How does an astable multivibrator LED blinking circuit work
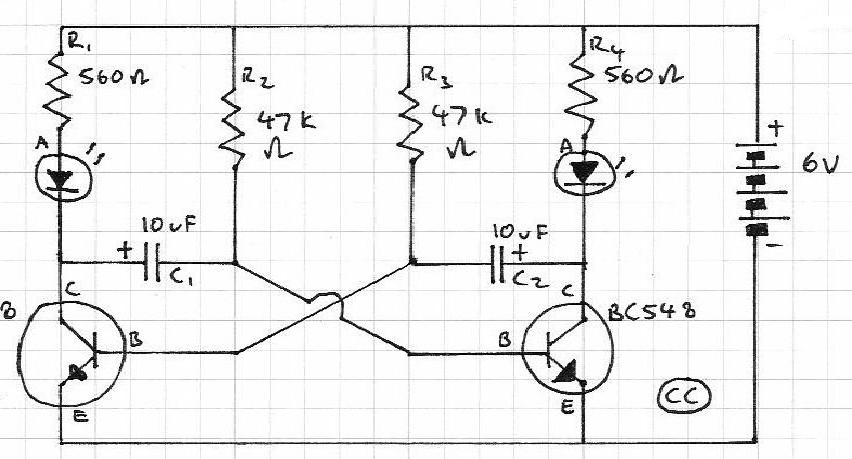
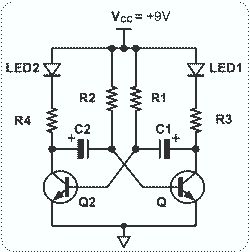
Blinks 2 LEDs in sequence. An explanation of its operation is requested. It is understood that a capacitor charges, causing the LED to turn off, and when it discharges, the LED turns on. However, clarification on the purpose of the transistors is needed.
The circuit described involves a sequential LED blinking mechanism, which can be achieved through a simple astable multivibrator configuration using transistors. The primary components typically include two light-emitting diodes (LEDs), a capacitor, resistors, and two NPN transistors.
In this configuration, the capacitor is crucial for timing. When the circuit is powered, the capacitor begins to charge through a resistor. This charging process causes the voltage across the capacitor to rise gradually. Once the voltage reaches a certain threshold, it turns on the first NPN transistor, allowing current to flow through the first LED, causing it to illuminate.
As the capacitor continues to charge, it eventually reaches a point where it can no longer sustain the first transistor's conduction, causing the transistor to turn off. This results in the first LED turning off. The discharge path for the capacitor is typically through the second transistor, which is connected in such a way that when the first transistor turns off, the second one turns on, allowing current to flow through the second LED.
The timing of the LED blinking is determined by the values of the resistors and the capacitor used in the circuit. By adjusting these components, one can control the rate at which the LEDs blink in sequence. The transistors serve as electronic switches that control the flow of current to each LED based on the charge state of the capacitor, thereby enabling the sequential blinking effect. This arrangement not only provides a visual indication of the circuit's operation but also serves as a fundamental demonstration of capacitor charging and discharging principles in electronics.Blinks 2 LEDs timely in sequence. Will somebody explain its working I know that capacitor will charge and during the charging the LED will off and whenthey discharge they will on the LED. But why transistor are there 🔗 External reference
The circuit described involves a sequential LED blinking mechanism, which can be achieved through a simple astable multivibrator configuration using transistors. The primary components typically include two light-emitting diodes (LEDs), a capacitor, resistors, and two NPN transistors.
In this configuration, the capacitor is crucial for timing. When the circuit is powered, the capacitor begins to charge through a resistor. This charging process causes the voltage across the capacitor to rise gradually. Once the voltage reaches a certain threshold, it turns on the first NPN transistor, allowing current to flow through the first LED, causing it to illuminate.
As the capacitor continues to charge, it eventually reaches a point where it can no longer sustain the first transistor's conduction, causing the transistor to turn off. This results in the first LED turning off. The discharge path for the capacitor is typically through the second transistor, which is connected in such a way that when the first transistor turns off, the second one turns on, allowing current to flow through the second LED.
The timing of the LED blinking is determined by the values of the resistors and the capacitor used in the circuit. By adjusting these components, one can control the rate at which the LEDs blink in sequence. The transistors serve as electronic switches that control the flow of current to each LED based on the charge state of the capacitor, thereby enabling the sequential blinking effect. This arrangement not only provides a visual indication of the circuit's operation but also serves as a fundamental demonstration of capacitor charging and discharging principles in electronics.Blinks 2 LEDs timely in sequence. Will somebody explain its working I know that capacitor will charge and during the charging the LED will off and whenthey discharge they will on the LED. But why transistor are there 🔗 External reference