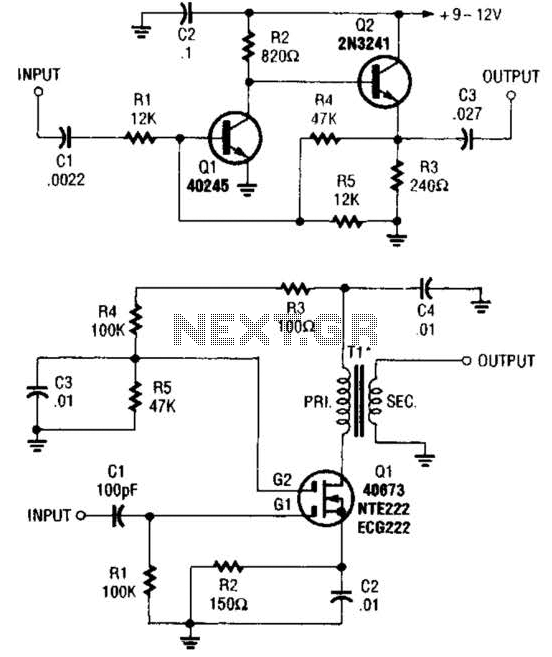
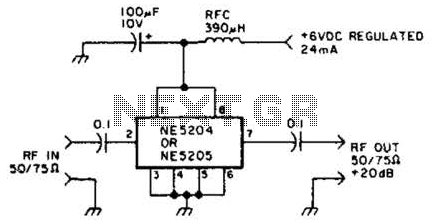
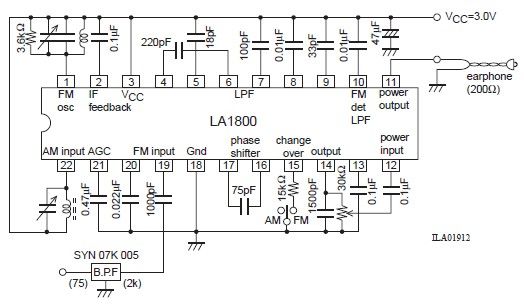
Hydrophone Pre-Amplifier Circuit

A hydrophone is a device similar to a microphone, designed specifically for use in underwater environments. When utilized to capture sound in air, its effectiveness diminishes.
A hydrophone operates by converting sound waves into electrical signals, making it an essential tool for underwater acoustics. The device typically consists of a sensitive transducer that is capable of detecting a wide range of frequencies, which is crucial for various applications such as marine biology, underwater communication, and seismic monitoring.
The construction of a hydrophone often includes a waterproof housing to protect the internal components from water damage. This housing is usually made from materials such as stainless steel or specialized plastics that can withstand high pressures found at greater depths. The transducer element itself may be piezoelectric, capacitive, or electromagnetic, depending on the design and intended frequency range.
In operation, sound waves traveling through the water induce vibrations in the hydrophone's transducer. These vibrations are converted into electrical signals that can be amplified and processed for analysis. The hydrophone's sensitivity and frequency response are critical parameters that determine its performance in capturing subtle underwater sounds, such as marine life communication or geological activity.
Hydrophones can be deployed in various configurations, including fixed installations on the seabed, towed arrays, or as part of autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs). The choice of configuration often depends on the specific application and the environment in which the hydrophone will operate.
Overall, the design and functionality of hydrophones are pivotal in advancing underwater research and exploration, providing valuable data for scientists and engineers alike.Hydrophone is a tool like microphone, but this tool is used in the underwater environment. When used to pick up a sound on the air then this tool becomes less.. 🔗 External reference
A hydrophone operates by converting sound waves into electrical signals, making it an essential tool for underwater acoustics. The device typically consists of a sensitive transducer that is capable of detecting a wide range of frequencies, which is crucial for various applications such as marine biology, underwater communication, and seismic monitoring.
The construction of a hydrophone often includes a waterproof housing to protect the internal components from water damage. This housing is usually made from materials such as stainless steel or specialized plastics that can withstand high pressures found at greater depths. The transducer element itself may be piezoelectric, capacitive, or electromagnetic, depending on the design and intended frequency range.
In operation, sound waves traveling through the water induce vibrations in the hydrophone's transducer. These vibrations are converted into electrical signals that can be amplified and processed for analysis. The hydrophone's sensitivity and frequency response are critical parameters that determine its performance in capturing subtle underwater sounds, such as marine life communication or geological activity.
Hydrophones can be deployed in various configurations, including fixed installations on the seabed, towed arrays, or as part of autonomous underwater vehicles (AUVs). The choice of configuration often depends on the specific application and the environment in which the hydrophone will operate.
Overall, the design and functionality of hydrophones are pivotal in advancing underwater research and exploration, providing valuable data for scientists and engineers alike.Hydrophone is a tool like microphone, but this tool is used in the underwater environment. When used to pick up a sound on the air then this tool becomes less.. 🔗 External reference