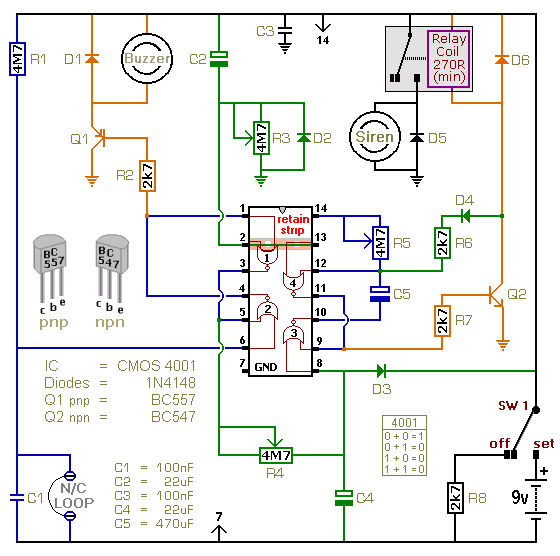
how to make car battery charger
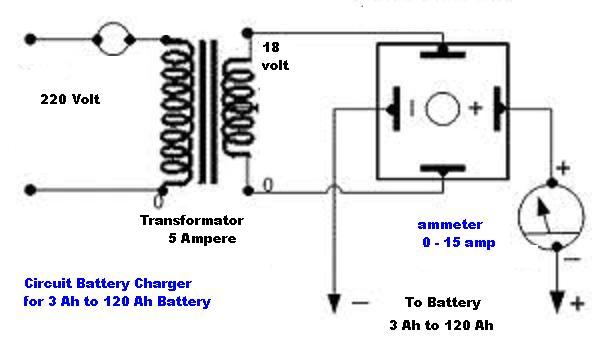
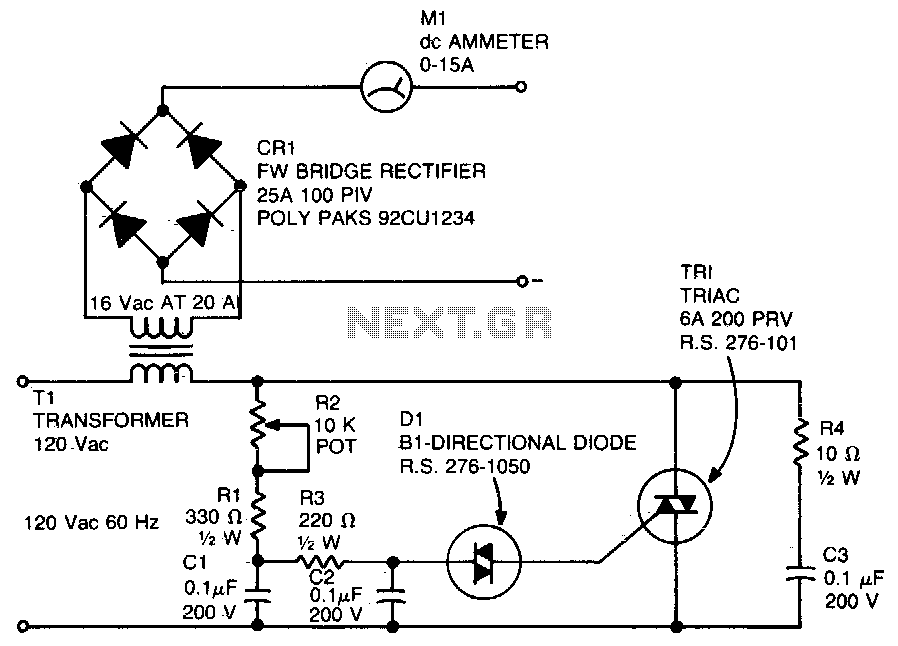
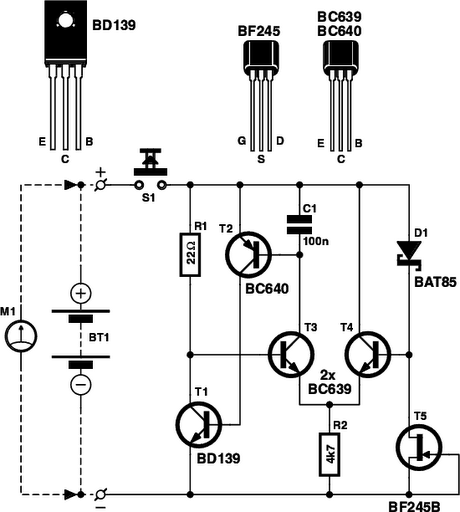
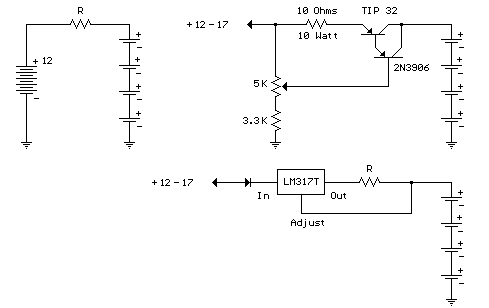
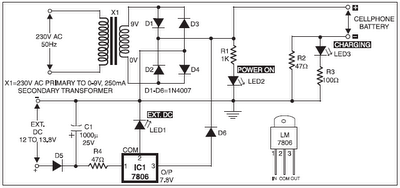
The circuit diagram of a simple and straightforward 12 V battery charger is presented here. This circuit can be utilized to charge various types of 12V rechargeable batteries, including car batteries and motorcycle batteries.
