in making incandescent lamps

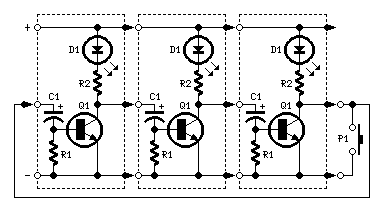
This simple circuit can be used to flash incandescent lamps with a power rating of up to 10W. The circuit is ideal for creating flashing beacons on automobiles and similar applications. It consists of an astable multivibrator based on transistors Q1 (BC557) and Q2 (BD139). The capacitor C1 serves as the primary timing element, determining the flashing rate of the circuit. The switch S1 functions as an ON/OFF switch. Fluorescent lamps or tube lamps (TL) exhibit good efficiency, making them suitable for battery-operated lighting applications. To drive the tube lamp, a high voltage is required to ionize the gas within the tube.
The circuit is designed around a basic astable multivibrator configuration, which generates a continuous square wave output. The transistors Q1 and Q2 are configured in a feedback loop, allowing them to alternately switch on and off, thus creating the flashing effect. The timing capacitor C1, in conjunction with resistors connected to the base of the transistors, sets the frequency of the oscillation. The value of C1, along with the resistors, can be adjusted to change the flashing rate according to the application requirements.
The inclusion of switch S1 allows for manual control of the circuit, providing the ability to turn the flashing effect on or off as needed. This feature is particularly useful in automotive applications where the flashing beacon may only be required in specific scenarios.
For applications involving fluorescent or tube lamps, it is crucial to ensure that the circuit can generate sufficient voltage to ionize the gas within the lamp. This typically involves a step-up transformer or a similar high-voltage circuit design that can provide the necessary ionization energy. The efficiency of fluorescent lamps makes them an excellent choice for battery-operated systems, as they consume less power compared to incandescent lamps while providing adequate illumination.
In summary, this circuit serves as a versatile solution for creating flashing light effects, suitable for various applications, particularly in automotive and portable lighting contexts. The design's simplicity and efficiency make it a practical choice for engineers and hobbyists alike.This simple circuit that can be used to flash incandescent lamps up to 10W power rating. The circuit is ideal for making flashing beacons on automobiles and other applications like that. The circuit is nothing but an astable multi vibrator based on Q1&Q2 ( BC557&BD139). The capacitor C1 is the main timing element which determines the flashing rate o f the circuit. The switch S1 can be used as an ON/OFF switch. Fluorescent lamp or tube lamp (TL) has good efficiency. This high efficiency feature make it suitable for battery operated lighting application. To drive the tube lamp, we need high voltage to make the gas inside the tube get ionized. 🔗 External reference
The circuit is designed around a basic astable multivibrator configuration, which generates a continuous square wave output. The transistors Q1 and Q2 are configured in a feedback loop, allowing them to alternately switch on and off, thus creating the flashing effect. The timing capacitor C1, in conjunction with resistors connected to the base of the transistors, sets the frequency of the oscillation. The value of C1, along with the resistors, can be adjusted to change the flashing rate according to the application requirements.
The inclusion of switch S1 allows for manual control of the circuit, providing the ability to turn the flashing effect on or off as needed. This feature is particularly useful in automotive applications where the flashing beacon may only be required in specific scenarios.
For applications involving fluorescent or tube lamps, it is crucial to ensure that the circuit can generate sufficient voltage to ionize the gas within the lamp. This typically involves a step-up transformer or a similar high-voltage circuit design that can provide the necessary ionization energy. The efficiency of fluorescent lamps makes them an excellent choice for battery-operated systems, as they consume less power compared to incandescent lamps while providing adequate illumination.
In summary, this circuit serves as a versatile solution for creating flashing light effects, suitable for various applications, particularly in automotive and portable lighting contexts. The design's simplicity and efficiency make it a practical choice for engineers and hobbyists alike.This simple circuit that can be used to flash incandescent lamps up to 10W power rating. The circuit is ideal for making flashing beacons on automobiles and other applications like that. The circuit is nothing but an astable multi vibrator based on Q1&Q2 ( BC557&BD139). The capacitor C1 is the main timing element which determines the flashing rate o f the circuit. The switch S1 can be used as an ON/OFF switch. Fluorescent lamp or tube lamp (TL) has good efficiency. This high efficiency feature make it suitable for battery operated lighting application. To drive the tube lamp, we need high voltage to make the gas inside the tube get ionized. 🔗 External reference