diodes for flyback protection. The transistor operates in a switching mode, allowing for rapid energy storage in the transformer’s magnetic field during the on-state and releasing it as high voltage during the off-state.
The schematic representation of the circuit will include the power supply input, the transistor with its gate/base drive circuitry, the flyback transformer, and the output stage. The design should incorporate feedback mechanisms to ensure stable operation and prevent over-voltage conditions, which can damage the components.
Additionally, the flyback driver may feature a snubber circuit to protect against voltage spikes and improve efficiency. The layout should be carefully designed to minimize parasitic inductances and capacitances, which can adversely affect performance. Proper heat dissipation methods, such as heat sinks or cooling fans, should also be considered to maintain the operational integrity of the transistor during high-frequency switching.
Overall, this high voltage flyback driver circuit is an effective solution for applications requiring high voltage generation, such as in CRT displays, gas tube lighting, or high-voltage ignition systems.Fully illustrated and schematised plans for a high performance, easy to build transistorised high voltage flyback driver.. 🔗 External reference
The high voltage flyback driver circuit is designed to efficiently convert low voltage DC into high voltage pulses suitable for driving flyback transformers. The circuit typically utilizes a transistor as the main switching element, which is responsible for rapidly turning the current on and off in the primary winding of the flyback transformer.
To construct this circuit, essential components include a high-voltage flyback transformer, a suitable N-channel MOSFET or BJT transistor, resistors for current limiting, capacitors for filtering, and diodes for flyback protection. The transistor operates in a switching mode, allowing for rapid energy storage in the transformer’s magnetic field during the on-state and releasing it as high voltage during the off-state.
The schematic representation of the circuit will include the power supply input, the transistor with its gate/base drive circuitry, the flyback transformer, and the output stage. The design should incorporate feedback mechanisms to ensure stable operation and prevent over-voltage conditions, which can damage the components.
Additionally, the flyback driver may feature a snubber circuit to protect against voltage spikes and improve efficiency. The layout should be carefully designed to minimize parasitic inductances and capacitances, which can adversely affect performance. Proper heat dissipation methods, such as heat sinks or cooling fans, should also be considered to maintain the operational integrity of the transistor during high-frequency switching.
Overall, this high voltage flyback driver circuit is an effective solution for applications requiring high voltage generation, such as in CRT displays, gas tube lighting, or high-voltage ignition systems.Fully illustrated and schematised plans for a high performance, easy to build transistorised high voltage flyback driver.. 🔗 External reference