The 12 V battery charger circuit typically consists of several key components that work together to ensure efficient charging of the batteries. The primary components include a transformer, a rectifier, a voltage regulator, and a charging control circuit.
1. **Transformer**: The transformer steps down the input AC voltage to a lower AC voltage suitable for charging a 12 V battery. It is crucial to select a transformer with an appropriate rating to handle the current required for charging.
2. **Rectifier**: The rectifier converts the AC voltage from the transformer into DC voltage. A bridge rectifier configuration is often used, which consists of four diodes arranged in a bridge format. This configuration allows for full-wave rectification, providing a smoother DC output suitable for battery charging.
3. **Voltage Regulator**: To prevent overcharging and ensure that the battery receives a stable voltage, a voltage regulator is employed. Commonly used regulators include the LM7812 or similar linear voltage regulators, which maintain the output voltage at a constant level despite variations in input voltage or load conditions.
4. **Charging Control Circuit**: This circuit monitors the battery voltage and adjusts the charging current accordingly. It may include components such as resistors, capacitors, and possibly a microcontroller for more advanced control. The goal is to terminate the charging process once the battery reaches its full charge state, thereby prolonging battery life and preventing damage.
5. **Protection Features**: Additional protective components, such as fuses or circuit breakers, can be integrated into the design to safeguard against overcurrent conditions. Furthermore, heat sinks may be employed on the voltage regulator to dissipate excess heat generated during operation.
The overall layout of the circuit should be carefully designed to minimize noise and interference, ensuring stable operation. Proper PCB design techniques, such as short trace lengths and adequate grounding, should be implemented to enhance performance and reliability.Here is the circuit diagram of a simple and straight forward 12 V battery charger circuit with diagram. This circuit can be used to charge all type of 12V rechargeable batteries including car batteries and motorcycle batteries.
🔗 External reference
The 12 V battery charger circuit typically consists of several key components that work together to ensure efficient charging of the batteries. The primary components include a transformer, a rectifier, a voltage regulator, and a charging control circuit.
1. **Transformer**: The transformer steps down the input AC voltage to a lower AC voltage suitable for charging a 12 V battery. It is crucial to select a transformer with an appropriate rating to handle the current required for charging.
2. **Rectifier**: The rectifier converts the AC voltage from the transformer into DC voltage. A bridge rectifier configuration is often used, which consists of four diodes arranged in a bridge format. This configuration allows for full-wave rectification, providing a smoother DC output suitable for battery charging.
3. **Voltage Regulator**: To prevent overcharging and ensure that the battery receives a stable voltage, a voltage regulator is employed. Commonly used regulators include the LM7812 or similar linear voltage regulators, which maintain the output voltage at a constant level despite variations in input voltage or load conditions.
4. **Charging Control Circuit**: This circuit monitors the battery voltage and adjusts the charging current accordingly. It may include components such as resistors, capacitors, and possibly a microcontroller for more advanced control. The goal is to terminate the charging process once the battery reaches its full charge state, thereby prolonging battery life and preventing damage.
5. **Protection Features**: Additional protective components, such as fuses or circuit breakers, can be integrated into the design to safeguard against overcurrent conditions. Furthermore, heat sinks may be employed on the voltage regulator to dissipate excess heat generated during operation.
The overall layout of the circuit should be carefully designed to minimize noise and interference, ensuring stable operation. Proper PCB design techniques, such as short trace lengths and adequate grounding, should be implemented to enhance performance and reliability.Here is the circuit diagram of a simple and straight forward 12 V battery charger circuit with diagram. This circuit can be used to charge all type of 12V rechargeable batteries including car batteries and motorcycle batteries.
🔗 External reference